Abstract
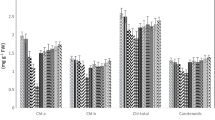
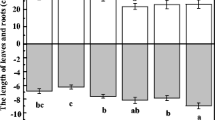
In this study, tea saponin (TS) was extracted from tea camellia seed by microwave-assisted extraction. The potential of TS was compared with ethylenediaminetetracetic acid (EDTA), which is used as a common chemical agent to enhance uptake of cadmium (Cd) by Amaranthus caudatus, an ornamental plant in the natural vegetation of Turkey under pot conditions. The enrichment coefficient (EC) and translocation factor (TF) values were calculated to evaluate the removal efficiency of the TS and EDTA. The results showed that an increase in both TS and EDTA concentration significantly increased Cd uptake by A. caudatus, accumulating Cd in different parts of the plant. Higher EC and TF values obtained from stems, leaves, and inflorescences of A. caudatus showed that this plant might be cultivated and used as a hyperaccumulator in the uptake of Cd from the Cd contaminated soils. Thus, the present technique can efficiently reduce the metal load in the food chain; hence, it could be applied in catchment areas of urban cities where Cd contamination has become an unavoidable factor.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amna, Ali, N., Masood, S., Mukhtar, T., Kamran, M. A., Rafique, M., et al. (2015). Differential effects of cadmium and chromium on growth, photosynthetic activity, and metal uptake of Linum usitatissimum in association with Glomus intraradices. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 187(6), 311. doi:10.1007/s10661-015-4557-8.
Arthur, E. L., Rice, P. J., Rice, P. J., Anderson, T. A., Baladi, S. M., Henderson, K. L. D., et al. (2005). Phytoremediation—an overview. Critical Reviews in Plant Sciences, 24(2), 109–122. doi:10.1080/07352680590952496.
Auguy, F., Fahr, M., Moulin, P., Brugel, A., Laplaze, L., Mzibri, M. E., et al. (2013). Lead tolerance and accumulation in Hirschfeldia incana, a Mediterranean Brassicaceae from metalliferous mine spoils. PLoS One, 8(5), e61932. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0061932.
Boran, H., Ciftci, C., Er, A., Kose, O., Kurtoglu, I.Z., & Kayis, S. (2015). Turkish Journal of Fisheries and Aquatic Sciences, 15(1). doi:10.4194/1303-2712-v15_1_06.
Cay, S., Uyanik, A., Engin, M. S., & Kutbay, H. G. (2015). Effect of EDTA and tannic acid on the removal of Cd, Ni, Pb and Cu from artificially contaminated soil by Althaea rosea Cavan. International Journal of Phytoremediation, 17(1–6), 568–574. doi:10.1080/15226514.2014.935285.
Chen, Y. H., Li, X. D., & Shen, Z. G. (2004). Leaching and uptake of heavy metals by ten different species of plants during an EDTA-assisted phytoextraction process. Chemosphere, 57(3), 187–196. doi:10.1016/j.chemosphere.2004.05.044.
Cheng, S. F., Huang, C. Y., Lin, Y. C., Lin, S. C., & Chen, K. L. (2015). Phytoremediation of lead using corn in contaminated agricultural land-an in situ study and benefit assessment. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 111, 72–77. doi:10.1016/j.ecoenv.2014.09.024.
Chigbo, C., & Batty, L. (2015). Chelate-assisted phytoremediation of cu-pyrene-contaminated soil using Z. mays. Water, Air, & Soil Pollution, 226(3), doi:10.1007/s11270-014-2277-2.
Choi, J. H., Nam, J. O., Kim, J. Y., Kim, J. M., Paik, H. D., & Kim, C. H. (2006). Antioxidant, antimicrobial, and antitumor activities of partially purified substance(s) from green tea seed. Food Science and Biotechnology, 15(5), 672–676.
Clemens, S., Palmgren, M. G., & Kramer, U. (2002). A long way ahead: understanding and engineering plant metal accumulation. Trends in Plant Science, 7(7), 309–315. doi:10.1016/S1360-1385(02)02295-1.
Ebrahimian, E., & Bybordi, A. (2014). Effect of organic acids on heavy-metal uptake and growth of canola grown in contaminated soil. Communications in Soil Science and Plant Analysis, 45(13), 1715–1725. doi:10.1080/00103624.2013.875206.
Engin, M. S. (2015). The assessment of trace metals at gill, muscle and liver tissue in Mugil cephalus. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 187(5), 255. doi:10.1007/s10661-015-4455-0.
Engin, M. S., Uyanik, A., Cay, S., & Icbudak, H. (2010). Effect of the adsorptive character of filter papers on the concentrations determined in studies involving heavy metal ions. Adsorption Science & Technology, 28(10), 837–846.
Han, W. Y., Kemmitt, S. J., & Brookes, P. C. (2007). Soil microbial biomass and activity in Chinese tea gardens of varying stand age and productivity. Soil Biology & Biochemistry, 39(7), 1468–1478. doi:10.1016/j.soilbio.2006.12.029.
He, J., Wu, Z.-Y., Zhang, S., Zhou, Y., Zhao, F., Peng, Z.-Q., et al. (2013). Optimization of microwave-assisted extraction of tea saponin and its application on cleaning of historic silks. Journal of Surfactants and Detergents, 17(5), 919–928. doi:10.1007/s11743-013-1523-8.
Jelusic, M., & Lestan, D. (2015). Remediation and reclamation of soils heavily contaminated with toxic metals as a substrate for greening with ornamental plants and grasses. Chemosphere, 138, 1001–1007. doi:10.1016/j.chemosphere.2014.12.047.
Luo, C. L., Shen, Z. G., & Li, X. D. (2005). Enhanced phytoextraction of Cu, Pb, Zn and Cd with EDTA and EDDS. Chemosphere, 59(1), 1–11. doi:10.1016/j.chemosphere.2004.09.100.
Mani, D., Kumar, C., Patel, N. K., & Sivakumar, D. (2014). Enhanced clean-up of lead-contaminated alluvial soil through Chrysanthemum indicum L. International Journal of Environmental Science and Technology, 12(4), 1211–1222. doi:10.1007/s13762-013-0488-5.
Miao, Q., & Yan, J. H. (2013). Comparison of three ornamental plants for phytoextraction potential of chromium removal from tannery sludge. Journal of Material Cycles and Waste Management, 15(1), 98–105. doi:10.1007/s10163-012-0095-4.
Neugschwandtner, R. W., Tlustos, P., Komarek, M., Szakova, J., & Jakoubkova, L. (2012). Chemically enhanced phytoextraction of risk elements from a contaminated agricultural soil using zea mays and triticum aestivum: performance and metal mobilization over a three year period. International Journal of Phytoremediation, 14(8), 754–771. doi:10.1080/15226514.2011.619231.
Perveen, A., Wahid, A., Mahmood, S., Hussain, I., & Rasheed, R. (2015). Possible mechanism of root-applied thiourea in improving growth, gas exchange and photosynthetic pigments in cadmium stressed maize (Zea mays). Brazilian Journal of Botany, 38(1), 71–79. doi:10.1007/s40415-014-0124-8.
Ramana, S., Biswas, A. K., Singh, A. B., Ajay, Ahirwar, N. K., & Rao, A. S. (2015). Tolerance of ornamental succulent plant crown of thorns (Euphorbia milli) to chromium and its remediation. International Journal of Phytoremediation, 17(4), 363–368. doi:10.1080/15226514.2013.862203.
Roy, D., Kommalapati, R. R., Mandava, S. S., Valsaraj, K. T., & Constant, W. D. (1997). Soil washing potential of a natural surfactant. Environmental Science & Technology, 31(3), 670–675. doi:10.1021/Es960181y.
Sabir, M., Hanafi, M. M., Zia-Ur-Rehman, M., Saifullah, Ahmad, H. R., Hakeem, K. R., et al. (2014). Comparison of low-molecular-weight organic acids and ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid to enhance phytoextraction of heavy metals by maize. Communications in Soil Science and Plant Analysis, 45(1), 42–52. doi:10.1080/00103624.2013.848879.
Shahid, M., Austruy, A., Echevarria, G., Arshad, M., Sanaullah, M., Aslam, M., et al. (2014). EDTA-enhanced phytoremediation of heavy metals: a review. Soil and Sediment Contamination, 23(4), 389–416. doi:10.1080/15320383.2014.831029.
Sheikh-Assadi, M., Khandan-Mirkohi, A., Alemardan, A., & Moreno-Jimenez, E. (2015). Mycorrhizal limonium sinuatum (L.) mill. Enhances accumulation of lead and cadmium. International Journal of Phytoremediation, 17(1-6), 556–562. doi:10.1080/15226514.2014.922928.
Sheoran, V., Sheoran, A. S., & Poonia, P. (2011). Role of hyperaccumulators in phytoextraction of metals from contaminated mining sites: a review. Critical Reviews in Environmental Science and Technology, 41(2), 168–214. doi:10.1080/10643380902718418.
Suthar, V., Memon, K. S., & Mahmood-ul-Hassan, M. (2014). EDTA-enhanced phytoremediation of contaminated calcareous soils: heavy metal bioavailability, extractability, and uptake by maize and sesbania. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 186(6), 3957–3968. doi:10.1007/s10661-014-3671-3.
Tandy, S., Schulin, R., & Nowack, B. (2006). The influence of EDDS on the uptake of heavy metals in hydroponically grown sunflowers. Chemosphere, 62(9), 1454–1463. doi:10.1016/j.chemosphere.2005.06.005.
Tanwar, A., Aggarwal, A., Charaya, M. U., & Kumar, P. (2013). Enhancement of lead uptake by fenugreek using EDTA and glomus mosseae. Communications in Soil Science and Plant Analysis, 44(22), 3431–3443. doi:10.1080/00103624.2013.847454.
Turan, M., & Bringu, A. (2007). Phytoremediation based on canola (Brassica napus L.) and Indian mustard (Brassica Juncea L.) planted on spiked soil by aliquot amount of Cd, Cu, Pb, and Zn. Plant, Soil and Environment, 53(1), 7–15.
Ullah, A., Javed, H. F., Wahid, A., & Sadia, B. (2016). Alleviating effect of exogenous application of ascorbic acid on growth and mineral nutrients in cadmium stressed barley (Hordeum vulgare) seedlings. International Journal of Agriculture and Biology, 18(1), 73–79. doi:10.17957/IJAB/15.0064.
Wang, S., & Liu, J. (2014). The effectiveness and risk comparison of EDTA with EGTA in enhancing Cd phytoextraction by Mirabilis jalapa L. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 186(2), 751–759. doi:10.1007/s10661-013-3414-x.
Wasay, S. A., Barrington, S. F., & Tokunaga, S. (1998). Remediation of soils polluted by heavy metals using salts of organic acids and chelating agents. Environmental Technology, 19(4), 369–379. doi:10.1080/09593331908616692.
Xia, H. L., Chi, X. Y., Yan, Z. J., & Cheng, W. W. (2009). Enhancing plant uptake of polychlorinated biphenyls and cadmium using tea saponin. Bioresource Technology, 100(20), 4649–4653. doi:10.1016/j.biortech.2009.04.069.
Zayed, A., Lytle, C. M., Qian, J. H., & Terry, N. (1998). Chromium accumulation, translocation and chemical speciation in vegetable crops. Planta, 206(2), 293–299. doi:10.1007/s004250050403.
Zulfiqar, S., Wahid, A., Farooq, M., Maqbool, N., & Arfan, M. (2012). Phytoremediation of soil cadmium by using Chenopodium species. Pakistan Journal of Agricultural Sciences, 49(4), 435–445.
Acknowledgments
The author thanks Suleyman Cay for his keen interest and very helpful contributions.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cay, S. Enhancement of cadmium uptake by Amaranthus caudatus, an ornamental plant, using tea saponin. Environ Monit Assess 188, 320 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-016-5334-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-016-5334-z