Summary
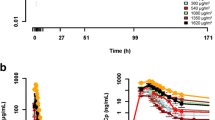
Objective To determine the recommended dose for phase II trials of elisidepsin (PM02734, Irvalec®) in combination with erlotinib in patients with advanced malignant solid tumors. Methods Open-label, dose-escalating, phase I study of intravenous elisidepsin administered weekly (days 1, 8 and 15) over 3 h as a flat dose (FD) and daily oral erlotinib, every 3 weeks. A pharmacokinetic analysis was done on blood samples collected around the first elisidepsin infusion. Results Thirty patients were treated across six different dose levels (DLs) ranging from elisidepsin 0.33–2.25 mg/erlotinib 100–150 mg. Two patients had dose-limiting toxicities: grade 3 bilirubin increase (DL3: 0.75 mg/150 mg) and a dose omission for > 2 weeks due to grade 3 alanine aminotransferase increase (DL6: 2.25 mg/100 mg). The daily erlotinib dose was escalated to 150 mg at DL2-DL5, but decreased to 100 mg at DL6, as most grade 3 toxicities were related to this agent only. The most frequent toxicities were transaminase increases (related to elisidepsin), and rash, pruritus and diarrhea (related to erlotinib). No objective responses were observed. Despite no overlapping toxicities, the combination was declared unfeasible due to frequent elisidepsin dose delays. The pharmacokinetics of elisidepsin/erlotinib was not significantly different from that of each agent alone. Conclusion The difficulty in combining elisidepsin with the standard dose of erlotinib (150 mg), together with the lack of antitumor activity, made the combination unattractive for further development. The trial was closed without having determined a recommended dose.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hamann MT, Otto CS, Scheuer PJ, Dunbar DC (1996) Kahalalides: bioactive peptides from a marine mollusk Elysia rufescens and its algal diet bryopsis sp. (1). J Org Chem 61(19):6594–600
Sparidans RW, Stokvis E, Jimeno JM, Lopez-Lazaro L, Schellens JH, Beijnen JH (2001) Chemical and enzymatic stability of a cyclic depsipeptide, the novel, marine-derived, anti-cancer agent kahalalide F. Anti-Cancer Drugs 12(7):575–82
Faircloth G, Cuevas C (2006) Kahalalide F and ES285: potent anticancer agents from marine molluscs. Prog Mol Subcell Biol 43:363–79
Provencio M, Sanchez A, Gasent J, Gomez P, Rosell R (2009) Cancer treatments: can we find treasures at the bottom of the sea? Clin Lung Cancer 10(4):295–300
Herrero AB, Astudillo AM, Balboa MA, Cuevas C, Balsinde J, Moreno S (2008) Levels of SCS7/FA2H-mediated fatty acid 2-hydroxylation determine the sensitivity of cells to antitumor PM02734. Cancer Res 68(23):9779–87
Molina-Guijarro JM, Macias A, Garcia C, Munoz E, Garcia-Fernandez LF, David M et al (2011) Irvalec inserts into the plasma membrane causing rapid loss of integrity and necrotic cell death in tumor cells. PLoS One 6(4), e19042
Ling YH, Aracil M, Zou Y, Yuan Z, Lu B, Jimeno J et al (2011) PM02734 (elisidepsin) induces caspase-independent cell death associated with features of autophagy, inhibition of the Akt/mTOR signaling pathway, and activation of death-associated protein kinase. Clin Cancer Res: Off J Am Assoc Cancer Res 17(16):5353–66
Takeda M, Okamoto I, Nakagawa K (2015) Pooled safety analysis of EGFR-TKI treatment for EGFR mutation-positive non-small cell lung cancer. Lung Cancer 88(1):74–9
Wang JP, Wu CY, Yeh YC, Shyr YM, Wu YY, Kuo CY et al. (2015) Erlotinib is effective in pancreatic cancer with epidermal growth factor receptor mutations: a randomized, open-label, prospective trial. Oncotarget
Janmaat ML, Rodriguez JA, Jimeno J, Kruyt FA, Giaccone G (2005) Kahalalide F induces necrosis-like cell death that involves depletion of ErbB3 and inhibition of Akt signaling. Mol Pharmacol 68(2):502–10
Teixido C, Mares R, Aracil M, Ramon y Cajal S, Hernandez-Losa J (2013) Epithelial-mesenchymal transition markers and HER3 expression are predictors of elisidepsin treatment response in breast and pancreatic cancer cell lines. PLoS One 8(1), e53645
Serova M, de Gramont A, Bieche I, Riveiro ME, Galmarini CM, Aracil M et al (2013) Predictive factors of sensitivity to elisidepsin, a novel Kahalalide F-derived marine compound. Mar Drugs 11(3):944–59
Teixido C, Arguelaguet E, Pons B, Aracil M, Jimeno J, Somoza R et al (2012) ErbB3 expression predicts sensitivity to elisidepsin treatment: in vitro synergism with cisplatin, paclitaxel and gemcitabine in lung, breast and colon cancer cell lines. Int J Oncol 41(1):317–24
Thomson S, Buck E, Petti F, Griffin G, Brown E, Ramnarine N et al (2005) Epithelial to mesenchymal transition is a determinant of sensitivity of non-small-cell lung carcinoma cell lines and xenografts to epidermal growth factor receptor inhibition. Cancer Res 65(20):9455–62
Amann J, Kalyankrishna S, Massion PP, Ohm JE, Girard L, Shigematsu H et al (2005) Aberrant epidermal growth factor receptor signaling and enhanced sensitivity to EGFR inhibitors in lung cancer. Cancer Res 65(1):226–35
Frolov A, Schuller K, Tzeng CW, Cannon EE, Ku BC, Howard JH et al (2007) ErbB3 expression and dimerization with EGFR influence pancreatic cancer cell sensitivity to erlotinib. Cancer Biol Ther 6(4):548–54
Buck EA, Eyzaguirre A, Gibson N, Cagnoni P, Haley JD, Iwata KK (2005) Identification of E-cadherin and HER3 as biomakers of sensitivity to the EGFR kinase inhibitor erlotinib in pancreatic and colorectal cancers. In: Proceedings of the AACR-NCI-EORTC International Conference. Molecular Targets and Cancer Therapeutics. Poster Session B: Biological Therapeutic Agents: Growth Factor Receptors and Other Surface Antigens as Targets for Therapy; Philadelphia, p. 142- Poster B66
Engelman JA, Janne PA, Mermel C, Pearlberg J, Mukohara T, Fleet C et al (2005) ErbB-3 mediates phosphoinositide 3-kinase activity in gefitinib-sensitive non-small cell lung cancer cell lines. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 102(10):3788–93
Salazar R, Metges JP, Anthoney DA, Laus G, Maqueda MA, Goncalves A et al. (2013) IMAGE, a randomized phase Ib/II study of elisidepsin (E) as a single agent in pretreated advanced gastroesophageal (GE) cancer. 2013 Gastrointestinal Cancers Symposium, Jan 24–26, 2013. San Francisco, California. J Clin Oncol 31(4 Supl) Abs N 92
Salazar R, Jones RJ, Oaknin A, Crawford D, Cuadra C, Hopkins C et al (2012) A phase I and pharmacokinetic study of elisidepsin (PM02734) in patients with advanced solid tumors. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 70(5):673–81
Bruce JY, Geary D, de las Heras B, Soto A, Garcia Paramio P, Yovine A et al. (2008) Phase I study of PM02734: association of dose-limiting hepatotoxicity with plasma concentrations. ASCO American Society of Clinical Oncology, 44th Annual Meeting, May 30- Jun 3, 2008. Chicago. Abs. N°2513
Burotto M, Ali SA, O’Sullivan Coyne G (2015) Class act: safety comparison of approved tyrosine kinase inhibitors for non-small-cell lung carcinoma. Expert Opin Drug Saf 14(1):97–110
Zhang WQ, Li T, Li H (2014) Efficacy of EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitors in non-small-cell lung cancer patients with/without EGFR-mutation: evidence based on recent phase III randomized trials. Med Sci Monit: Int Med J Exp Clin Res 20:2666–76
Goldwasser F, Faivre S, Alexandre J, Coronado C, Fernandez-Garcia EM, Kahatt CM et al (2014) Phase I study of elisidepsin (Irvalec(R)) in combination with carboplatin or gemcitabine in patients with advanced malignancies. Investig New Drugs 32(3):500–9
Therasse P, Arbuck SG, Eisenhauer EA, Wanders J, Kaplan RS, Rubinstein L et al (2000) New guidelines to evaluate the response to treatment in solid tumors. European Organization for Research and Treatment of Cancer, National Cancer Institute of the United States, National Cancer Institute of Canada. J Natl Cancer Inst 92(3):205–16
Simon R, Freidlin B, Rubinstein L, Arbuck SG, Collins J, Christian MC (1997) Accelerated titration designs for phase I clinical trials in oncology. J Natl Cancer Inst 89(15):1138–47
Ratain MJ, Geary D, Undevia SD, Coronado C, Alfaro V, Iglesias JL et al (2015) First-in-human, phase I study of elisidepsin (PM02734) administered as a 30-min or as a 3-hour intravenous infusion every three weeks in patients with advanced solid tumors. Investig New Drugs 33(4):901–10
National Cancer Institute Common Terminology Criteria for Adverse Events. Version 3.0. http://ctep.cancer.gov/forms/CTCAEv3.pdf. Accessed 10 July 2008
Yin J, Aviles P, Lee W, Ly C, Guillen MJ, Munt S et al (2006) Development of a liquid chromatography/tandem mass spectrometry assay for the quantification of PM02734, a novel antineoplastic agent, in dog plasma. Rapid Commun Mass Spectrom: RCM 20(18):2735–40
Giaccone G, Herbst RS, Manegold C, Scagliotti G, Rosell R, Miller V et al (2004) Gefitinib in combination with gemcitabine and cisplatin in advanced non-small-cell lung cancer: a phase III trial--INTACT 1. J Clin Oncol: Off J Am Soc Clin Oncol 22(5):777–84
Herbst RS, Giaccone G, Schiller JH, Natale RB, Miller V, Manegold C et al (2004) Gefitinib in combination with paclitaxel and carboplatin in advanced non-small-cell lung cancer: a phase III trial--INTACT 2. J Clin Oncol: Off J Am Soc Clin Oncol 22(5):785–94
Herbst RS, Prager D, Hermann R, Fehrenbacher L, Johnson BE, Sandler A et al (2005) TRIBUTE: a phase III trial of erlotinib hydrochloride (OSI-774) combined with carboplatin and paclitaxel chemotherapy in advanced non-small-cell lung cancer. J Clin Oncol: Off J Am Soc Clin Oncol 23(25):5892–9
Gatzemeier U, Pluzanska A, Szczesna A, Kaukel E, Roubec J, De Rosa F et al (2007) Phase III study of erlotinib in combination with cisplatin and gemcitabine in advanced non-small-cell lung cancer: the Tarceva Lung Cancer Investigation Trial. J Clin Oncol: Off J Am Soc Clin Oncol 25(12):1545–52
Minami S, Kijima T (2014) Does erlotinib add beneficial effect on cytotoxic agent for patients with pretreated advanced non-small cell lung cancer? Cancer Cell Microenviron 1, e57. doi:10.14800/ccm.57
Hidalgo M, Siu LL, Nemunaitis J, Rizzo J, Hammond LA, Takimoto C et al (2001) Phase I and pharmacologic study of OSI-774, an epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitor, in patients with advanced solid malignancies. J Clin Oncol: Off J Am Soc Clin Oncol 19(13):3267–79
Acknowledgments
We thank all the staff who contributed to the care of the patients included in this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Cinthya Coronado, Eva M. Fernández-García, Jorge Luis Iglesias Dios and Bernardo Miguel-Lillo are employees of Pharma Mar.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Goel, S., Viteri, S., Morán, T. et al. Phase I, dose-escalating study of elisidepsin (Irvalec®), a plasma membrane-disrupting marine antitumor agent, in combination with erlotinib in patients with advanced malignant solid tumors. Invest New Drugs 34, 75–83 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10637-015-0305-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10637-015-0305-8