Abstract
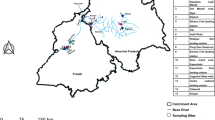
Seagrasses constitute a significant part of coral reef ecosystems, representing high primary productivity and one of the most important coastal habitats in marine ecosystems. Though seagrasses possess irreplaceable ecological services to the marine environment, taxonomical ambiguity still exists due to similar morphological characters and phenotypic plasticity. As an emerging technology, DNA barcoding can effectively identify cryptic species using a short orthologous DNA region. In this study, we collected samples from five different locations (Daya Bay, Xincun Bay, Sanya Bay, Xisha Islands, and Nansha Islands), and three seagrass species Cymodocea rotundata, Thalassia hemprichii and Halophila ovalis was evaluated. Moreover, ITS, matK and rbcL genes were used as DNA barcodes. The results indicated that single ITS and concatenated ITS/matK/rbcL both conducted better species resolution than single matK and rbcL. Nevertheless, single ITS was more convenient. Furthermore, in all the four topology trees, three species resolved as 3 clusters as well H. ovalis and T. hemprichii grouped as sister clade. In the meantime, differentiation lay in intra-species based on the result of single ITS and three-locus analysis. Within H. ovalis and T. hemprichii separately, individuals from Xisha Islands first group together, then grouped with individuals from Nansha Islands and/or Xincun Bay and/or Sanya Bay and/or Daya Bay, which indicated that geographical distribution influenced population evolution. However, intra-species differentiation did not emerge in the tree of matK or rbcL.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ackerman JD (2006) Sexual reproduction of seagrasses. In: Larkum AWD, Orth RJ, Duarte CM (Eds.) Seagrasses: Biology, ecology and conservation. Springer, The Netherlands, p 89109
Beck MW, Heck KL, Able KW, Childers DL, Eggleston DB, Gillanders BM et al. (2001) The identification, conservation, and management of estuarine and marine nurseries for fish and invertebrates. BioScience 51:633–641
Bonanno G, Orlando-Bonaca M (2017) Trace elements in Mediterranean seagrasses: accumulation, tolerance and biomonitoring. A review Mar Pollut Bull 125:8–18
Bricker E, Waycott M, Calladine A, Zieman JC (2011) High connectivity across environmental gradients and implications for phenotypic plasticity in a marine plant. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 423:57–67
Burkholder JM, Tomasko DA, Touchette BW (2007) Seagrasses and eutrophication. J Exp Mar Biol Ecol 350:46–72
CBOL Plant Working Group (2009) A DNA barcode for land plants. Proc Natl Acad Sci U.S.A. 106:12794–12797
Chase MW, Cowan RS, Hollingsworth PM, van den Berg C, Madrinan S, Petersen G et al. (2007) A proposal for a standardised protocol to barcode all land plants. Taxon 56:295–299
Coyer JA, Hoarau G, Kuo J, Tronholm A, Veldsink J, Olsen JL (2013) Phylogeny and temporal divergence of the seagrass family Zosteraceae using one nuclear and three chloroplast loci. Syst Biodivers 11:271–284
Darriba D, Taboada GL, Doallo R, Posada D (2012) jModelTest 2: more models, new heuristics and parallel computing. Nat Methods 9:772–772
de Boer WF (2007) Seagrass-sediment interactions, positive feedbacks and critical thresholds for occurrence: a review. Hydrobiologia 591:5–24
Den Hartog C (1970) The sea-grasses of the world. Amsterdam Publishing Company, North-Holland
Duffy JE (2006) Biodiversity and the functioning of seagrass ecosystems. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 311:233–250
Evans SM, Sinclair EA, Poore AGB, Steinberg PD, Kendrick GA, Verges A (2014) Genetic diversity in threatened Posidonia australis seagrass meadows. Conser Genet 15:717–728
Franks SJ (2009) Genetics, evolution, and conservation of Island plants. J Plant Biol 53:1–9
Ghosh S, Bankura B, Das M (2016) DNA Barcoding: a tool to assess and conserve Marine Biodiversity. Springer International Publishing Switzerland: 43–61
Halpern BS, Walbridge S, Selkoe KA, Kappel CV, Micheli F, D’Agrosa C et al. (2008) A global map of human impact on marine ecosystems. Science 319:948–952
Han Q, Liu D (2014) Macroalgae blooms and their effects on seagrass ecosystems. J Ocean Univ China 13:791–798
Harrison PG, Bigley RE (1982) The recent introduction of the seagrass zostera-japonica aschers and graebn to the Pacific Coast of North-America. Can J Fisher Aquat Sci 39:1642–1648
Hebert PDN, Cywinska A, Ball SL, DeWaard JR (2003) Biological identifications through DNA barcodes. Proc Biol Sci 270:313-321
Hemminga M, Duarte CM (2000) Seagrass Ecology. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge (United Kingdom)
Hendriks IE, Olsen YS, Ramajo L, Basso L, Steckbauer A, Moore TS et al. (2014) Photosynthetic activity buffers ocean acidification in seagrass meadows. Biogeosciences 11:333–346
Hollingsworth PM, Forrest LL, Spouge JL, Hajibabaei M, Ratnasingham S, van der Bank M et al. (2009) A DNA barcode for land plants. Proc Natl Acad Sci U.S.A. 106:12794–12797
Hosokawa S, Nakaoka M, Miyoshi E, Kuwae T (2015) Seed dispersal in the seagrass Zostera marina is mostly within the parent bed in a protected bay. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 523:41–56
Hughes AR, Stachowicz J J (2004) Genetic diversity enhances the resistance of a seagrass ecosystem to disturbance. Proc Natl Acad Sci U.S.A. 101:8998–9002
Jiang ZJ, Liu SL, Zhang JP, Zhao CY, Wu YC, Yu S et al. (2017) Newly discovered seagrass beds and their potential for blue carbon in the coastal seas of Hainan Island, South China Sea. Mar Pollut Bull 125:513–521
Kendrick GA, Waycott M, Carruthers TJB, Cambridge ML, Hovey R, Krauss SL et al. (2012) The central role of dispersal in the maintenance and persistence of seagrass populations. BioScience 62:56–65
Kilminster K, McMahon K, Waycott M, Kendrick GA, Scanes P, McKenzie L et al. (2015) Unravelling complexity in seagrass systems for management: Australia as a microcosm. Sci Total Environ 534:97–109
Kress WJ, Wurdack KJ, Zimmer E A, Weigt LA, Janzen DH (2005) Use of DNA barcodes to identify flowering plants. Proc Natl Acad Sci U.S.A. 102:8369-8374
Lai S, Gillis LG, Mueller C, Bouma TJ, Guest JR, Last KS et al. (2013) First experimental evidence of corals feeding on seagrass matter. Coral Reefs 32:1061–1064
Li DZ, Gao LM, Li HT, Wang H, Ge XJ, Liu JQ et al. (2011) Comparative analysis of a large dataset indicates that internal transcribed spacer (ITS) should be incorporated into the core barcode for seed plants. Proc Natl Acad Sci U.S.A. 108:19641–19646
Li Y, Song N, Li WT, Gao TX (2012) Population genetics of Zostera marina Linnaeus (Zosteraceae) based on AFLP analysis. Biochem Syst Ecol 44:216–223
Ling J, Lin X, Zhang Y, Zhou W, Yang Q, Lin L et al. (2018) Community composition and transcriptional activity of ammonia-oxidizing prokaryotes of seagrass Thalassia hemprichii in coral reef ecosystems. Front Microbiol 9:7
Lucas C, Thangaradjou T, Papenbrock J (2012) Development of a DNA barcoding system for seagrasses: successful but not simple. PLoS One 7:e29987
McMahon K, van Dijk KJ, Ruiz-Montoya L, Kendrick GA, Krauss SL, Waycott M et al. (2014) The movement ecology of seagrasses Proc Biol Sci 281:20140878
Nguyen XV, Höfler S, Glasenapp Y, Thangaradjou T, Lucas C, Papenbrock J (2015) New insights into DNA barcoding of seagrasses. Syst Biodivers 13:496–508
Nguyen XV, Holzmeyer L, Papenbrock J (2013) New record of the seagrass species Halophila major (Zoll.) Miquel in Vietnam: evidence from leaf morphology and ITS analysis. Bot Mar 56:313–321
Nguyen XV, Thirunavukarassu T, Papenbrock J (2013) Genetic variation among Halophila ovalis (Hydrocharitaceae) and closely related seagrass species from the coast of Tamil Nadu, India — an AFLP fingerprint approach. Systematics and Biodiversity 11:467–476
Orth RJ, Carruthers TJB, Dennison WC, Duarte CM, Fourqurean JW, Heck KL et al. (2006) A global crisis for seagrass ecosystems. BioScience 56:987
Petersen G, Seberg O, Short FT, Fortes MD (2014) Complete genomic congruence but non-monophyly of Cymodocea (Cymodoceaceae), a small group of seagrasses. Taxon 63:3–8
Ronquist F, Teslenko M, van der Mark P, Ayres DL, Darling A, Hohna S et al. (2012) MrBayes 3.2: Efficient bayesian phylogenetic inference and model choice across a large model space. Syst Biol 61:539–542
Serrano O, Mateo MA, Duenas-Bohorquez A, Renom P, Lopez-Saez JA, Martinez Cortizas A (2011) The Posidonia oceanica marine sedimentary record: a Holocene archive of heavy metal pollution. Sci Total Environ 409:4831–4840
Short FT, Carruthers TIB, Dennison WC, Waycott M (2007) Global seagrass distribution and diversity: a bioregional mode. J Exp Mar Biol Ecol 350:3–20
Short FT, Moore GE, Peyton KA (2010) Halophila ovalis in the Tropical Atlantic Ocean. Aquatic Botany 93:141–146
Short FT, Polidoro B, Livingstone SR, Carpenter K, Bandeira S, Bujang JS et al. (2011) Extinction risk assessment of the world’s seagrass species. Biol Conserv 144:1961–1971
Sinclair EA, Krauss SL, Anthony J, Hovey R, Kendrick GA (2014) The interaction of environment and genetic diversity within meadows of the seagrass Posidonia australis (Posidoniaceae). Mar Ecol Prog Ser 506:87–98
Tamura K, Stecher G, Peterson D, Filipski A, Kumar S (2013) MEGA6: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis version 6.0. Mol Biol Evol 30:2725–2729
Tanaka N, Setoguchi H, Murata J (1997) Phylogeny of the family hydrocharitaceae inferred from rbcL and matK gene sequence data. J Plant Res. 110:329–337
Titlyanov EA, Titlyanova TV (2012) Marine plants in a coral reef ecosystem. Russ J Mar Biol 38:201–210
Travis SE, Sheridan P (2006) Genetic structure of natural and restored shoalgrass Halodule wrightii populations in the NW Gulf of Mexico. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 322:117–127
Uchimura M, Faye EJ, Shimada S, Inoue T, Nakamura Y (2008) A reassessment of Halophila species (Hydrocharitaceae) diversity with special reference to Japanese representatives. Bot Mar 51:258–268
Wang D, Wu Z, Chen C, Lan J, Wu R, Chen X, Zhang G, Li Y (2012) Distribution of seagrass resources and existing threat in Hainan Island. Mar. Environ. Sci. 31:34–38
Ward RD, Zemlak TS, Innes BH, Last PR, Hebert PDN (2005) DNA barcoding Australia’s fish species. Philos Trans R Soc B Biol Sci 360:1847–1857
Waycott M (2000) Genetic factors in the conservation of seagrasses. Pac Conserv Biol 5:269–276
Waycott M, Duarte CM, Carruthers TJB, Orth RJ, Dennison WC, Olyarnik S et al (2009) Accelerating loss of seagrasses across the globe threatens coastal ecosystems. Proc Natl Acad Sci U.S.A. 106:12377–12381
Zhang X, Zhou Y, Xue DX, Liu JX (2016) Genetic divergence of the endangered seagrass Zostera japonica Ascherson & Graebner between temperate and subtropical coasts of China based on partial sequences of matK and ITS. Biochem Syst Ecol 68:51–57
Zheng F, Qiu G, Fan H, Zhang W(2013) Diversity, distribution and conservation of Chinese seagrass species. Biodiv Sci 21:517–526
Zipperle AM, Coyer JA, Reise K, Stam WT, Olsen JL (2011) An evaluation of small-scale genetic diversity and the mating system in Zostera noltii on an intertidal sandflat in the Wadden Sea. Ann Bot 107:127–134
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank all of the members of the Tropical Marine Biological Research Station in Hainan for their helping work in sample collecting.
Funding
The research was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (41676163, 41276114), Strategic Priority Research Program of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (XDA13020300), Key Special Project for Introduced Talents Team of Southern Marine Science and Engineering Guangdong Laboratory (GML2019ZD0402), Innovation Academy of South China Sea Ecology and Environmental Engineering, Chinese Academy of Sciences (ISEE2018ZD02), National Key Research and Development Program of China (2017YFC0506301, 2018YFC1406505, 2018FY100105), Guangdong Province Public Welfare Research and Capacity Building Project (2015A020216016), Pearl River S&T Nova Program of Guangzhou (201806010017), and Science and Technology Planning Project of Guangdong Province, China (2020B1212060058).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lin, X., Dong, J., Yang, Q. et al. Identification of three seagrass species in coral reef ecosystem by using multiple genes of DNA barcoding. Ecotoxicology 30, 919–928 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10646-021-02397-3
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10646-021-02397-3