Abstract
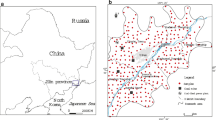
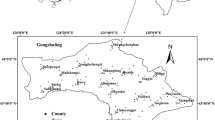
Understanding regional variations of soil heavy metals and their anthropogenic influence are very important for environmental planning. In this study, 286 surface soil samples were collected in Fuyang county, and the ‘total’ metals for copper (Cu), zinc (Zn), lead (Pb), cadmium (Cd) and nickel (Ni) were measured in 2005. Statistic analysis showed that Cu, Zn, Pb and Cd had been added by exterior factors, and Ni was mainly controlled by natural factors. The combination of multivariate statistical and geostatistical analysis successfully grouped three groups (Cu, Zn and Pb; Cd; and Ni) of heavy metals from different sources. Through pollution evaluation, it was found that 15.76% of the study area for Cu, Zn and Pb, and 46.14% for Cd suffered from moderate or severe pollution. Further spatial analysis identified the limestone mining activities, paper mills, cement factory and metallurgic activities were the main sources for the concentration of Cu, Zn, Pb and Cd in soils, and soil Ni was mainly determined by the parent materials.
Similar content being viewed by others

References
Adamuns, C. L., & Bergman, M. J. (1995). Estimating nonpoint source pollution loads with a GIS screening model. Water Resources Bulletin, 31, 647–655.
Agricultural Chemistry Committee of China (1983). Conventional methods of soil and agricultural chemistry analysis. Beijing: Science Press.
Al-Khashman, O. A., & Shawabkeh, R. A. (2006). Metals distribution in soils around the cement factory in southern Jordan. Environmental Pollution, 140, 387–394.
Alloway, B. J. (1990). Heavy metals in soils. London: Blackie.
Biasioli, M., Barberis, R., & Ajmone-Marsan, F. (2006). The influence of a large city on some soil properties and metals content. Science of the Total Environment, 356, 154–164.
Chen, J. (2007). Rapid urbanization in China: A real challenge to soil protection and food security. Catena, 69, 1–15.
Chen, T., Liu, X. M., Zhu, M. Z., Zhao, K. L., Wu, J. J., Xu, J. M., et al. (2007). Identification of trace element sources and associated risk assessment in vegetable soils of the urban-rural transitional area of Hangzhou, China. Environmental Pollution, 151, 1–12.
Facchinelli, A., Sacchi, E., & Mallen, L. (2001). Multivariate statistical and GIS-based approach to identify heavy metal sources in soils. Environmental Pollution, 114, 313–324.
Fazeli, M. S., Khosravan, F., Hossini, M., Sathyanarayan, S., & Satish, P. N. (1998). Enrichment of heavy metals in paddy crops irrigated by paper mill effluents near Nanjangud, Mysore District, Karnatake, India. Environmental Geology, 34, 297–302.
Gallego, J. L. R., Ordonez, A., & Loredo, J. (2002). Investigation of trace element sources from an industrialized area (Aviles, northern Spain) using multivariate statistical methods. Environment International, 27, 589–596.
Goovaerts, P. (1999). Geostatistics in soil science: State-of-the-art and perspectives. Geoderma, 89, 1–45.
Hafen, M. R., & Brinkmann, R. (1996). Analysis of lead in soils adjacent to an interstate highway in Tampa, Florida. Environmental Geochemistry and Health, 18, 171–179.
Han, Y., Du, P., Cao, J., & Posmentier, E. S. (2006). Multivariate analysis of heavy metal contamination in urban dusts of Xi’an, Central China. Science of the Total Environment, 355, 176–186
He, T. B., Dong, L. L., Liu, Y. S., Shu, Y. G., Luo, H. B., & Liu, F. (2006). Changes of physical-chemical properties and heavy metal element in soil from different parent material/rock. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation, 6, 157–162 (in Chinese).
Jiang, L., Yang, X., Ye, H., Shi, W., & Jiang, Y. (2002). Effect of copper refining on spatial distribution of heavy metal in surrounding soils and crops. Journal of Zhejiang University (Agriculture & Life Science), 28, 689–693.
Jones, K., & Mcdonald, A. (1983). The efficiency of different methods of extracting lead from street dust. Environmental Pollution, 692, 133–143.
Keegan, T. J., Farago, M. E., Thornton, I., Hong, B., Colvile, R. N., Pesch, B., et al. (2006). Dispersion of As and selected heavy metals around a coal-burning power station in central Slovakia. Science of the Total Environment, 358, 61–71.
Lee, C. S., Li, X. D., Shi, W. Z., Cheung, S. C., & Thornton, I. (2006). Metal contamination in urban, suburban, and country park soils of Hong Kong: A study based on GIS and multivariate statistics. Science of the Total Environment, 356, 45–61.
Leharne, S. (1992). A survey of metal levels in street dusts in an inner London neighbourhood. Environment International, 18, 263–270.
Lin, Y. P., Teng, T. P., & Chang, T. K. (2002). Multivariate analysis of soil heavy metal pollution and landscape pattern in Changhua county in Taiwan. Landscape and Urban Planning, 62, 19–35.
Little, P., & Martin, M. H. (1972). A survey of zinc, lead and cadmium in soil and natural vegetation around a smelting complex. Environmental Pollution, 3, 241–254.
Liu, X., Wu, J., & Xu, J. (2006). Characterizing the risk assessment of heavy metals and sampling uncertainty analysis in paddy field by geostatistics and GIS. Environmental Pollution, 141, 257–264.
Luo, W., Wang, T. Y., Lu, Y. L., Giesy, J. P., Shi, Y. J., Zheng, Y. M., et al. (2007). Landscape ecology of the Guanting Reservoir, Beijing, China: Multivariate and geostatisticsl analyses of metals in soils. Environmental Pollution, 146, 567–576.
Markus, J., & McBratney, A. B. (2001). A review of the contamination of soil with lead II. Spatial distribution and risk assessment of soil lead. Environment International, 27, 399–411.
Martley, E., Gulson, B. L., & Pfeifer, H. R. (2004). Metal concentrations in soils around the copper smelter and surrounding industrial complex of Port Kembla, NSW, Australia. Science of the Total Environment, 325, 113–127.
McGrath, D., Zhang, C. S., & Owen, C. T. (2004). Geostatistical analyses and hazard assessment on soil lead in Silvermines area, Ireland. Environmental Pollution, 127, 239–248.
Nagerotte, S. M., & Day, J. P. (1998). Lead concentrations and isotope ratios in street dust determined by electrothemal atomic absorption spectrometry and inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry. Analyst (London), 123, 59–62.
Nóvoa-Muñoz, J. C., Queijeiro, J. M. G., Blanco-Ward, D., Álvarez-Olleros, C., Martínez-Cortizas, A., & García-Rodeja, E. (2007). Total copper content and its distribution in acid vineyards soils developed from granitic rocks. Science of the Total Environment, 378, 23–27.
Pietrzak, U., & McPhail, D. C. (2004). Copper accumulation, distribution and fraction in vineyard soils of Victoris, Australia. Geoderma, 122, 151–166.
Prasad, B. R., Basavaiah, S., Subba, R. A., & Subba, R. I. V. (1984). Forms of copper in soils of grape orchards. Journal of the Indian Society of Soil Science, 32, 318–322.
Radha, R., Tripathi, R. M., Vinod, K. A., Sathe, A. P., Khandekar, R. N., & Nambi, K. S. V. (1997). Assessment of Pb, Cd, Cu, and Zn exposures of 6- to 10-year-old children in Mumbai. Environmental Research, A80, 215–221.
Rong, Q. H., Xu, K. X., & Zhang, Y. Q. (1992). Environmental background levels of trace elements in major soil categories in Zhejiang Province. Journal of Zhejiang University, 26, 172–178.
Saby, N., Arrouays, D., Boulonne, L., Jolivet, C., & Pochot, A. (2006). Geostatistical assessment of Pb in soil around Paris, France. Science of the Total Environment, 367, 212–221.
Wang, J. Z. (2006). China has 20, 000 t food contaminated by heavy metals every year. Country Practical Technique, 11, 27–27.
Wang, M., & Zhang, M. (2004). The comparison of soil properties in different function zones of urban and suburban districts in Hangzhou city. Acta Agricultural Zhejiangensis, 16, 377–380.
Wang, X., Qin, Y., & Chen, Y. K. (2006). Heavy metals in urban roadside soils, part 1: Effect of particle size fractions on heavy metals partitioning. Environmental Geology, 50, 1061–1066.
Webster, R. (1994). The development of pedometrics. Geoderma, 62, 1–15.
Xiao, H. G., & Wei, J. (2007). Relating landscape characteristics to non-point source pollution in mine waste-locate watersheds using geospatial techniques. Journal of Environmental Management, 82, 111–119.
Xie, Z., Li, J., Xu, J., Ye, L., & Wang, B. L. (2006). Evaluation on environmental quality of Pb, Zn and Cu contents in vegetable plantation soils and vegetables in Hangzhou Suburb. Environmental Sciences (Tokyo), 27, 742–747.
Zhang, C. (2006). Using multivariate analyses and GIS to identify pollutants and their spatial patterns in urban soils in Galway, Ireland. Environmental Pollution, 142, 501–511.
Zhejiang Soil Survey Office (1994). Zhejiang soils. Hangzhou: Zhejiang Technology Press.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, X.Y., Lin, F.F., Wong, M.T.F. et al. Identification of soil heavy metal sources from anthropogenic activities and pollution assessment of Fuyang County, China. Environ Monit Assess 154, 439–449 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-008-0410-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-008-0410-7