Abstract
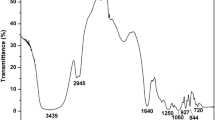
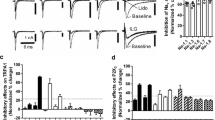
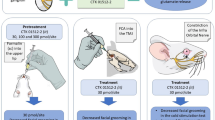
Curcumin, a major bioactive component of turmeric, has diverse therapeutic effects such as anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, anticancer, and antinociceptive activities. The acid-sensing ion channels (ASICs), which can be activated by acute drops in the extracellular pH, play an important role in nociception. However, very little is known about the interaction between ASICs and curcumin in nociception of inflammation. In our study, we investigated whether the antinociceptive effects of curcumin are mediated via ASICs using an orofacial nociceptive model and in vitro western blotting, immunofluorescence, whole-cell patch-clamp recordings in the trigeminal system. Intraperitoneally administered curcumin at a dose of 50 mg/kg can reduce hyperalgesia in both the phases of a formalin-induced orofacial nociceptive model. Curcumin reduced the amplitude of ASICs currents in a dose-dependent manner in trigeminal ganglion (TG) neurons, and curcumin also reduced the protein quantity but did not change the distribution of ASICs in TG. Thus, our results indicate that curcumin can reduce formalin-induced ASICs activation and thus inhibit ASICs-mediated inflammatory pain hypersensitivity.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aggarwal BB, Sundaram C, Malani N, Ichikawa H (2007) Curcumin: the Indian solid gold. Adv Exp Med Biol 595:1–75. doi:10.1007/978-0-387-46401-5_1
Agrawal DK, Mishra PK (2010) Curcumin and its analogues: potential anticancer agents. Med Res Rev 30:818–860. doi:10.1002/med.20188
Banerjee M, Tripathi LM, Srivastava VM, Puri A, Shukla R (2003) Modulation of inflammatory mediators by ibuprofen and curcumin treatment during chronic inflammation in rat. Immunopharmacol Immunotoxicol 25:213–224
Chainani-Wu N (2003) Safety and anti-inflammatory activity of curcumin: a component of tumeric (Curcuma longa). J Altern Complement Med 9(1):161–168
Chan MM-Y, Huang H-I, Fenton MR, Fong D (1998) In vivo inhibition of nitric oxide synthase gene expression by curcumin, a cancer preventive natural product with anti-inflammatory properties. Biochem Pharmacol 55:1955–1962. doi:10.1016/S0006-2952(98)00114-2
Chen CC, England S, Akopian AN, Wood JN (1998) A sensory neuron-specific, proton-gated ion channel. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 95:10240–10245
Deval E et al (2011) Acid-sensing ion channels in postoperative pain. J Neurosci 31:6059–6066
Duan B et al (2007) Upregulation of acid-sensing ion channel ASIC1a in spinal dorsal horn neurons contributes to inflammatory pain hypersensitivity. J Neurosci 27:11139–11148. doi:10.1523/jneurosci.3364-07.2007
Fu H et al (2016) Acid-sensing ion channels in trigeminal ganglion neurons innervating the orofacial region contribute to orofacial inflammatory pain. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol 43:193–202. doi:10.1111/1440-1681.12510
Goel A, Boland CR, Chauhan DP (2001) Specific inhibition of cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) expression by dietary curcumin in HT-29 human colon cancer cells. Cancer Lett 172:111–118. doi:10.1016/S0304-3835(01)00655-3
Hsu CH, Cheng AL (2007) Clinical studies with curcumin. Adv Exp Med Biol 595:471–480. doi:10.1007/978-0-387-46401-5_21
Hu Z-L et al (2010) Disruption of PICK1 attenuates the function of ASICs and PKC regulation of ASICs. Am J Physiol 299:C1355–C1362
Julius D, Basbaum AI (2001) Molecular mechanisms of nociception. Nature 413:203–210
Jurenka JS (2009) Anti-inflammatory properties of curcumin, a major constituent of Curcuma longa: a review of preclinical and clinical research. Altern Med Rev 14:141–153
Krishtal O (2003) The ASICs: signaling molecules? Modulators? Trends Neurosci 26:477–483. doi:10.1016/s0166-2236(03)00210-8
Lingueglia E (2007) Acid-sensing ion channels in sensory perception. J Biol Chem 282:17325–17329. doi:10.1074/jbc.R700011200
Luccarini P, Childeric A, Gaydier A-M, Voisin D, Dallel R (2006) The orofacial formalin test in the mouse: a behavioral model for studying physiology and modulation of trigeminal nociception. J Pain 7:908–914
Mamet J, Baron A, Lazdunski M, Voilley N (2002) Proinflammatory mediators, stimulators of sensory neuron excitability via the expression of acid-sensing ion channels. J Neurosci 22:10662–10670
Raboisson P, Dallel R (2004) The orofacial formalin test. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 28:219–226. doi:10.1016/j.neubiorev.2003.12.003
Steen K, Reeh P (1993) Sustained graded pain and hyperalgesia from harmless experimental tissue acidosis in human skin. Neurosci Lett 154:113–116
Ugawa S, Ueda T, Ishida Y, Nishigaki M, Shibata Y, Shimada S (2002) Amiloride-blockable acid-sensing ion channels are leading acid sensors expressed in human nociceptors. J Clin Investig 110:1185–1190. doi:10.1172/jci15709
Voilley N, de Weille J, Mamet J, Lazdunski M (2001) Nonsteroid anti-inflammatory drugs inhibit both the activity and the inflammation-induced expression of acid-sensing ion channels in nociceptors. J Neurosci 21:8026–8033
Xu YX, Pindolia KR, Janakiraman N, Chapman RA, Gautam SC (1997) Curcumin inhibits IL1 alpha and TNF-alpha induction of AP-1 and NF-kB DNA-binding activity in bone marrow stromal cells. Hematop Mol Hematol 11:49–62
Yeon K et al (2010) Curcumin produces an antihyperalgesic effect via antagonism of TRPV1. J Dent Res 89:170–174
Zhou T, Chen D, Li Q, Sun X, Song Y, Wang C (2013) Curcumin inhibits inflammatory response and bone loss during experimental periodontitis in rats. Acta Odontol Scand 71:349–356. doi:10.3109/00016357.2012.682092
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Medical Scientific Research Foundation of GuangDong (No. A2015356) and the Construct TCM Research Program of GuangDong (No. 20141151) to Dr. H. Fu.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wu, Y., Qin, D., Yang, H. et al. Evidence for the Participation of Acid-Sensing Ion Channels (ASICs) in the Antinociceptive Effect of Curcumin in a Formalin-Induced Orofacial Inflammatory Model. Cell Mol Neurobiol 37, 635–642 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10571-016-0399-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10571-016-0399-3