Abstract
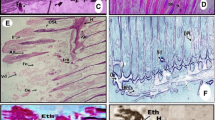
Heavy metal pollution in aquatic bodies is a matter of serious concern for aquatic fauna and human health. This study evaluated the effect of heavy metals on structural aberrations in fish scales of freshwater Indian major carp Labeo rohita. Scales from two size groups—lesser than and equal to 40 cm and greater than 40 cm—collected from three markets of Ludhiana district for a period of 6 months were assessed. The values of Pb, Zn and Cr in fish scales exceeded the permissible limits. Structural alterations such as distorted focus, damaged and eroded circuli, distorted pattern of circuli, damaged margins of scales, dispersed chromatophores, disorganised radii and damaged tubercles were observed on the dorsal surface of scales using light microscopy. It is postulated that heavy metals would be responsible for structural anomalies on scales as their accumulation was higher in larger fishes which have been exposed to metals for longer duration. These observations clearly suggest that fish scales are effective non-invasive indicator of water quality where fish have been reared and cultured.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdullah, S., Javed, J., & Javid, A. (2007). Studies on acute toxicity of metals to the fish (Labeo rohita). International Journal of Agriculture and Biology, 9(2), 333–337.
Avram, A., Frentiu, T., Horovitz, O., Mocanu, A., Goga, F., & Tomoala-cotisel, M. (2017). Hydroxyapatite for removal of heavy metals from wastewater. Studia Ubb Chemia, 4, 93–104.
Brraich, O. S., & Jangu, S. (2012). Scales of fish Cyprinus carpio (Linnaeus) as heavy metal pollution indicator in Harike wetland (Ramsar site). Trends in Fisheries Research, 3, 5–8.
Brraich, O. S., & Jangu, S. (2016). Comparative account of accumulation of heavy metals and structural alterations in scales of five species from Harike wetland, India. Iranian Journal of Ichthyology, 3(4), 275–282.
Cavas, T., & Ergene-Gozukara, S. (2005). Induction of micronuclei and nuclear abnormalities in Oreochromis niloticus following exposure to petroleum refinery and chromium processing plant effluents. Aquatic Toxicology, 74, 264–271.
Chatta, A. M., Khan, M. N., Mirza, Z. S., & Ali, A. (2016). Heavy metal (cadmium, lead and chromium) contamination in farmed fish: a potential risk for consumers’ health. Turkish Journal of Zoology, 40, 248–256.
Chaudhry, A. S., & Jabeen, F. (2011). Assessing metal, protein and DNA profiles in Labeo rohita from the Indus River in Mianwali, Pakistan. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 107, 665–679.
Dinodia, G. S., Gupta, R. K., & Jain, K. L. (2002). Effect of cadmium toxicity on liver glycogen in some freshwater fishes. Proceeding of XI National Symposium on Environment, 11, 236–238.
Dwivedi, S., & Sehgal, N. (2017). Scale of murrel: a non-invasive approach to monitor heavy metals in freshwater. Journal of Biological Sciences and Medicine, 3(3), 15–23.
ECDG (European Commission DG ENV) (2002). Heavy metals in waste final report. E3 Project ENV. E.3/ETU/0058.
FAO/WHO (2011). Joint FAO/WHO expert committee on food additives. Sixty-first meeting Rome, 10-19 June 2003.
Gao, X., & Chen, C.-T. A. (2012). Heavy metal pollution status in surface sediments of the coastal Bohali Bay. Water Res., 46, 1901–1911.
Jarup, L. (2003). Hazards of heavy metal contamination. British Medical Bulletin, 68, 167–182.
Javed, M., & Usmani, N. (2011). Accumulation of heavy metals in fishes: a human health concern. Int Journal of Environmental Science, 2, 659–664.
Jindal, R., & Handa, K. (2019). Hexavalent chromium-induced toxic effects on the antioxidant levels, histopathological alterations and expression of Nrf2 and MT2 genes in the branchial tissue of Ctenopharyngodon idellus, Chemosphere, 144-156.
Jindal, R., & Kaur, M. (2014). Acetylcholinesterase inhibition and assessment of its recovery response in different organs of Ctenopharyngodon idellus on exposure to chlorpyrifos. International Journal of science, environment and technology, 3, 473–480.
Jindal, R., & Kaur, M. (2015). Ultrastructural alterations in scales of Ctenopharyngodon idellus (Cuvier & Valenciennes) induced by chlorpyrifos: a promising tool as bioindicator of pesticide pollution. International Journal of Fisheries and Aquatic Studies, 2(3), 58–62.
Jindal, R., & Sharma, C. (2011). Studies on water quality of Sutlej River around Ludhiana with reference to physicochemical parameters. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 174, 417–425.
Jindal, R., & Verma, S. (2015). In vivo genotoxicity and cytotoxicity assessment of cadmium chloride in peripheral erythrocytes of Labeo rohita (Hamilton). Ecotoxicology and Environmental safety, 118, 1–10.
Kalay, M., & Canli, M. (1999). Elimination of essential (Cu, Zn) and non-essential (Cd, Pb) metals from tissues of a freshwater fish Tilapia zilli. Environmental Pollution, 121, 429–436.
Kaur, R., & Dua, A. (2012). Fish scales as indicators of wastewater toxicity from an international water channel Tung Dhab drain. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 184, 2729–2740.
Kaur, R., & Dua, A. (2015). Scales of freshwater fish Labeo rohita as bioindicators of water pollution in Tung Dhab drain, Amritsar, Punjab, India. Guru Nanak Dev university campus, Amritsar, Punjab, India. Journal of Toxicology and Environmental Health Part A, 78, 388–396.
Kumar, R., & Banerjee, T. K. (2012). Impact of sodium arsenite on certain biomolecules of nutritional importance of the edible components of the economically important catfish C. batrachus Linn. Ecology of food and nutrition, 51, 114–127.
Lin-Sun, P., Hawkins, W. E., Overstreet, R. M., & Brown-Peterson, N. J. (2009). Morphological deformities as biomarkers in fish from contaminated rivers in Taiwan. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 6, 2307–2331.
Ma, Q. Y., Logan, T. J., & Traina, S. J. (1995). Lead immobilization from aqueous solutions and contaminated soils using phosphate rocks. Environmental Science and Technology, 29, 1118–1126.
Mahboob, S., Sultana, S., Ashraf, H. M., Sultana, T., Al-Ghanim, K. A., & Al-Misned, F. (2015). Fish scales as a nonlethal screening tool for assessing the effects of surface water contaminants in Cyprinus carpio. Fresenius Environmental Bulletin, 24, 4628–4634.
Mercy, B., & Dhanalakshmi, B. (2017). Toxicological evalution of heavy metals in tissues of Fresh water fish, Oreochromis niloticus collected from lakes of Coimbatore District, Tamil nadu, India. International Research Journal of Pharmacy, 8(1), 41–45.
Mohiseni, M., Asayesh, S., Bazarnoie, S., Mohseni, F., Moradi, N., Matouri, M., & Mirzaee, N. (2016). Biochemical alteration induced by cadmium and lead in common carp via an experimental food chain. Iranian Journal of Toxicolology, 10(4), 25–32.
More, T. G., Rajput, R. A., & Bandela, N. N. (2003). Impact of heavy metas on DNA content in the whole body of freshwater bivalve, Lamelleiden marginalis. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 22, 605–616.
Negi, R. K., & Maurya, A. (2015). Heavy metal concentrations in tissues of major carp and exotic carp from Bhagwanpur Fish Pond, India. Journal of Fisheries and Aquatic Sciences, 10(6), 543–552.
Olaifa, F. G., Olaifa, A. K., & Onwude, T. E. (2004). Lethal and effects of copper to the African catfish (Clarius gariepinus). African Journal of Biomedical Research, 7(1), 65–70.
Shaikh, M. (2014). Bioaccumulation of heavy metals in tissues of Labeo rohita from Nathsagar Dam, Near Aurangabad, Maharashtra. International Journal of Advances in Agricultural and Environmental Engineering, 1(1), 54–56.
Shikha, S., & Sushma, D. (2011). Effect of fly ash pollution on fish scales. Research Journal of Chemical Sciences, 19 1(9), 24-28.
Sultana, T., Siddique, A., Sultana, S., Mahboob, S., Al-Ghanim, K., & Ahmed, Z. (2017). Fish scales as a non-lethal tool of the toxicity of wastewater from the River Chenab. Environmental Sciences and Pollution Research, 24(3), 2464–2475.
Szentmihalyi, K., & Then, M. (2007). Examination of microelements in medicinal plants of carpathion basin. Acta Alimentaria, 36, 231–236.
Takeuchi, Y., & Arai, H. (1990). Removal of coexisting Pb2+, Cu 2+ and Cd2+ ions from water by addition of hydroxyapatite powder, 3. pH and sample conditioning effects. Journal of Chemical Engineering of Japan, 23, 75–80.
Tao, S., Li, H., Lui, C., & Lam, K. C. (2000). Fish uptake of inorganic and mucus complexes of lead. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 46, 174–180.
Yousafzai, A. M., Douglas, P., Khan, A. R., Ahmed, I., & Siraj, M. (2010). Comparison of heavy metals burden in two freshwater fishes Wallago attu and Labeo dyocheilus with regard to their feeding habits in natural ecosystem. Pakistan Journal of Zoology, 42, 537–544.
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank the Head of the Department of Zoology, Punjab Agricultural University, Ludhiana district, Punjab (India), for providing the necessary infrastructural facilities to carry out this research work.
Funding
The authors received financial support from the Head of the Department of Zoology, Punjab Agricultural University, Ludhiana district, Punjab, India.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Vaid, V., Hundal, S.S. Light microscopic studies to evaluate fish scales as non-invasive indicators of heavy metal–contaminated waters. Environ Monit Assess 191, 638 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-019-7801-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-019-7801-9