Abstract
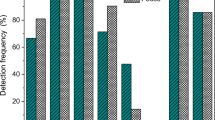
Sulfonamides (SAs) are applied widely as feed additives in the farming of livestock and poultry. It can lead to the excretion of large amounts of SAs in manure and result in persistent environmental pollution. We evaluated the fate of four SAs, sulfamerazine (SM1), sulfachloropyridazine (SCP), sulfadimoxine (SDM′) and sulfaquinoxaline (SQ), from oral administration to excretion in urine and feces in pigs. The four SAs were added to homemade feed to make them reach the required concentration gradient, which were 0, 50 and 100 mg/kg (low, normal and high concentrations, respectively). In different treatments, excretions of the four SAs were 35.68–86.88 %. With regard to total excretion, the order was SQ > SCP > SM1 > SDM′ for all treatments. The concentration of SAs in the feed had significant effects on the amount of the four SAs excreted every day. The concentration of SAs in feces and in the urine for different treatments was 15.03–26.55 and 14.54–69.22 %, respectively. In each treatment, excretions of SCP, SDM′ and SQ in feces were lower than that in urine. The four SAs remained longer in urine than in feces. Excretions in urine and feces were lower if SAs were administered orally rather than by injection.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aga, D. S., O’Connor, S., Ensley, S., Payero, J. O., Snow, D., & Tarkalson, D. (2005). Determination of the persistence of tetracycline antibiotics and their degradates in manure-amended soil using enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay and liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry. Journal of Agriculture and Food Chemistry, 53(18), 7165–7171.
Alcock, R. E., Sweetman, A., & Jones, K. C. (1999). Assessment of organic contanhnant fate in waste water treatment plants I: Selected compounds and physicochemical properties. Chemosphere, 38(10), 2247–2262.
Baran, W., Adamek, E., Ziemiańska, J., & Sobczak, A. (2011). Effects of the presence of sulfonamides in the environment and their influence on human health. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 196, 1–15.
Bevill, R. F., Dittert, L. W., & Bourne, D. W. (1977). Disposition of sulfonamides in food-producing animals IV: Pharmacokinetics of sulfamethazine in cattle following administration of an intravenous dose and three oral dosage forms. Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences, 66(5), 619–623.
Bourne, D., Bialer, M., Dittert, L., Hayashi, M., Rudawsky, G., Koritz, G., & Bevill, R. (1981). Disposition of sulfadimethoxine in cattle: Inclusion of protein binding factors in a pharmacokinetic model. Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences, 70(9), 1068–1072.
Boxenbaum, H., Fellig, J., Hanson, L., Snyder, W., & Kaplan, S. (1977). Pharmacokinetics of sulphadimethoxine in cattle. Research in Veterinary Science, 23(1), 24–28.
Chee-Sanford, J. C., Mackie, R. I., Koike, S., Krapac, I. G., Lin, Y.-F., Yannarell, A. C., et al. (2009). Fate and transport of antibiotic residues and antibiotic resistance genes following land application of manure waste. Journal of Environmental Quality, 38(3), 1086–1108.
Elmund, G. K., Morrison, S., Grant, D., & Nevins, M. (1971). Role of excreted chlortetracycline in modifying the decomposition process in feedlot waste. Bulletin of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 6(2), 129–132.
Halling-Sørensen, B., Jensen, J., Tjørnelund, J., & Montforts, M. (2001). Worst-case estimations of predicted environmental soil concentrations (PEC) of selected veterinary antibiotics and residues used in Danish agriculture. Pharmaceuticals in the Environment (pp. 143–157). Berlin: Springer.
Halling-Sørensen, B., Nors Nielsen, S., Lanzky, P., Ingerslev, F., Holten Lützhøft, H., & Jørgensen, S. (1998). Occurrence, fate and effects of pharmaceutical substances in the environment-a review. Chemosphere, 36(2), 357–393.
Hruska, K., & Franek, M. (2012). Sulfonamides in the environment: a review and a case report. Veterinarni Medicina, 57(1), 1–35.
Kuchta, S. L., & Cessna, A. J. (2009). Lincomycin and spectinomycin concentrations in liquid swine manure and their persistence during simulated manure storage. Journal of Archives of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 57(1), 1–10.
Kumar, K., Gupta, S., Baidoo, S., Chander, Y., & Rosen, C. (2005). Antibiotic uptake by plants from soil fertilized with animal manure. Journal of Environmental Quality, 34(6), 2082–2085.
Martínez-Carballo, E., González-Barreiro, C., Scharf, S., & Gans, O. (2007). Environmental monitoring study of selected veterinary antibiotics in animal manure and soils in Austria. Environmental Pollution, 148(2), 570–579.
Nouws, J. F., Vree, T. B., Degen, M., & Mevius, D. (1991). Pharmacokinetics of sulphamethoxazole in calves and cows. Veterinary Quarterly, 13(1), 10–15.
Phillips, I., Casewell, M., Cox, T., De Groot, B., Friis, C., Jones, R., et al. (2004). Does the use of antibiotics in food animals pose a risk to human health? A critical review of published data. Journal of Antimicrobial Chemotherapy, 53(1), 28–52.
Rynk, R. (1992). On-farm composting handbook.
Sarmah, A. K., Meyer, M. T., & Boxall, A. (2006). A global perspective on the use, sales, exposure pathways, occurrence, fate and effects of veterinary antibiotics (VAs) in the environment. Chemosphere, 65(5), 725–759.
Tolls, J. (2001). Sorption of veterinary pharmaceuticals in soils: a review. Environmental Science and Technology, 35(17), 3397–3406.
Watanabe, N., Bergamaschi, B. A., Loftin, K. A., Meyer, M. T., & Harter, T. (2010). Use and environmental occurrence of antibiotics in freestall dairy farms with manured forage fields. Environmental Science and Technology, 44(17), 6591–6600.
Winckler, C., & Grafe, A. (2001). Use of veterinary drugs in intensive animal production: Evidence for persistence of tetracyline in pig slurry. Journal of Soils Sediments, 1(2), 66–70.
Witkamp, R., Yun, H., Van’t Klooster, G., Van Mosel, J., Van Mosel, M., Ensink, J., et al. (1992). Comparative aspects and sex differentiation of plasma sulfamethazine elimination and metabolite formation in rats, rabbits, dwarf goats, and cattle. American Journal of Veterinary Research, 53(10), 1830.
Zhao, L., Dong, Y. H., & Wang, H. (2010). Residues of veterinary antibiotics in manures from feedlot livestock in eight provinces of China. Science of the Total Environment, 408(5), 1069–1075.
Acknowledgments
We thank the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Research Institutes and Major Science and Technology Program for Water Pollution and Treatment (2014ZX0726001) for funding this project. The Special Fund of Chinese Central Government for Basic Scientific Research Operations in Commonweal Research Institutes (PM-zx021-201406-035).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Qiu, J., Zhao, T., Liu, Q. et al. Residual veterinary antibiotics in pig excreta after oral administration of sulfonamides. Environ Geochem Health 38, 549–556 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10653-015-9740-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10653-015-9740-x