Abstract
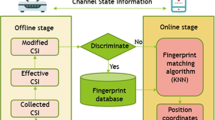
With the increasing demand of location-based services, indoor localization based on fingerprinting has become an increasingly important technique due to its high accuracy and low hardware requirement. The paper presents a novel fingerprinting system with a fine-grained information known as channel state information (CSI). The proposed fingerprint exploits multiple antennas and subcarriers of the IEEE 802.11n network using multiple input multiple output (MIMO)–orthogonal frequency division multiplexing system and takes account into the distance of features in each fingerprint. The experimental performance of the fingerprint is compared with RSSI-based Fingerprinting system and the CSI–MIMO Fingerprinting system. The experiment results show that the system achieves the accuracy of 0.61 and 0.9 m in static and dynamic scenarios respectively.














Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hu, Y., Zhang, L., Gao, L., et al.: Linear system construction of multilateration based on error propagation estimation. EURASIP J. Wirel. Commun. Netw. 2016(1), 1–10 (2016)
Bahl, P., Padmanabhan, V.N.: RADAR: an in-building RF-based user location and tracking system. In: Proceedings of the INFOCOM 2000. Nineteenth Joint Conference of the IEEE Computer and Communications Societies, vol. 2, pp. 775–784. IEEE Xplore (2000)
Youssef, M., Agrawala, A.: The horus WLAN location determination system. In: International Conference on Mobile Systems, Applications, and Services, pp. 205–218. DBLP (2005)
Yang, Z., Zhou, Z., Liu, Y.: From RSSI to CSI: indoor localization via channel response. ACM Comput. Surv. 46(2), 25 (2013)
Wu, C., Yang, Z., Zhou, Z., et al.: PhaseU: real-time LOS identification with WiFi. In: IEEE International Conference on Computer Communications, pp. 2038–2046. IEEE (2015)
Wu, K., Xiao, J., Yi, Y., et al.: FILA: fine-grained indoor localization. Proc. IEEE INFOCOM 131(5), 2210–2218 (2012)
Zhou, Z., Wu, C., Yang, Z., et al.: Sensorless sensing with WiFi. Tsinghua Sci. Technol. 20(1), 1–6 (2015)
Sen, S., Lee, J., Kim, K.H., et al.: Avoiding multipath to revive inbuilding WiFi localization. In: Proceeding of the International Conference on Mobile Systems, Applications, and Services, pp. 249–262. ACM, New York (2013)
Halperin, D., Hu, W., Sheth, A., et al.: Tool release: gathering 802.11n traces with channel state information. ACM SIGCOMM Comput. Commun. Rev. 41(1), 53–53 (2011)
Sen, S., Radunovic, B., Choudhury, R.R., et al.: You are facing the Mona Lisa: spot localization using PHY layer information. In: International Conference on Mobile Systems, Applications, and Services, pp. 183–196. ACM, New York (2012)
Kotaru, M., Joshi, K., Bharadia, D., et al.: SpotFi: decimeter level localization using WiFi. ACM SIGCOMM Comput. Commun. Rev. 45(5), 269–282 (2015)
Zhang, Y., Chen, X., Wang, H., et al.: Accurate indoor localization with channel state information. In: The International Workshop, pp. 35–36 (2015)
Tian, Z., Li, Z., Zhou, M., et al.: PILA: sub-meter localization using CSI from commodity Wi-Fi devices. Sensors 16(10), 1664 (2016)
Demeechai, T., Kukieattikool, P., Ngo, T., et al.: Localization based on standard wireless LAN infrastructure using MIMO-OFDM channel state information. EURASIP J. Wirel. Commun. Netw. 2016(1), 146 (2016)
Xiao, J., Wu, K., Yi, Y., et al.: FIFS: fine-grained indoor fingerprinting system. In: International Conference on Computer Communications and Networks, pp. 1–7. IEEE (2012)
Chapre, Y., Ignjatovic, A., Seneviratne, A., et al.: CSI-MIMO: an efficient Wi-Fi fingerprinting using channel state information with MIMO. Pervasive Mobile Comput. 23, 89–103 (2015)
Tse, D., Viswanath, P.: Fundamentals of wireless communications. Eth Zrich Lect. Script 3(5), B6-1–B6-5 (2005)
Perahia, E.: IEEE 802.11n-2009 Standard + IEEE 802.11n Mac Layer e-Learning Course Bundle. IEEE (2012)
Brunato, M., Battiti, R.: Statistical learning theory for location fingerprinting in wireless LANs. Comput. Netw. 47(6), 825–845 (2005)
Zhou, Z., Yang, Z., Wu, C., et al.: WiFi-based indoor line-of-sight identification. IEEE Trans. Wirel. Commun. 14(11), 6125–6136 (2015)
Caffery, J.J.J.: A new approach to the geometry of TOA location. In: Vehicular Technology Conference, 2000. IEEE-VTS FALL VTC 2000, vol. 4, pp. 1943–1949. IEEE (2000)
Kumar, S., Kumar, S., Katabi, D.: Decimeter-level localization with a single WiFi access point. In: Usenix conference on networked systems design and implementation, pp. 165–178. USENIX Association (2016)
Qian, K., Wu, C., Yang, Z., et al.: PADS: passive detection of moving targets with dynamic speed using PHY layer information. In: IEEE International Conference on Parallel and Distributed Systems, pp. 1–8. IEEE (2014)
Kakade, S.M., Shalev-Shwartz, S., Tewari, A.: Regularization techniques for learning with matrices. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 13(1), 1865–1890 (2009)
Luenberger, D.G., Ye, Y.: Linear and nonlinear programming. Int. Encycl. Soc. Behav. Sci. 67(2), 8868–8874 (2008)
Halperin, D., Hu, W., Sheth, A., et al.: Predictable 802.11 packet delivery from wireless channel measurements. ACM SIGCOMM Comput. Commun. Rev. 40(4), 159–170 (2010)
Acknowledgements
This work is supported partly by the Natural Science Foundation of Jiangsu Province under Grant (No: BK20140216), the National Key Technology Research and Development Program of the Ministry of Science and Technology of China under Grant (No: 2012BAH12B01), and the National Key Technology Research and Development Program of the Ministry of Science and Technology of China under Grant (No: 2012BAH27B04).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, L., Ding, E., Zhao, Z. et al. A novel fingerprinting using channel state information with MIMO–OFDM. Cluster Comput 20, 3299–3312 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10586-017-1072-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10586-017-1072-4