Abstract
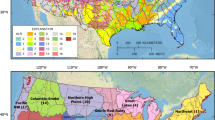
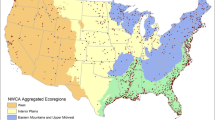
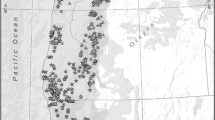
A 1988 survey, funded by the US Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) and conducted by the American Fisheries Society, identified the need to standardize the approaches for evaluating risks and developing fish consumption advisories that are comparable across different jurisdictions. A major tool for evaluating the progress in developing such nationally consistent information is EPA’s web-based National Listing of Fish Advisories (NLFA) database, which has archived fish advisory information since 1993. The NLFA comprises both a database and Geographic Information System mapping components that are implemented using the National Hydrography Dataset (NHD). EPA and the US Geological Survey have developed an enhanced NHD product (NHDPlus) that is applied to define an interstate waters framework for the conterminous USA. This NHDPlus-based framework provides an efficient watershed-oriented approach for identifying interstate advisories from NLFA. We provide summaries of (1) the degree of consistency documented for inland waters where states have issued advisories for shared interstate NHD reaches and (2) the patterns for interstate advisories organized according to the ecoregions developed for EPA’s Wadeable Streams Assessment. Approaches are also discussed for addressing interstate consistency issues for fish advisories in coastal waters making use of the NHDPlus combined with other nationally consistent frameworks, such as the 12-digit hydrologic unit code subwatersheds in the Watershed Boundary Dataset. Probability survey methods are recommended as a way to promote increased interjurisdictional consistency in the development of the monitoring and risk assessment conclusions reflected in NLFA, as well as in other EPA water quality-based programs.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Benke, A., & Cushing, C. (Eds.) (2005). Rivers of North America. Burlington: Elsevier.
Buchanan, G. A. (2005). Advisories in shared waters—two states achieve consistent advice. In Proceedings of the 2005 national forum on contaminants in fish. Baltimore, MD, 18–21 September 2005. EPA-823-R-05–006. Washington, DC: U.S. EPA, Office of Water.
Cooter, W. (2004). Clean water act assessment processes in relation to changing U.S. environmental protection agency management strategies. Environmental Science and Technology, 38(20), 5265–5273.
Cooter, W., Ilieve, P., Sparks, K., Miller, A., Spoerri, C., McCarthy, M., et al. (2000). Detailed, nationally consistent mapping and spatial analysis of section 303(d) and 305(b) waterbodies using the EPA reach file and the national hydrography dataset. In Proceedings of the WEF watershed 2000 conference. Vancouver, British Columbia, Canada, 8–12 July 2000. Alexandria, VA: Water Environment Federation.
Cunningham, P., McCarthy, J., & Zeitlin, D. (1990). Results of the 1989 census of state fish/shellfish consumption advisory programs. Prepared for the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency, Office of Water Regulations and Standards, Assessment and Watershed Protection Division, by RTI International, Research Triangle Park, NC.
Cunningham, P. A., Smith, S. L., Tippett, J. P., & Greene, A. (1994). A national fish consumption advisory database: A step toward consistency. Fisheries, 19(5), 14–23.
Dettmann, E., Moore, R., Robinson, K., Walker, H., & Palter, J. (2004). Use of output from the New England SPARROW model to estimate concentrations of total nitrogen in estuaries. In Presented at the environmental monitoring and assessment program (EMAP) symposium 2004: Integrated monitoring and assessment for effective water quality management; 3–7 May 2004. Newport, RI. Narragansett, RI: U.S. Environmental Protection Agency, Office of Research and Development.
Diaz-Ramos, S., Stevens, D. L. Jr., & Olsen, A. R. (1996). EMAP statistical methods manual. EPA/620/R-96/002. Corvallis: U.S. Environmental Protection Agency, Office of Research and Development, National Health and Environmental Effects Research Laboratory.
Downing, D., Winer, C., & Wood, L. (2003). Navigating through Clean Water Act jurisdiction: A legal review. Wetlands, 23(3), 475–493.
Freeman, M., Pringle, C., & Jackson, C. (2007). Hydrologic connectivity and the contribution of stream headwaters to ecological integrity at regional scales. Journal of the American Water Resources Association, 43(1), 5–14.
Frohmberg, E. (2005). Atlantic coast striped bass and bluefish PCB advisory. In Proceedings of the 2005 national forum on contaminants in fish. Baltimore, MD, 18–21 September 2005. EPA-823-R-05–006. Washington, DC: U.S. Environmental Protection Agency, Office of Water.
Gleyzer, A., Denisyuk, M., Rimmer, A., & Salingar, Y. (2004). A fast recursive GIS algorithm for computing Strahler stream order in braided and nonbraided networks. Journal of the American Water Resources Association, 40(4), 937–946.
Houck, O. (2002). Clean water act TMDL program: Law, policy, and implementation (2nd ed.). Washington, DC: The Environmental Law Institute.
Ilieve, P., Miller, A., Kramer, W., & Bryan J. (2001). Mapping of water quality standards to the national hydrography dataset. In Proceedings of the ESRI user conference 2001. San Diego, CA, 9–13 July 2001.
Laitta, M., Legleiter, K., & Hanson, K. (2004). The national watershed boundary dataset. Hydro line, Summer 2004 (p. 1). ESRI Water Resources Group. Available at http://www.esri.com/library/newsletters/hydroline/hydroline_summer2004.pdf. Accessed 15 July 2009.
Lanfear, K. (1990). A fast algorithm for automatically computing Strahler stream order. Water Resources Bulletin (Journal of the American Water Resources Association), 26(6), 977–981.
Lasrado, J., Santerre, C., Stahl, J., Noltemeyer, T., & Deardorff, D. C. D. (2003). Measurement of PCBs in fish tissue by GC/ECD and enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). Journal of Food Science, 67(6), 1209–1213.
Lieber, H. (1975). Federalism and clean waters: The 1972 water pollution control act. Lexington: Lexington Books.
McDonald, M., Blair, R., Dlugosz, J., Hale, S., Hedtke, S., Heggem, D., et al. (2002). Environmental protection agency’s environmental monitoring and assessment program (EMAP) in the 21st century. Hydrological Science and Technology, 18, 133–44.
Milazzo, P. C. (2006). Unlikely environmentalists: Congress and clean water, 1945–1972. Lawrence: University Press of Kansas.
Moore, R., Johnston, C., Robinson, K., & Deacon, J. (2004). Estimation of total nitrogen and phosphorus in New England streams using spatially referenced regression models. Scientific investigations report 2004–5012. Denver: U.S. Geological Survey in cooperation with the New England Interstate Water Pollution Control Commission and the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency.
Nadeau, T., & Rains, M. (2007). Hydrological connectivity between headwater streams and downstream waters: How science can inform policy. Journal of the American Water Resources Association, 43(1), 118–133.
NRC (National Research Council) (2001). Assessing the TMDL approach to water quality management. Washington, DC: National Academies Press.
Olson, J. (2005). Dealing with interstate inconsistencies in fish consumption advisory protocols in the Upper Mississippi River Basin. In Proceedings of the 2005 national forum on contaminants in fish. Baltimore, MD, 18–21 September 2005. EPA-823-R-05–006. Washington, DC: U.S. Environmental Protection Agency, Office of Water.
Rineer, J., Miller, A., Sinnott, J., & Plastino, M. (2004). WebRIT: An EPA enterprise tool for Web-based locational data improvement. In Proceedings of the 24th annual ESRI international user’s conference. San Diego, CA, 9–13 August 2004. Redlands, CA: ESRI.
Sekerke, J. (2005). Gulf of Mexico advisory for king mackerel. In Proceedings of the 2005 national forum on contaminants in fish. Baltimore, MD, 18–21 September 2005. EPA-823-R-05–006. Washington, DC: U.S. Environmental Protection Agency, Office of Water.
Simley, J. (2008). Applying the national hydrography dataset. Water Resources Impact, 10(1), 5–8.
Spoerri, C., Miller, A., & Dabolt, T. (2000). The reach indexing tool for the national hydrography dataset: Functionality and impacts on state water programs. In Proceedings of the ESRI user conference 2000. San Diego, CA, 26–30 June 2000.
Stahl, L., Snyder, B., Olsen, A., & Pitt, J. (2008). Contaminants in fish tissue from U.S. lakes and reservoirs: A national probabilistic study. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 150(1), 3–19.
Stegner, W. (1992). Beyond the hundredth meridian: John Wesley Powell and the second opening of the West. New York: Penguin.
US Census Bureau (2009). 2008 TIGER/Line shapefiles. Washington, DC: US Census Bureau, Geography Division. Available at http://www2.census.gov/cgi-bin/shapefiles/national-files. Accessed 15 July 2009.
US EPA (Environmental Protection Agency) (2000). Guidance for assessing chemical contaminant data for use in fish advisories. Fish sampling and analysis (Vol. 1, 3rd ed.). EPA 823-B-00–007, Washington, DC: US Environmental Protection Agency, Office of Science and Technology, Office of Water.
US EPA (Environmental Protection Agency) (2002). Ecoregional nutrient criteria. EPA-822-F-02–008. Washington DC: US Environmental Protection Agency, Office of Water. Available at http://www.epa.gov/waterscience/criteria/nutrient/ecoregions/index.html. Accessed 15 July 2009.
US EPA (Environmental Protection Agency) (2004). The incidence and severity of sediment contamination in surface waters of the United States, national sediment quality survey (2nd ed.). EPA 823-R-04–007. Washington DC: US Environmental Protection Agency, Office of Water.
US EPA (Environmental Protection Agency) (2005a). EPA factsheet: 2004 national listing of fish advisories. EPA 823-F-05–004. Washington DC: US Environmental Protection Agency, Office of Water.
US EPA (Environmental Protection Agency) (2005b). The national study of chemical residues in lake fish tissue. EPA-823-F-05–012. Washington DC: US Environmental Protection Agency, Office of Water.
US EPA (Environmental Protection Agency) (2006a). National listing of fish advisories: 2005 advisory data. Washington DC: US Environmental Protection Agency, Office of Water. Available at http://www.epa.gov/waterscience/fish/advisories. Accessed 15 July 2009.
US EPA (Environmental Protection Agency) (2006b). Wadeable streams assessment: A collaborative survey of the nation’s streams. EPA 841-B-06–002. Washington, DC: US Environmental Protection Agency, Office of Research and Development. Available at www.epa.gov/owow/streamsurvey. Accessed 15 July 2009.
US EPA (Environmental Protection Agency) (2007a). National listing of fish advisories: 2005/06 national listing fact sheet. EPA-823-F-07–003. Washington, DC: US Environmental Protection Agency, Office of Water.
US EPA (Environmental Protection Agency) (2007b). Level III ecoregions of the continental United States (map). Corvallis: Western Ecology Division. Available at http://www.epa.gov/wed/pages/ecoregions/level_iii.htm. Accessed 15 July 2009.
US EPA (Environmental Protection Agency) (2009a). Better assessment science integrating point and non-point sources (BASINS): Metadata. Washington, DC: US Environmental Protection Agency, Office of Water. Available at http://www.epa.gov/waterscience/basins/metadata.htm. Accessed 15 July 2009.
US EPA (Environmental Protection Agency) (2009b). National aquatic resource surveys: A progress report. Washington, DC: US Environmental Protection Agency, Office of Water. Available at http://www.epa.gov/owow/monitoring/pdf/narsprogress.pdf. Accessed 15 July 2009.
US GAO (Government Accountability Office) (2000). Water quality: Key EPA and state decisions limited by inconsistent and incomplete data. GAO/RCED-00–54. Washington, DC: US General Accounting Office (now Government Accountability Office).
US GAO (Government Accountability Office) (2002). Water quality: Inconsistent state approaches complicate nation’s efforts to identify its most polluted waters. GAO-02–186. Washington, DC: US General Accounting Office (now Government Accountability Office).
USGS (US Geological Survey) (2007). A national water quality monitoring network for U.S. coastal waters and their tributaries. Advisory Committee on Water Information (ACWI) and the National Water Quality Monitoring Council. Available at http://acwi.gov/monitoring/network/network_brochure.pdf. Accessed 15 July 2009.
USGS (US Geological Survey) (2009a). NHDPlus user guide. US Geological Survey and US Environmental Protection Agency. Available at ftp://ftp.horizon-systems.com/NHDPlus/documentation/NHDPLUS_UserGuide.doc. Accessed 15 July 2009.
USGS (US Geological Survey) (2009b). National atlas of the United States, state boundaries of the United States. Available at http://www.nationalatlas.gov/mld/statesp.html and http://water.usgs.gov/GIS/metadata/usgswrd/XML/states2m.xml. Accessed 15 July 2009.
USGS (US Geological Survey) (2009c). NHD tools: NHD ArcView toolkit. Available at http://nhd.usgs.gov/tools.html. Accessed 15 July 2009.
USGS (US Geological Survey) (2009d). Geographic names information system—GNIS. Available at http://nhd.usgs.gov/gnis.html. Accessed 15 July 2009.
Van Zandt, F. K. (1976). Boundaries of the United States and the several states. Geological Survey Professional Paper 909. Washington, DC: United States Government Printing Office.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cooter, W., Cunningham, P., Rineer, J. et al. A nationally consistent framework for identifying interstate waters with applications for the national listing of fish advisories. Environ Monit Assess 172, 67–89 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-010-1318-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-010-1318-6