Summary
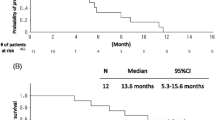
Background The efficacy and safety of bevacizumab in elderly patients with non-small cell lung cancer remain controversial. This study focused on both selecting fit elderly patients and overcoming interpatient variability with respect to pharmacodynamics. Methods Elderly (age: ≥70 years) patients with advanced non-squamous non-small cell lung cancer were enrolled. Patients with uncontrolled congestive heart failure and uncontrolled diabetes were excluded. The treatment regimen comprised carboplatin at an area under the curve of 5 mg/ml/min on day 1, paclitaxel at 90 mg/m2 on days 1 and 8, and bevacizumab at 15 mg/kg on day 1 every 21 days for up to 4 cycles, followed by maintenance bevacizumab. Dose reduction due to side effects was performed, with a wide range of doses of paclitaxel from 23 mg/m2/week to 60 mg/m2/week. Results Of the 36 patients entered, 38.9% required a dose reduction or cancellation of paclitaxel administration on day 8, and 75% patients were able to complete 4 cycles of triplet therapy. The response rate, primary endpoint, was 69.4% (95% confidence interval [CI]: 51.9–83.7). The median progression free survival and overall survival were 8.4 months and 29.2 months, respectively. The most common adverse events included neutropenia, hypertension, anemia, and infection. Although Grade ≥ 3 adverse events were observed in 24 patients (66.7%), there were no deaths due to toxicity. Conclusion Carboplatin plus weekly paclitaxel with bevacizumab is a feasible, effective first-line regimen for elderly non-small cell lung cancer patients. (UMIN00006622).



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Siegel RL, Miller KD, Jemal A (2016) Cancer statistics, 2016. CA Cancer J Clin 66(1):7–30. doi:10.3322/caac.21332
Wedding U, Honecker F, Bokemeyer C, Pientka L, Hoffken K (2007) Tolerance to chemotherapy in elderly patients with cancer. Cancer Control : Journal of the Moffitt Cancer Center 14(1):44–56
Jennens RR, Giles GG, Fox RM (2006) Increasing underrepresentation of elderly patients with advanced colorectal or non-small-cell lung cancer in chemotherapy trials. Intern Med J 36(4):216–220. doi:10.1111/j.1445-5994.2006.01033.x
Yee KW, Pater JL, Pho L, Zee B, Siu LL (2003) Enrollment of older patients in cancer treatment trials in Canada: why is age a barrier? J Clin Oncol 21(8):1618–1623. doi:10.1200/jco.2003.12.044
The Elderly Lung Cancer Vinorelbine Italian Study Group (1999) Effects of vinorelbine on quality of life and survival of elderly patients with advanced non-small-cell lung cancer. J Natl Cancer Inst 91(1):66–72
Quoix E, Zalcman G, Oster JP, Westeel V, Pichon E, Lavole A, Dauba J, Debieuvre D, Souquet PJ, Bigay-Game L, Dansin E, Poudenx M, Molinier O, Vaylet F, Moro-Sibilot D, Herman D, Bennouna J, Tredaniel J, Ducolone A, Lebitasy MP, Baudrin L, Laporte S, Milleron B (2011) Carboplatin and weekly paclitaxel doublet chemotherapy compared with monotherapy in elderly patients with advanced non-small-cell lung cancer: IFCT-0501 randomised, phase 3 trial. Lancet 378(9796):1079–1088. doi:10.1016/s0140-6736(11)60780-0
Ferrara N, Gerber HP, LeCouter J (2003) The biology of VEGF and its receptors. Nat Med 9(6):669–676. doi:10.1038/nm0603-669
Sandler A, Gray R, Perry MC, Brahmer J, Schiller JH, Dowlati A, Lilenbaum R, Johnson DH (2006) Paclitaxel-carboplatin alone or with bevacizumab for non-small-cell lung cancer. N Engl J Med 355(24):2542–2550. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa061884
Ramalingam SS, Dahlberg SE, Langer CJ, Gray R, Belani CP, Brahmer JR, Sandler AB, Schiller JH, Johnson DH (2008) Outcomes for elderly, advanced-stage non small-cell lung cancer patients treated with bevacizumab in combination with carboplatin and paclitaxel: analysis of eastern cooperative oncology group trial 4599. J Clin Oncol 26(1):60–65. doi:10.1200/jco.2007.13.1144
Kearns CM, Gianni L, Egorin MJ (1995) Paclitaxel pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics. Semin Oncol 22(3 Suppl 6):16–23
Shammas FV, Dickstein K (1988) Clinical pharmacokinetics in heart failure. An updated review. Clin Pharmacokinet 15(2):94–113. doi:10.2165/00003088-198815020-00002
Spigel DR, Hainsworth JD, Shipley DL, Ervin TJ, Kohler PC, Lubiner ET, Peyton JD, Waterhouse DM, Burris HA 3rd, Greco FA (2012) A randomized phase II trial of pemetrexed/gemcitabine/bevacizumab or pemetrexed/carboplatin/bevacizumab in the first-line treatment of elderly patients with advanced non-small cell lung cancer. J Thorac Oncol 7(1):196–202. doi:10.1097/JTO.0b013e3182307efe
Dy GK, Molina JR, Qi Y, Ansari R, Thomas S, Ross HJ, Soori G, Anderson D, Aubry MC, Meyers J, Adjei AA, Mandrekar S, Adjei AA (2014) NCCTG N0821 (alliance): a phase II first-line study of pemetrexed, carboplatin, and bevacizumab in elderly patients with advanced nonsquamous non-small-cell lung cancer with good performance status. J Thorac Oncol 9(8):1146–1153. doi:10.1097/jto.0000000000000217
Choueiri TK, Mayer EL, Je Y, Rosenberg JE, Nguyen PL, Azzi GR, Bellmunt J, Burstein HJ, Schutz FA (2011) Congestive heart failure risk in patients with breast cancer treated with bevacizumab. J Clin Oncol 29(6):632–638. doi:10.1200/jco.2010.31.9129
Verma N, Swain SM (2011) Bevacizumab and heart failure risk in patients with breast cancer: a thorn in the side? J Clin Oncol 29(6):603–606. doi:10.1200/jco.2010.32.9060
Pfister R, Schneider CA (2009) ESC guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of acute and chronic heart failure 2008: application of natriuretic peptides. Eur Heart J 30(3):382–383 . doi:10.1093/eurheartj/ehn560author reply 383
Kubota T, Okano Y, Sakai M, Takaoka M, Tsukuda T, Anabuki K, Kawase S, Miyamoto S, Ohnishi H, Hatakeyama N, Machida H, Urata T, Yamamoto A, Ogushi F, Yokoyama A (2016) Carboplatin plus weekly paclitaxel with bevacizumab for first-line treatment of non-small cell lung cancer. Anticancer Res 36(1):307–312
Langer CJ, Socinski MA, Patel JD, Sandler AB, Schiller JH, Leon L, Hazard SJ, Ramalingam SS (2016) Isolating the role of bevacizumab in elderly patients with previously untreated nonsquamous non-small cell lung cancer: secondary analyses of the ECOG 4599 and PointBreak trials. Am J Clin Oncol 39(5):441–447. doi:10.1097/coc.0000000000000163
Takano T, Fukui T, Ohe Y, Tsuta K, Yamamoto S, Nokihara H, Yamamoto N, Sekine I, Kunitoh H, Furuta K, Tamura T (2008) EGFR mutations predict survival benefit from gefitinib in patients with advanced lung adenocarcinoma: a historical comparison of patients treated before and after gefitinib approval in Japan. J Clin Oncol 26(34):5589–5595. doi:10.1200/jco.2008.16.7254
Takagi Y, Toriihara A, Nakahara Y, Yomota M, Okuma Y, Hosomi Y, Shibuya M, Okamura T (2013) Eligibility for bevacizumab as an independent prognostic factor for patients with advanced non-squamous non-small cell lung cancer: a retrospective cohort study. PLoS One 8(3):e59700. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0059700
Sculier JP, Chansky K, Crowley JJ, Van Meerbeeck J, Goldstraw P (2008) The impact of additional prognostic factors on survival and their relationship with the anatomical extent of disease expressed by the 6th edition of the TNM classification of malignant tumors and the proposals for the 7th edition. J Thorac Oncol 3(5):457–466. doi:10.1097/JTO.0b013e31816de2b8
Masters GA, Temin S, Azzoli CG, Giaccone G, Baker S Jr, Brahmer JR, Ellis PM, Gajra A, Rackear N, Schiller JH, Smith TJ, Strawn JR, Trent D, Johnson DH (2015) Systemic therapy for stage IV non-small-cell lung cancer: American Society of Clinical Oncology clinical practice guideline update. J Clin Oncol 33(30):3488–3515. doi:10.1200/jco.2015.62.1342
Acknowledgements
We thank the patients and their families for their support and participation in this study. We thank the data management staff of The Tokyo Cooperative Oncology Group (TCOG) data center, especially Hiromi Odagiri, and the data analysis staff of the Medical TOUKEI Corporation. The authors also thank Dr. Keiichi Nagao, Dr. Yushi Nakai, and Dr. Hiroshi Tanaka for their assistance as the Safety Monitoring Committee.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Satoru Miura, Shunichi Sugawara, Kunihiko Kobayashi, Yuichi Takiguchi and Akihiko Gemma has received lecture fees from Chugai Pharmaceutical Co. Makoto Maemondo, Akira Inoue Yuichi Takiguchi has received lecture fees from Chugai and Bristol-Myers Squibb. All other authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Financial support
This study was supported by the North East Japan Study Group (NEJSG).
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards. This study was approved by the institutional review boards of all participating sites.
Informed consent
All study participants provided written informed consent prior to enrollment.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Miura, S., Maemondo, M., Iwashima, A. et al. A phase II study of carboplatin plus weekly paclitaxel with bevacizumab for elderly patients with non-squamous non-small-cell lung cancer (NEJ016). Invest New Drugs 35, 227–234 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10637-017-0436-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10637-017-0436-1