Abstract
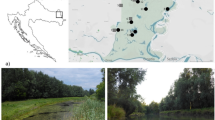
This study assessed the enrichment of mercury in the food web from the different community habitats in a zinc-smelting area of China. We used a nitrogen stable isotope technique to analyze trophic level relationships among arthropods and found that the first trophic level consisted of plants in the different community habitats, the second trophic level consisted of herbivores such as locusts and grasshoppers (primary consumers), and the third trophic level included spiders and mantes (secondary consumers). Mercury enrichment in the primary consumers was not evident, but enrichment in arthropods of the third trophic level was significant. The average of enrichment coefficients in spiders and mantes was greater than 1. The δ15N values indicated that mercury concentrations accumulated from primary producers to top carnivorous arthropods increased. In this zinc-smelting area, the biological amplification of mercury in the food web is significant. It is reasonable to assume that humans, located at the top of the food chain, are exposed to biomagnified levels of mercury.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Al-Maslamani, I., Walton, M. E. M., Kennedy, H., & Le Vay, L. (2012). Sources of primary production supporting food webs in an arid coastal embayment. Marine Biology, 159, 1753–1762.
Bai, J. H., Jia, J., Huang, C., Wang, Q. G., Wang, W., Zhang, G. L., et al. (2017). Selective uptake of nitrogen by Suaeda salsa under drought and salt stresses and nitrogen fertilization using 15N. Ecological Engineering, 102, 542–545.
Beneditto, A. P. M. D., Bittar, V. T., Camargo, P. B., Rezende, C. E., & Kehrig, H. A. (2012). Mercury and nitrogen isotope in a marine species from a tropical coastal food web. Archives of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 62, 264–271.
Cai, D. L., Hong, X. G., Mao, X. H., Zhang, S. F., Han, Y. B., & Gao, S. L. (2001). Preliminary studies on trophic structure of tidal zone in the Laoshan Bay by using carbon stable isotopes. Acta Oceanologica Sinica, 23, 41–47.
Clayden, M. G., Kidd, K. A., Chételat, J., Hall, B. D., & Garcia, E. (2014). Environmenta, geographic and trophic influences on methylmercury concentrations in macroinvertebrates from lakes and wetlands across Canada. Ecotoxicology, 23, 273–284.
De Niro, M. J., & Epstein, S. (1981). Influence of diet on the distribution of nitrogen isotopes in animals. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 45, 341–351.
Devkota, B., & Schmidt, G. H. (2000). Accumulation of heavy metals in food plants and grasshoppers from the Taigetos Mountains, Greece. Agriculture, Ecosystems & Environment, 78, 85–91.
Doi, H., Matsumasa, M., Toya, T., Nobuya, S., Chitoshi, M., Yonosuke, M., et al. (2005). Spatial shifts in food sources for macrozoobenthos in an estuarine ecosystem: Carbon and nitrogen stable isotope analyses. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science, 64, 316–322.
Feng, X. B., Li, P., Qiu, G. L., Wang, S., Li, G. H., Shang, L. H., et al. (2008). Human exposure to methylmercury through rice intake in mercury mining areas, Guizhou Province, China. Environmental Science and Technology, 42, 326–332.
Hobson, K. A., & Welch, H. E. (1992). Determination of trophic relationships within a high arctic marine food web using 13C and 15N analysis. Marine Ecology-progress Series, 84, 9–18.
Horvat, M., Nolde, N., Fajon, V., Milena, H., Nataša, N., Vesna, F., et al. (2003). Total mercury, methylmercury and selenium in mercury polluted areas in the province Guizhou, China. The Science of the Total Environment, 304, 231–256.
Li, D. H., & Su, X. M. (2012). The studies on the food web structures and trophic relationships in Guangxi Dongfang Cave by means of stable carbon and nitrogen isotopes. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 32, 3497–3504.
Liu, R. H., Wang, Q. C., Lu, X. G., Fang, F. M., & Wang, Y. (2004). Distribution and speciation of mercury in the peat bog of Xiaoxing’ an Mountain, northeastern China. Environmental Pollution, 124, 39–46.
Minagawa, M., & Wada, E. (1984). Stepwise enrichment of 15N along food chains: further evidence and the relation between δ15N and animal age. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 48, 1135–1140.
Ostrom, P. H., Colunga-Garcia, M., & Gage, S. H. (1997). Establishing pathways of flow for insect predators using stable isotope ratios: field and laboratory evidence. Oecologia, 109, 108–113.
Peterson, B. J. (1999). Stable isotopes as tracers of organic matter input and transfer in benthic food webs: A review. Acta Oecologia, 20, 479–487.
Peterson, B. J., & Fry, B. (1987). Stable isotopes in ecosystem studies. Annual Review of Ecology and Systematics, 18, 293–320.
Post, D. M. (2002). Using stable isotopes to estimate trophic position: models, methods, and assumptions. Ecology, 83, 703–718.
Thimdee, W., Deein, G., & Sangrungruang, C. (2004). Analysis of primary food sources and trophic relationships of aquatic animals in a mangrove-fringed estuary, Khung Krabaen Bay (Thailand) using dual stable isotope techniques. Wetlands Ecology and Management, 12, 135–144.
Ullrich, S. M., Ilyushchenko, M. A., Tanton, T. W., & Uskov, G. A. (2007). Mercury contamination in the vicinity of derelict chlor-alkali plant Part II: Contamination of the aquatic and terrestrial food chain and potential risks to the local population. Science of the Total Environment, 381, 290–306.
Vander Zanden, J. M., Cabana, G., & Rasmussen, B. J. (1997). Comparing trophic position of freshwater fish calculated using stable nitrogen isotope ratios (δ15N) and literature dietary data. Canadian Journal of Fisheries and Aquatic Sciences, 54, 1142–1158.
Vander Zanden, J. M., Casselman, M. J., & Rasmussen, B. J. (1999). Stable isotope evidence for the food web consequences of species invasions in lakes. Nature, 401, 464–467.
Vander Zanden, J. M., & Rasmussen, B. J. (1999). Primary consumer δ13C and δ15N and the trophic position of aquatic consumers. Ecology, 80, 1395–1404.
Vander Zanden, M. J., & Rasmussen, J. B. (2001). Variation in δ13C and δ15N trophic fractionation: Implications for aquatic food web studies. Limnology and Oceanography, 46, 2061–2066.
Wang, J. Z., Lin, G. H., Huang, J. H., & Han, X. G. (2004). The application of stable isotope in the study of the relationship between terrestrial ecosystems—plant. Chinese Science Bulletin, 49, 2141–2149.
Wang, N., Zhu, Y. M., Sheng, L. X., & Meng, D. (2005). Mercury pollution in Rana Chensinensis in Weisha River reach, in the up-stream region of Songhua River. Chinese Science Bulletin, 50, 1589–1593.
Xue, L. Q. (2009). Huludao Zinc industry Company, Huludao zinc plant investigate the status of mercury pollution research and control strategies. Environmental Science and Management, 34, 115–118.
Yang, Y. Q., Yi, X. F., & Li, N. (2009). Analysis trophic level structure through stable isotope technique about water birds in Qinghai Lake. Zoological Research, 30, 418–422.
Yoshioka, T. E., Wada, E., & Hayashi, H. (1994). A stable isotope study on seasonal food wed dynamics in a eutrophic lake. Ecology, 75, 835–846.
Zhang, D., Min, Q. W., Cheng, S. K., Wang, Y. Y., Yang, H. L., & He, L. (2010). Ecological studies on the food wed structures and trophic relationships of multiple species coexistence in paddy fields using stable carbon and nitrogen isotopes. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 30, 6734–6742.
Zhang, L., & Wang, Q. C. (2006). Preliminary study on health risk from mercury exposure to residents of Wujiazhan town on the Di’er Songhua River Northeast China. Environmental Geochemistry and Health, 28(1–2), 67–71.
Zhang, Z. S., Zheng, D. M., Wang, Q. C., & Lu, X. G. (2009). Bioaccumulation of total and methyl mercury in three earthworm species (Drawida sp., Allolobophorasp., and Limnodrilus sp.). Bulletin of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 83, 937–942.
Zheng, D. M., Li, X. X., & Luo, Q. (2012). Mercury pollution in cricket in different biotopes suffering from pollution by zinc smelting. Environmental Science, 33, 3680–3684.
Zheng, D. M., Wang, Q. C., Zheng, N., & Zhang, S. Q. (2007). The spatial distribution of soil mercury in the area suffering combined pollution by zinc smelting and chlor-alkai production. Chinese Journal of Soil Science, 38, 361–364.
Zheng, D. M., Zhang, Z. S., & Wang, Q. C. (2010). Total and methyl mercury contents and distribution characteristics in cicada, Cryptotympana atrata (Fabricius). Bulletin of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 84, 749–753.
Acknowledgements
The authors are grateful to the support of the national natural science foundation (41571085, 41771106) and competitive selection project of Shenyang scientific undertaking.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zheng, D., Liu, X., Jin, D. et al. Mercury bioaccumulation in arthropods from typical community habitats in a zinc-smelting area. Environ Geochem Health 40, 1329–1337 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10653-017-0059-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10653-017-0059-7