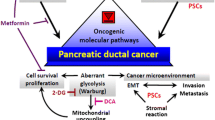
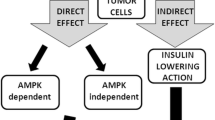
Abstract
Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma continues to be a lethal disease, for which efficient treatment options are very limited. Increasing efforts have been taken to understand how to prevent or intercept this disease at an early stage. There is convincing evidence from epidemiologic and preclinical studies that the antidiabetic drug metformin possesses beneficial effects in pancreatic cancer, including reducing the risk of developing the disease and improving survival in patients with early-stage disease. This review will summarize the current literature about the epidemiological data on metformin and pancreatic cancer as well as describe the preclinical evidence illustrating the anticancer effects of metformin in pancreatic cancer. Underlying mechanisms and targets of metformin will also be discussed. These include direct effects on transformed pancreatic epithelial cells and indirect, systemic effects on extra-pancreatic tissues.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Siegel, R. L., Miller, K. D., Fuchs, H. E., & Jemal, A. (2021). Cancer statistics, 2021. CA: A Cancer Journal for Clinicians, 71(1), 7–33. https://doi.org/10.3322/caac.21654
Siegel, R. L., Miller, K. D., & Jemal, A. (2016). Cancer statistics, 2016. CA: A Cancer Journal for Clinicians, 66(1), 7–30. https://doi.org/10.3322/caac.21332
Rahib, L., Smith, B. D., Aizenberg, R., Rosenzweig, A. B., Fleshman, J. M., & Matrisian, L. M. (2014). Projecting cancer incidence and deaths to 2030: The unexpected burden of thyroid, liver, and pancreas cancers in the United States. Cancer Research, 74(11), 2913–2921. https://doi.org/10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-14-0155
Albini, A., DeCensi, A., Cavalli, F., & Costa, A. (2016). Cancer prevention and interception: A new era for chemopreventive approaches. Clinical Cancer Research, 22(17), 4322–4327.
Meyskens, F. L., Mukhtar, H., Rock, C. L., Cuzick, J., Kensler, T. W., Yang, C. S., Ramsey, S. D., Lippman, S. M., & Alberts, D. S. (2016). Cancer prevention: Obstacles, challenges, and the road ahead. Journal of the National Cancer Institute, 108(2), djv309. https://doi.org/10.1093/jnci/djv309
Maitra, A., Fukushima, N., Takaori, K., & Hruban, R. H. (2005). Precursors to invasive pancreatic cancer. Advances in Anatomic Pathology, 12(2), 81–91.
Eibl, G., & Rozengurt, E. (2019). KRAS, YAP, and obesity in pancreatic cancer: A signaling network with multiple loops. Seminars in Cancer Biology, 54, 50–62. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.semcancer.2017.10.007
Hingorani, S. R., Petricoin, E. F., Maitra, A., Rajapakse, V., King, C., Jacobetz, M. A., Ross, S., Conrads, T. P., Veenstra, T. D., Hitt, B. A., Kawaguchi, Y., Johann, D., Liotta, L. A., Crawford, H. C., Putt, M. E., Jacks, T., Wright, C. V., Hruban, R. H., Lowy, A. M., et al. (2003). Preinvasive and invasive ductal pancreatic cancer and its early detection in the mouse. Cancer Cell, 4(6), 437–450.
Hingorani, S. R., Wang, L., Multani, A. S., Combs, C., Deramaudt, T. B., Hruban, R. H., Rustgi, A. K., Chang, S., & Tuveson, D. A. (2005). Trp53R172H and KrasG12D cooperate to promote chromosomal instability and widely metastatic pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma in mice. Cancer Cell, 7(5), 469–483. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ccr.2005.04.023
Ying, H., Dey, P., Yao, W., Kimmelman, A. C., Draetta, G. F., Maitra, A., & DePinho, R. A. (2016). Genetics and biology of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Genes & Development, 30(4), 355–385. https://doi.org/10.1101/gad.275776.115
Collins, M. A., Bednar, F., Zhang, Y., Brisset, J.-C., Galbán, S., Galbán, C. J., Rakshit, S., Flannagan, K. S., Adsay, N. V., & Pasca di Magliano, M. (2012). Oncogenic Kras is required for both the initiation and maintenance of pancreatic cancer in mice. The Journal of Clinical Investigation, 122(2), 639–653. https://doi.org/10.1172/JCI59227
Arslan, A. A., Helzlsouer, K. J., Kooperberg, C., Shu, X.-O., Steplowski, E., Bueno-de-Mesquita, H. B., Fuchs, C. S., Gross, M. D., Jacobs, E. J., LaCroix, A. Z., Petersen, G. M., Stolzenberg-Solomon, R. Z., Zheng, W., Albanes, D., Amundadottir, L., Bamlet, W. R., Barricarte, A., Bingham, S. A., Boeing, H., et al. (2010). Anthropometric measures, body mass index, and pancreatic cancer: A pooled analysis from the pancreatic cancer cohort consortium (PanScan). Archives of Internal Medicine, 170(9), 791–802. https://doi.org/10.1001/archinternmed.2010.63
Giovannucci, E., Harlan, D. M., Archer, M. C., Bergenstal, R. M., Gapstur, S. M., Habel, L. A., Pollak, M., Regensteiner, J. G., & Yee, D. (2010). Diabetes and cancer: A consensus report. CA: A Cancer Journal for Clinicians, 60, 207–221.
Rebours, V., Gaujoux, S., d’Assignies, G., Sauvanet, A., Ruszniewski, P., Lévy, P., Paradis, V., Bedossa, P., & Couvelard, A. (2015). Obesity and fatty pancreatic infiltration are risk factors for pancreatic precancerous lesions (PanIN). Clinical Cancer Research, 21(15), 3522–3528. https://doi.org/10.1158/1078-0432.ccr-14-2385
Lauby-Secretan, B., Scoccianti, C., Loomis, D., Grosse, Y., Bianchini, F., & Straif, K. (2016). Body fatness and cancer — viewpoint of the IARC working group. New Engl J Med, 375(8), 794–798. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMsr1606602
Bethea, T. N., Kitahara, C. M., Sonderman, J., Patel, A. V., Harvey, C., Knutsen, S. F., Park, Y., Park, S. Y., Fraser, G. E., Jacobs, E. J., Purdue, M. P., Stolzenberg-Solomon, R. Z., Gillanders, E. M., Blot, W. J., Palmer, J. R., & Kolonel, L. N. (2014). A pooled analysis of body mass index and pancreatic cancer mortality in African Americans. Cancer Epidemiology, Biomarkers & Prevention, 23(10), 2119–2125. https://doi.org/10.1158/1055-9965.EPI-14-0422
Lega, I. C., & Lipscombe, L. L. (2019). Review: Diabetes, obesity, and cancer—Pathophysiology and clinical implications. Endocrine Reviews, 41(1), 33–52. https://doi.org/10.1210/endrev/bnz014
Dawson, D. W., Hertzer, K., Moro, A., Donald, G., Chang, H. H., Go, V. L., Pandol, S. J., Lugea, A., Gukovskaya, A. S., Li, G., Hines, O. J., Rozengurt, E., & Eibl, G. E. (2013). High Fat, high calorie diet promotes early pancreatic neoplasia in the conditional KrasG12D mouse model. Cancer Prevention Research (Philadelphia, Pa.), 6, 1064–1073.
Chang, H.-H., Moro, A., Takakura, K., Su, H.-Y., Mo, A., Nakanishi, M., Waldron, R. T., French, S. W., Dawson, D. W., Hines, O. J., Li, G., Go, V. L. W., Sinnett-Smith, J., Pandol, S. J., Lugea, A., Gukovskaya, A. S., Duff, M. O., Rosenberg, D. W., Rozengurt, E., et al. (2017). Incidence of pancreatic cancer is dramatically increased by a high fat, high calorie diet in KrasG12D mice. PLoS ONE, 12(9), e0184455. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0184455
Lashinger, L. M., Harrison, L. M., Rasmussen, A. J., Logsdon, C. D., Fischer, S. M., McArthur, M. J., & Hursting, S. D. (2013). Dietary energy balance modulation of Kras- and Ink4a/Arf+/–driven pancreatic cancer: The role of insulin-like growth factor-I. Cancer Prevention Research (Philadelphia, Pa.), 6(10), 1046–1055. https://doi.org/10.1158/1940-6207.CAPR-13-0185
Philip, B., Roland, C. L., Daniluk, J., Liu, Y., Chatterjee, D., Gomez, S. B., Ji, B., Huang, H., Wang, H., Fleming, J. B., Logsdon, C. D., & Cruz-Monserrate, Z. (2013). A high-fat diet activates oncogenic Kras and COX2 to induce development of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma in mice. Gastroenterology, 145(6), 1449–1458. https://doi.org/10.1053/j.gastro.2013.08.018
Chung, K. M., Singh, J., Lawres, L., Dorans, K. J., Garcia, C., Burkhardt, D. B., Robbins, R., Bhutkar, A., Cardone, R., Zhao, X., Babic, A., Vayrynen, S. A., Dias Costa, A., Nowak, J. A., Chang, D. T., Dunne, R. F., Hezel, A. F., Koong, A. C., Wilhelm, J. J., et al. (2020). Endocrine-exocrine signaling drives obesity-associated pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Cell, 181(4), 832-847.e818. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2020.03.062
Flier, J. S. (2004). Obesity wars: Molecular progress confronts an expanding epidemic. Cell, 116(2), 337–350.
Calle, E. E., & Kaaks, R. (2004). Overweight, obesity and cancer: Epidemiological evidence and proposed mechanisms. Nature Reviews Cancer, 4(8), 579–591. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrc1408
Calle, E. E., & Thun, M. J. (2004). Obesity and cancer. Oncogene, 23(38), 6365–6378.
Muoio, D. M., & Newgard, C. B. (2006). Obesity-related derangements in metabolic regulation. Annual Review of Biochemistry, 75, 367–401.
Abbruzzese, J. L., Andersen, D. K., Borrebaeck, C. A. K., Chari, S. T., Costello, E., Cruz-Monserrate, Z., Eibl, G., Engleman, E. G., Fisher, W. E., Habtezion, A., Kim, S. K., Korc, M., Logsdon, C., Lyssiotis, C. A., Pandol, S. J., Rustgi, A., Wolfe, B. M., Zheng, L., & Powers, A. C. (2018). The interface of pancreatic cancer with diabetes, obesity, and inflammation: Research gaps and opportunities: Summary of a National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases Workshop. Pancreas, 47(5), 516–525. https://doi.org/10.1097/MPA.0000000000001037
Andersen, D. K., Andren-Sandberg, A., Duell, E. J., Goggins, M., Korc, M., Petersen, G. M., Smith, J. P., & Whitcomb, D. C. (2013). Pancreatitis-diabetes-pancreatic cancer: Summary of an NIDDK-NCI workshop. Pancreas, 42(8), 1227–1237. https://doi.org/10.1097/MPA.0b013e3182a9ad9d
Andersen, D. K., Korc, M., Petersen, G. M., Eibl, G., Li, D., Rickels, M. R., Chari, S. T., & Abbruzzese, J. L. (2017). Diabetes, pancreatogenic diabetes, and pancreatic cancer. Diabetes, 66(5), 1103–1110. https://doi.org/10.2337/db16-1477
Eibl, G., Cruz-Monserrate, Z., Korc, M., Petrov, M. S., Goodarzi, M. O., Fisher, W. E., Habtezion, A., Lugea, A., Pandol, S. J., Hart, P. A., Andersen, D. K., & Consortium for the Study of Chronic Pancreatitis, Diabetes, and Pancreatic, Cancer. (2018). Diabetes mellitus and obesity as risk factors for pancreatic cancer. Journal of the Academy of Nutrition and Dietetics, 118(4), 555–567. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jand.2017.07.005
Kahn, B. B., Alquier, T., Carling, D., & Hardie, D. G. (2005). AMP-activated protein kinase: Ancient energy gauge provides clues to modern understanding of metabolism. Cell Metabolism, 1(1), 15–25. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cmet.2004.12.003
Foretz, M., Hébrard, S., Leclerc, J., Zarrinpashneh, E., Soty, M., Mithieux, G., Sakamoto, K., Andreelli, F., & Viollet, B. (2010). Metformin inhibits hepatic gluconeogenesis in mice independently of the LKB1/AMPK pathway via a decrease in hepatic energy state. The Journal of Clinical Investigation, 120(7), 2355–2369. https://doi.org/10.1172/jci40671
Wu, T., Horowitz, M., & Rayner, C. K. (2017). New insights into the anti-diabetic actions of metformin: From the liver to the gut. Expert Review of Gastroenterology & Hepatology, 11(2), 157–166. https://doi.org/10.1080/17474124.2017.1273769
Rena, G., Hardie, D. G., & Pearson, E. R. (2017). The mechanisms of action of metformin. Diabetologia, 60(9), 1577–1585. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00125-017-4342-z
Duca, F. A., Côté, C. D., Rasmussen, B. A., Zadeh-Tahmasebi, M., Rutter, G. A., Filippi, B. M., & Lam, T. K. (2015). Metformin activates a duodenal Ampk-dependent pathway to lower hepatic glucose production in rats. Nature Medicine, 21(5), 506–511. https://doi.org/10.1038/nm.3787
Li, D., Yeung, S. C., Hassan, M. M., Konopleva, M., & Abbruzzese, J. L. (2009). Antidiabetic therapies affect risk of pancreatic cancer. Gastroenterology, 137(2), 482–488. https://doi.org/10.1053/j.gastro.2009.04.013
de Jong, R. G., Burden, A. M., de Kort, S., van Herk-Sukel, M. P., Vissers, P. A., Janssen, P. K., Haak, H. R., Masclee, A. A., de Vries, F., & Janssen-Heijnen, M. L. (2017). No decreased risk of gastrointestinal cancers in users of metformin in the netherlands; a time-varying analysis of metformin exposure. Cancer Prevention Research (Philadelphia, Pa.), 10(5), 290–297. https://doi.org/10.1158/1940-6207.CAPR-16-0277
Decensi, A., Puntoni, M., Goodwin, P., Cazzaniga, M., Gennari, A., Bonanni, B., & Gandini, S. (2010). Metformin and cancer risk in diabetic patients: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Cancer Prevention Research (Philadelphia, Pa.), 3(11), 1451–1461. https://doi.org/10.1158/1940-6207.CAPR-10-0157
Zhang, P., Li, H., Tan, X., Chen, L., & Wang, S. (2013). Association of metformin use with cancer incidence and mortality: A meta-analysis. Cancer Epidemiology, 37(3), 207–218. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.canep.2012.12.009
Yu, H., Zhong, X., Gao, P., Shi, J., Wu, Z., Guo, Z., Wang, Z., & Song, Y. (2019). The potential effect of metformin on cancer: An umbrella review. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne), 10, 617. https://doi.org/10.3389/fendo.2019.00617
Sadeghi, N., Abbruzzese, J. L., Yeung, S. C., Hassan, M., & Li, D. (2012). Metformin use is associated with better survival of diabetic patients with pancreatic cancer. Clinical Cancer Research, 18(10), 2905–2912. https://doi.org/10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-11-2994
Jang, W. I., Kim, M. S., Kang, S. H., Jo, A. J., Kim, Y. J., Tchoe, H. J., Park, C. M., Kim, H. J., Choi, J. A., Choi, H. J., Paik, E. K., Seo, Y. S., Yoo, H. J., Kang, J. K., Han, C. J., Kim, Y. J., Kim, S. B., & Ko, M. J. (2017). Association between metformin use and mortality in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus and localized resectable pancreatic cancer: a nationwide population-based study in korea. Oncotarget, 8(6), 9587–9596. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.14525
Chaiteerakij, R., Petersen, G. M., Bamlet, W. R., Chaffee, K. G., Zhen, D. B., Burch, P. A., Leof, E. R., Roberts, L. R., & Oberg, A. L. (2016). Metformin use and survival of patients with pancreatic cancer: A cautionary lesson. Journal of Clinical Oncology, 34(16), 1898–1904. https://doi.org/10.1200/JCO.2015.63.3511
Kordes, S., Pollak, M. N., Zwinderman, A. H., Mathot, R. A., Weterman, M. J., Beeker, A., Punt, C. J., Richel, D. J., & Wilmink, J. W. (2015). Metformin in patients with advanced pancreatic cancer: A double-blind, randomised, placebo-controlled phase 2 trial. The lancet Oncology, 16(7), 839–847. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1470-2045(15)00027-3
Zhou, P. T., Li, B., Liu, F. R., Zhang, M. C., Wang, Q., Li, Y. Y., Xu, C., Liu, Y. H., Yao, Y., & Li, D. (2017). Metformin is associated with survival benefit in pancreatic cancer patients with diabetes: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Oncotarget, 8(15), 25242–25250. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.15692
Shi, Y. Q., Zhou, X. C., Du, P., Yin, M. Y., Xu, L., Chen, W. J., & Xu, C. F. (2020). Relationships are between metformin use and survival in pancreatic cancer patients concurrent with diabetes: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Medicine (Baltimore), 99(37), e21687. https://doi.org/10.1097/MD.0000000000021687
Yoo, D., Kim, N., Hwang, D. W., Song, K. B., Lee, J. H., Lee, W., Kwon, J., Park, Y., Hong, S., Lee, J. W., Hwang, K., Shin, D., Tak, E., & Kim, S. C. (2020). Association between metformin use and clinical outcomes following pancreaticoduodenectomy in patients with type 2 diabetes and pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 9(6), E1953. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm9061953
Wei, M., Liu, Y., Bi, Y., & Zhang, Z. J. (2019). Metformin and pancreatic cancer survival: Real effect or immortal time bias? International Journal of Cancer, 145(7), 1822–1828. https://doi.org/10.1002/ijc.32254
Tamburrino, D., Guarneri, G., Pagnanelli, M., Crippa, S., Partelli, S., Belfiori, G., Capurso, G., & Falconi, M. (2021). Chemopreventive agents after pancreatic resection for ductal adenocarcinoma: Legend or scientific evidence? Annals of Surgical Oncology, 28(4), 2312–2322. https://doi.org/10.1245/s10434-020-09097-y
Kim, J., Bae, Y. J., Lee, J. W., Kim, Y. S., Kim, Y., You, H. S., Kim, H. S., Choi, E. A., Han, Y. E., & Kang, H. T. (2021). Metformin use in cancer survivors with diabetes reduces all-cause mortality, based on the Korean National Health Insurance Service between 2002 and 2015. Medicine (Baltimore), 100(11), e25045. https://doi.org/10.1097/MD.0000000000025045
Li, X., Li, T., Liu, Z., Gou, S., & Wang, C. (2017). The effect of metformin on survival of patients with pancreatic cancer: A meta-analysis. Science and Reports, 7(1), 5825. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-06207-x
Schneider, M. B., Matsuzaki, H., Haorah, J., Ulrich, A., Standop, J., Ding, X. Z., Adrian, T. E., & Pour, P. M. (2001). Prevention of pancreatic cancer induction in hamsters by metformin. Gastroenterology, 120(5), 1263–1270. https://doi.org/10.1053/gast.2001.23258
Cifarelli, V., Lashinger, L. M., Devlin, K. L., Dunlap, S. M., Huang, J., Kaaks, R., Pollak, M. N., & Hursting, S. D. (2015). Metformin and rapamycin reduce pancreatic cancer growth in obese prediabetic mice by distinct microRNA-regulated mechanisms. Diabetes, 64(5), 1632–1642. https://doi.org/10.2337/db14-1132
Yue, W., Zheng, X., Lin, Y., Yang, C. S., Xu, Q., Carpizo, D., Huang, H., DiPaola, R. S., & Tan, X. L. (2015). Metformin combined with aspirin significantly inhibit pancreatic cancer cell growth in vitro and in vivo by suppressing anti-apoptotic proteins Mcl-1 and Bcl-2. Oncotarget, 6(25), 21208–21224. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.4126
Incio, J., Suboj, P., Chin, S. M., Vardam-Kaur, T., Liu, H., Hato, T., Babykutty, S., Chen, I., Deshpande, V., Jain, R. K., & Fukumura, D. (2015). Metformin reduces desmoplasia in pancreatic cancer by reprogramming stellate cells and tumor-associated macrophages. PLoS ONE, 10(12), e0141392. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0141392
Kato, K., Iwama, H., Yamashita, T., Kobayashi, K., Fujihara, S., Fujimori, T., Kamada, H., Kobara, H., & Masaki, T. (2016). The anti-diabetic drug metformin inhibits pancreatic cancer cell proliferation in vitro and in vivo: Study of the microRNAs associated with the antitumor effect of metformin. Oncology Reports, 35(3), 1582–1592. https://doi.org/10.3892/or.2015.4496
Shi, Y., He, Z., Jia, Z., & Xu, C. (2016). Inhibitory effect of metformin combined with gemcitabine on pancreatic cancer cells in vitro and in vivo. Molecular Medicine Reports, 14(4), 2921–2928. https://doi.org/10.3892/mmr.2016.5592
Wang, C., Zhang, T., Liao, Q., Dai, M., Guo, J., Yang, X., Tan, W., Lin, D., Wu, C., & Zhao, Y. (2021). Metformin inhibits pancreatic cancer metastasis caused by SMAD4 deficiency and consequent HNF4G upregulation. Protein & Cell, 12(2), 128–144. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13238-020-00760-4
Rajeshkumar, N. V., Yabuuchi, S., Pai, S. G., De Oliveira, E., Kamphorst, J. J., Rabinowitz, J. D., Tejero, H., Al-Shahrour, F., Hidalgo, M., Maitra, A., & Dang, C. V. (2017). Treatment of pancreatic cancer patient-derived xenograft panel with metabolic inhibitors reveals efficacy of phenformin. Clinical Cancer Research, 23(18), 5639–5647. https://doi.org/10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-17-1115
Lipner, M. B., Marayati, R., Deng, Y., Wang, X., Raftery, L., O’Neil, B. H., & Yeh, J. J. (2016). Metformin treatment does not inhibit growth of pancreatic cancer patient-derived xenografts. PLoS ONE, 11(1), e0147113. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0147113
Kisfalvi, K., Eibl, G., Sinnett-Smith, J., & Rozengurt, E. (2009). Metformin disrupts crosstalk between G protein-coupled receptor and insulin receptor signaling systems and inhibits pancreatic cancer growth. Cancer Research, 69(16), 6539–6545. https://doi.org/10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-09-0418
Kisfalvi, K., Moro, A., Sinnett-Smith, J., Eibl, G., & Rozengurt, E. (2013). Metformin inhibits the growth of human pancreatic cancer xenografts. Pancreas, 42(5), 781–785. https://doi.org/10.1097/MPA.0b013e31827aec40
Tan, X. L., Bhattacharyya, K. K., Dutta, S. K., Bamlet, W. R., Rabe, K. G., Wang, E., Smyrk, T. C., Oberg, A. L., Petersen, G. M., & Mukhopadhyay, D. (2015). Metformin suppresses pancreatic tumor growth with inhibition of NFkappaB/STAT3 inflammatory signaling. Pancreas, 44(4), 636–647. https://doi.org/10.1097/MPA.0000000000000308
Chen, K., Qian, W., Jiang, Z., Cheng, L., Li, J., Sun, L., Zhou, C., Gao, L., Lei, M., Yan, B., Cao, J., Duan, W., & Ma, Q. (2017). Metformin suppresses cancer initiation and progression in genetic mouse models of pancreatic cancer. Molecular Cancer, 16(1), 131. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12943-017-0701-0
Qian, W., Li, J., Chen, K., Jiang, Z., Cheng, L., Zhou, C., Yan, B., Cao, J., Ma, Q., & Duan, W. (2018). Metformin suppresses tumor angiogenesis and enhances the chemosensitivity of gemcitabine in a genetically engineered mouse model of pancreatic cancer. Life Sciences, 208, 253–261. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lfs.2018.07.046
Chang, H. H., Moro, A., Chou, C. E. N., Dawson, D. W., French, S., Schmidt, A. I., Sinnett-Smith, J., Hao, F., Hines, O. J., Eibl, G., & Rozengurt, E. (2018). Metformin decreases the incidence of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma promoted by diet-induced obesity in the conditional KrasG12D mouse model. Science and Reports, 8(1), 5899. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-018-24337-8
Dong, T. S., Chang, H. H., Hauer, M., Lagishetty, V., Katzka, W., Rozengurt, E., Jacobs, J. P., & Eibl, G. (2019). Metformin alters the duodenal microbiome and decreases the incidence of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma promoted by diet-induced obesity. American Journal of Physiology. Gastrointestinal and Liver Physiology, 317(6), G763–G772. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajpgi.00170.2019
Eibl, G. (2020). Endocrine-exocrine signals in obesity-associated pancreatic cancer. Nature Reviews. Gastroenterology & Hepatology, 17(8), 455–456. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41575-020-0324-6
Foretz, M., Guigas, B., Bertrand, L., Pollak, M., & Viollet, B. (2014). Metformin: From mechanisms of action to therapies. Cell Metabolism, 20(6), 953–966. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cmet.2014.09.018
Pollak, M. (2017). The effects of metformin on gut microbiota and the immune system as research frontiers. Diabetologia, 60(9), 1662–1667. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00125-017-4352-x
Pollak, M. N. (2012). Investigating metformin for cancer prevention and treatment: The end of the beginning. Cancer Discovery, 2(9), 778–790. https://doi.org/10.1158/2159-8290.CD-12-0263
Pollak, M. (2010). Metformin and other biguanides in oncology: Advancing the research agenda. Cancer Prevention Research (Philadelphia, Pa.), 3(9), 1060–1065. https://doi.org/10.1158/1940-6207.CAPR-10-0175
Coll, A. P., Chen, M., Taskar, P., Rimmington, D., Patel, S., Tadross, J. A., Cimino, I., Yang, M., Welsh, P., Virtue, S., Goldspink, D. A., Miedzybrodzka, E. L., Konopka, A. R., Esponda, R. R., Huang, J. T., Tung, Y. C. L., Rodriguez-Cuenca, S., Tomaz, R. A., Harding, H. P., et al. (2020). GDF15 mediates the effects of metformin on body weight and energy balance. Nature, 578(7795), 444–448. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-019-1911-y
Rozengurt, E., & Eibl, G. (2019). Central role of Yes-associated protein and WW-domain-containing transcriptional co-activator with PDZ-binding motif in pancreatic cancer development. World Journal of Gastroenterology, 25(15), 1797–1816. https://doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v25.i15.1797
Foretz, M., Guigas, B., & Viollet, B. (2019). Understanding the glucoregulatory mechanisms of metformin in type 2 diabetes mellitus. Nature Reviews. Endocrinology, 15(10), 569–589. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41574-019-0242-2
Hawley, S. A., Ross, F. A., Chevtzoff, C., Green, K. A., Evans, A., Fogarty, S., Towler, M. C., Brown, L. J., Ogunbayo, O. A., Evans, A. M., & Hardie, D. G. (2010). Use of cells expressing gamma subunit variants to identify diverse mechanisms of AMPK activation. Cell Metabolism, 11(6), 554–565. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cmet.2010.04.001
Ben Sahra, I., Laurent, K., Loubat, A., Giorgetti-Peraldi, S., Colosetti, P., Auberger, P., Tanti, J. F., Le Marchand-Brustel, Y., & Bost, F. (2008). The antidiabetic drug metformin exerts an antitumoral effect in vitro and in vivo through a decrease of cyclin D1 level. Oncogene, 27(25), 3576–3586. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1211024
Kalender, A., Selvaraj, A., Kim, S. Y., Gulati, P., Brule, S., Viollet, B., Kemp, B. E., Bardeesy, N., Dennis, P., Schlager, J. J., Marette, A., Kozma, S. C., & Thomas, G. (2010). Metformin, independent of AMPK, inhibits mTORC1 in a rag GTPase-dependent manner. Cell Metabolism, 11(5), 390–401. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cmet.2010.03.014
LaMoia, T. E., & Shulman, G. I. (2021). Cellular and molecular mechanisms of metformin action. Endocrine Reviews, 42(1), 77–96. https://doi.org/10.1210/endrev/bnaa023
Wang, L. W., Li, Z. S., Zou, D. W., Jin, Z. D., Gao, J., & Xu, G. M. (2008). Metformin induces apoptosis of pancreatic cancer cells. World Journal of Gastroenterology, 14(47), 7192–7198. https://doi.org/10.3748/wjg.14.7192
Bao, B., Wang, Z., Ali, S., Ahmad, A., Azmi, A. S., Sarkar, S. H., Banerjee, S., Kong, D., Li, Y., Thakur, S., & Sarkar, F. H. (2012). Metformin inhibits cell proliferation, migration and invasion by attenuating CSC function mediated by deregulating miRNAs in pancreatic cancer cells. Cancer Prevention Research (Philadelphia, Pa.), 5(3), 355–364. https://doi.org/10.1158/1940-6207.CAPR-11-0299
Nair, V., Sreevalsan, S., Basha, R., Abdelrahim, M., Abudayyeh, A., Rodrigues Hoffman, A., & Safe, S. (2014). Mechanism of metformin-dependent inhibition of mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) and Ras activity in pancreatic cancer: Role of specificity protein (Sp) transcription factors. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 289(40), 27692–27701. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M114.592576
Yan, Y., Zhou, X. E., Xu, H. E., & Melcher, K. (2018). Structure and Physiological Regulation of AMPK. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 19(11), 3534. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19113534
Hardie, D. G. (2015). AMPK: Positive and negative regulation, and its role in whole-body energy homeostasis. Current Opinion in Cell Biology, 33, 1–7. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceb.2014.09.004
Olivier, S., Foretz, M., & Viollet, B. (2018). Promise and challenges for direct small molecule AMPK activators. Biochem Pharmacol, 153, 147–158. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bcp.2018.01.049
Hezel, A. F., & Bardeesy, N. (2008). LKB1; linking cell structure and tumor suppression. Oncogene, 27(55), 6908–6919. https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2008.342
Bridges, H. R., Jones, A. J., Pollak, M. N., & Hirst, J. (2014). Effects of metformin and other biguanides on oxidative phosphorylation in mitochondria. The Biochemical Journal, 462(3), 475–487. https://doi.org/10.1042/bj20140620
Pryor, R., & Cabreiro, F. (2015). Repurposing metformin: An old drug with new tricks in its binding pockets. The Biochemical Journal, 471(3), 307–322. https://doi.org/10.1042/bj20150497
Hardie, D. G., Ross, F. A., & Hawley, S. A. (2012). AMPK: A nutrient and energy sensor that maintains energy homeostasis. Nature Reviews Molecular Cell Biology, 13(4), 251–262.
Ming, M., Sinnett-Smith, J., Wang, J., Soares, H. P., Young, S. H., Eibl, G., & Rozengurt, E. (2014). Dose-dependent AMPK-dependent and independent mechanisms of berberine and metformin inhibition of mTORC1, ERK, DNA synthesis and proliferation in pancreatic cancer cells. PLoS ONE, 9(12), e114573. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0114573
Sinnett-Smith, J., Kisfalvi, K., Kui, R., & Rozengurt, E. (2013). Metformin inhibition of mTORC1 activation, DNA synthesis and proliferation in pancreatic cancer cells: Dependence on glucose concentration and role of AMPK. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications, 430(1), 352–357. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2012.11.010
Carroll, B., & Dunlop, E. A. (2017). The lysosome: A crucial hub for AMPK and mTORC1 signalling. The Biochemical Journal, 474(9), 1453–1466. https://doi.org/10.1042/BCJ20160780
Taniguchi, C. M., Emanuelli, B., & Kahn, C. R. (2006). Critical nodes in signalling pathways: Insights into insulin action. Nature Reviews Molecular Cell Biology, 7(2), 85–96.
Rozengurt, E. (2014). Mechanistic target of rapamycin (mTOR): A point of convergence in the action of insulin/IGF-1 and G protein-coupled receptor agonists in pancreatic cancer cells. Frontiers in Physiology, 5, 357. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphys.2014.00357
Rozengurt, E., Soares, H. P., & Sinnet-Smith, J. (2014). Suppression of feedback loops mediated by PI3K/mTOR induces multiple overactivation of compensatory pathways: An unintended consequence leading to drug resistance. Molecular Cancer Therapeutics, 13(11), 2477–2488. https://doi.org/10.1158/1535-7163.mct-14-0330
Soares, H. P., Ni, Y., Kisfalvi, K., Sinnett-Smith, J., & Rozengurt, E. (2013). Different patterns of Akt and ERK feedback activation in response to rapamycin, active-site mTOR inhibitors and metformin in pancreatic cancer cells. PLoS ONE, 8(2), e57289. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0057289
Soares, H. P., Ming, M., Mellon, M., Young, S. H., Han, L., Sinnet-Smith, J., & Rozengurt, E. (2015). Dual PI3K/mTOR inhibitors induce rapid overactivation of the MEK/ERK pathway in human pancreatic cancer cells through suppression of mTORC2. Molecular Cancer Therapeutics, 14(4), 1014–1023. https://doi.org/10.1158/1535-7163.mct-14-0669
Lee, J. W., Park, S., Takahashi, Y., & Wang, H.-G. (2010). The association of AMPK with ULK1 regulates autophagy. PLoS ONE, 5(11), e15394.
Saxton, R. A., & Sabatini, D. M. (2017). mTOR signaling in growth, metabolism, and disease. Cell, 168(6), 960–976. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2017.02.004
Um, S. H., D’Alessio, D., & Thomas, G. (2006). Nutrient overload, insulin resistance, and ribosomal protein S6 kinase 1, S6K1. Cell Metabolism, 3(6), 393–402.
Ali, S. M., & Sabatini, D. M. (2005). Structure of S6 kinase 1 determines whether Raptor-mTOR or Rictor-mTOR phosphorylates its hydrophobic motif site. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 280, 19445–19448.
Long, X., Muller, F., & Avruch, J. (2004). TOR action in mammalian cells and in Caenorhabditis elegans. Current Topics in Microbiology and Immunology, 279, 115–138.
Armengol, G., Rojo, F., Castellvi, J., Iglesias, C., Cuatrecasas, M., Pons, B., Baselga, J., & Ramon y Cajal, S. . (2007). 4E-binding protein 1: A key molecular “funnel factor” in human cancer with clinical implications. Cancer Research, 67(16), 7551–7555.
Inoki, K., Zhu, T., & Guan, K. L. (2003). TSC2 mediates cellular energy response to control cell growth and survival. Cell, 115(5), 577–590. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0092-8674(03)00929-2
Shaw, R. J., Bardeesy, N., Manning, B. D., Lopez, L., Kosmatka, M., DePinho, R. A., & Cantley, L. C. (2004). The LKB1 tumor suppressor negatively regulates mTOR signaling. Cancer Cell, 6(1), 91–99. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ccr.2004.06.007
Inoki, K., Ouyang, H., Zhu, T., Lindvall, C., Wang, Y., Zhang, X., Yang, Q., Bennett, C., Harada, Y., Stankunas, K., Wang, C. Y., He, X., MacDougald, O. A., You, M., Williams, B. O., & Guan, K. L. (2006). TSC2 integrates Wnt and energy signals via a coordinated phosphorylation by AMPK and GSK3 to regulate cell growth. Cell, 126(5), 955–968. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2006.06.055
Gwinn, D. M., Shackelford, D. B., Egan, D. F., Mihaylova, M. M., Mery, A., Vasquez, D. S., Turk, B. E., & Shaw, R. J. (2008). AMPK phosphorylation of raptor mediates a metabolic checkpoint. Molecular Cell, 30(2), 214–226. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molcel.2008.03.003
Tzatsos, A., & Tsichlis, P. N. (2007). Energy depletion inhibits phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/Akt signaling and induces apoptosis via AMP-activated protein kinase-dependent phosphorylation of IRS-1 at Ser-794. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 282(25), 18069–18082. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M610101200
Ning, J., & Clemmons, D. R. (2010). AMP-activated protein kinase inhibits IGF-I signaling and protein synthesis in vascular smooth muscle cells via stimulation of insulin receptor substrate 1 S794 and tuberous sclerosis 2 S1345 phosphorylation. Molecular Endocrinology, 24(6), 1218–1229. https://doi.org/10.1210/me.2009-0474
Piccolo, S., Dupont, S., & Cordenonsi, M. (2014). The biology of YAP/TAZ: Hippo signaling and beyond. Physiological Reviews, 94(4), 1287–1312. https://doi.org/10.1152/physrev.00005.2014
Yu, F. X., Zhao, B., & Guan, K. L. (2015). Hippo Pathway in Organ Size Control, Tissue Homeostasis, and Cancer. Cell, 163(4), 811–828. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2015.10.044
Enzo, E., Santinon, G., Pocaterra, A., Aragona, M., Bresolin, S., Forcato, M., Grifoni, D., Pession, A., Zanconato, F., Guzzo, G., Bicciato, S., & Dupont, S. (2015). Aerobic glycolysis tunes YAP/TAZ transcriptional activity. EMBO J, 34(10), 1349–1370. https://doi.org/10.15252/embj.201490379
Wang, Z., Wu, Y., Wang, H., Zhang, Y., Mei, L., Fang, X., Zhang, X., Zhang, F., Chen, H., Liu, Y., Jiang, Y., Sun, S., Zheng, Y., Li, N., & Huang, L. (2014). Interplay of mevalonate and Hippo pathways regulates RHAMM transcription via YAP to modulate breast cancer cell motility. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A, 111(1), E89-98. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1319190110
Santinon, G., Pocaterra, A., & Dupont, S. (2016). Control of YAP/TAZ Activity by Metabolic and Nutrient-Sensing Pathways. Trends in Cell Biology, 26(4), 289–299. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tcb.2015.11.004
Ardestani, A., Lupse, B., & Maedler, K. (2018). Hippo signaling: Key emerging pathway in cellular and whole-body metabolism. Trends in Endocrinology and Metabolism , 29(7), 492–509. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tem.2018.04.006
Koo, J. H., & Guan, K. L. (2018). Interplay between YAP/TAZ and Metabolism. Cell Metabolism, 28(2), 196–206. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cmet.2018.07.010
Plouffe, S. W., Lin, K. C., Moore, J. L., 3rd., Tan, F. E., Ma, S., Ye, Z., Qiu, Y., Ren, B., & Guan, K. L. (2018). The Hippo pathway effector proteins YAP and TAZ have both distinct and overlapping functions in the cell. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 293(28), 11230–11240. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.RA118.002715
Callus, B. A., Finch-Edmondson, M. L., Fletcher, S., & Wilton, S. D. (2019). YAPping about and not forgetting TAZ. FEBS Letters, 593(3), 253–276. https://doi.org/10.1002/1873-3468.13318
Zhang, W., Nandakumar, N., Shi, Y., Manzano, M., Smith, A., Graham, G., Gupta, S., Vietsch, E. E., Laughlin, S. Z., Wadhwa, M., Chetram, M., Joshi, M., Wang, F., Kallakury, B., Toretsky, J., Wellstein, A., & Yi, C. (2014). Downstream of mutant KRAS, the transcription regulator YAP is essential for neoplastic progression to pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Science Signaling, 7(324), ra42. https://doi.org/10.1126/scisignal.2005049
Gruber, R., Panayiotou, R., Nye, E., Spencer-Dene, B., Stamp, G., & Behrens, A. (2016). YAP1 and TAZ Control Pancreatic Cancer Initiation in Mice by Direct Up-regulation of JAK-STAT3 Signaling. Gastroenterology, 151(3), 526–539. https://doi.org/10.1053/j.gastro.2016.05.006
Tu, B., Yao, J., Ferri-Borgogno, S., Zhao, J., Chen, S., Wang, Q., Yan, L., Zhou, X., Zhu, C., Bang, S., Chang, Q., Bristow, C. A., Kang, Y., Zheng, H., Wang, H., Fleming, J. B., Kim, M., Heffernan, T. P., Draetta, G. F., et al. (2019). YAP1 oncogene is a context-specific driver for pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. JCI Insight, 4(21), e130811. https://doi.org/10.1172/jci.insight.130811
Rozengurt, E., Sinnett-Smith, J., & Eibl, G. (2018). Yes-associated protein (YAP) in pancreatic cancer: At the epicenter of a targetable signaling network associated with patient survival. Signal Transduction and Targeted Therapy, 3, 11. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41392-017-0005-2
Kapoor, A., Yao, W., Ying, H., Hua, S., Liewen, A., Wang, Q., Zhong, Y., Wu, C. J., Sadanandam, A., Hu, B., Chang, Q., Chu, G. C., Al-Khalil, R., Jiang, S., Xia, H., Fletcher-Sananikone, E., Lim, C., Horwitz, G. I., Viale, A., et al. (2014). Yap1 activation enables bypass of oncogenic Kras addiction in pancreatic cancer. Cell, 158(1), 185–197. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2014.06.003
Yang, S., Zhang, L., Purohit, V., Shukla, S. K., Chen, X., Yu, F., Fu, K., Chen, Y., Solheim, J., Singh, P. K., Song, W., & Dong, J. (2015). Active YAP promotes pancreatic cancer cell motility, invasion and tumorigenesis in a mitotic phosphorylation-dependent manner through LPAR3. Oncotarget, 6(34), 36019–36031. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.5935
Morvaridi, S., Dhall, D., Greene, M. I., Pandol, S. J., & Wang, Q. (2015). Role of YAP and TAZ in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma and in stellate cells associated with cancer and chronic pancreatitis. Science and Reports, 5, 16759. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep16759
Murakami, S., Shahbazian, D., Surana, R., Zhang, W., Chen, H., Graham, G. T., White, S. M., Weiner, L. M., & Yi, C. (2017). Yes-associated protein mediates immune reprogramming in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Oncogene, 36(9), 1232–1244. https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2016.288
Mueller, S., Engleitner, T., Maresch, R., Zukowska, M., Lange, S., Kaltenbacher, T., Konukiewitz, B., Ollinger, R., Zwiebel, M., Strong, A., Yen, H. Y., Banerjee, R., Louzada, S., Fu, B., Seidler, B., Gotzfried, J., Schuck, K., Hassan, Z., Arbeiter, A., et al. (2018). Evolutionary routes and KRAS dosage define pancreatic cancer phenotypes. Nature, 554(7690), 62–68. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature25459
Hajimoradi Javarsiani, M., Sajedianfard, J., & Haghjooy Javanmard, S. (2020). The effects of metformin on the hippo pathway in the proliferation of melanoma cancer cells: a preclinical study. Archives of Physiology and Biochemistry, pp, 1–6. https://doi.org/10.1080/13813455.2020.1760304.
Liu, J., Li, J., Chen, H., Wang, R., Li, P., Miao, Y., & Liu, P. (2020). Metformin suppresses proliferation and invasion of drug-resistant breast cancer cells by activation of the Hippo pathway. Journal of Cellular and Molecular Medicine, 24(10), 5786–5796. https://doi.org/10.1111/jcmm.15241
Jin, D., Guo, J., Wu, Y., Chen, W., Du, J., Yang, L., Wang, X., Gong, K., Dai, J., Miao, S., Li, X., & Su, G. (2020). Metformin-repressed miR-381-YAP-snail axis activity disrupts NSCLC growth and metastasis. Journal of Experimental & Clinical Cancer Research, 39(1), 6. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13046-019-1503-6
Wu, Y., Zheng, Q., Li, Y., Wang, G., Gao, S., Zhang, X., Yan, X., Zhang, X., Xie, J., Wang, Y., Sun, X., Meng, X., Yin, B., & Wang, B. (2019). Metformin targets a YAP1-TEAD4 complex via AMPKalpha to regulate CCNE1/2 in bladder cancer cells. Journal of Experimental & Clinical Cancer Research, 38(1), 376. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13046-019-1346-1
Yuan, X., Wei, W., Bao, Q., Chen, H., Jin, P., & Jiang, W. (2018). Metformin inhibits glioma cells stemness and epithelial-mesenchymal transition via regulating YAP activity. Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy, 102, 263–270. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopha.2018.03.031
Tian, Y., Tang, B., Wang, C., Sun, D., Zhang, R., Luo, N., Han, Z., Liang, R., Gao, Z., & Wang, L. (2016). Metformin mediates resensitivity to 5-fluorouracil in hepatocellular carcinoma via the suppression of YAP. Oncotarget, 7(29), 46230–46241. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.10079
Mo, J. S., Meng, Z., Kim, Y. C., Park, H. W., Hansen, C. G., Kim, S., Lim, D. S., & Guan, K. L. (2015). Cellular energy stress induces AMPK-mediated regulation of YAP and the Hippo pathway. Nature Cell Biology, 17(4), 500–510. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncb3111
Wang, W., Xiao, Z. D., Li, X., Aziz, K. E., Gan, B., Johnson, R. L., & Chen, J. (2015). AMPK modulates Hippo pathway activity to regulate energy homeostasis. Nature Cell Biology, 17(4), 490–499. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncb3113
Omkumar, R. V., Darnay, B. G., & Rodwell, V. W. (1994). Modulation of Syrian hamster 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-CoA reductase activity by phosphorylation. Role of serine 871. J Biol Chem, 269(9), 6810–6814.
Moroishi, T., Hansen, C. G., & Guan, K. L. (2015). The emerging roles of YAP and TAZ in cancer. Nature Reviews Cancer, 15(2), 73–79. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrc3876
DeRan, M., Yang, J., Shen, C. H., Peters, E. C., Fitamant, J., Chan, P., Hsieh, M., Zhu, S., Asara, J. M., Zheng, B., Bardeesy, N., Liu, J., & Wu, X. (2014). Energy stress regulates hippo-YAP signaling involving AMPK-mediated regulation of angiomotin-like 1 protein. Cell Reports, 9(2), 495–503. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.celrep.2014.09.036
Shaw, R. J., Lamia, K. A., Vasquez, D., Koo, S. H., Bardeesy, N., Depinho, R. A., Montminy, M., & Cantley, L. C. (2005). The kinase LKB1 mediates glucose homeostasis in liver and therapeutic effects of metformin. Science, 310(5754), 1642–1646. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1120781
Berker, B., Emral, R., Demirel, C., Corapcioglu, D., Unlu, C., & Kose, K. (2004). Increased insulin-like growth factor-I levels in women with polycystic ovary syndrome, and beneficial effects of metformin therapy. Gynecological Endocrinology, 19(3), 125–133. https://doi.org/10.1080/09513590400007309
Goodwin, P. J., Pritchard, K. I., Ennis, M., Clemons, M., Graham, M., & Fantus, I. G. (2008). Insulin-lowering effects of metformin in women with early breast cancer. Clinical Breast Cancer, 8(6), 501–505. https://doi.org/10.3816/CBC.2008.n.060
Mutgan, A. C., Besikcioglu, H. E., Wang, S., Friess, H., Ceyhan, G. O., & Demir, I. E. (2018). Insulin/IGF-driven cancer cell-stroma crosstalk as a novel therapeutic target in pancreatic cancer. Molecular Cancer, 17(1), 66. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12943-018-0806-0
Zheng, Y., Wu, C., Yang, J., Zhao, Y., Jia, H., Xue, M., Xu, D., Yang, F., Fu, D., Wang, C., Hu, B., Zhang, Z., Li, T., Yan, S., Wang, X., Nelson, P. J., Bruns, C., Qin, L., & Dong, Q. (2020). Insulin-like growth factor 1-induced enolase 2 deacetylation by HDAC3 promotes metastasis of pancreatic cancer. Signal Transduction and Targeted Therapy, 5(1), 53. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41392-020-0146-6
Trajkovic-Arsic, M., Kalideris, E., & Siveke, J. T. (2013). The role of insulin and IGF system in pancreatic cancer. Journal of Molecular Endocrinology, 50(3), R67-74. https://doi.org/10.1530/JME-12-0259
Renehan, A. G., Frystyk, J., & Flyvbjerg, A. (2006). Obesity and cancer risk: The role of the insulin-IGF axis. Trends in Endocrinology and Metabolism , 17(8), 328–336. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tem.2006.08.006
Subramani, R., Lopez-Valdez, R., Arumugam, A., Nandy, S., Boopalan, T., & Lakshmanaswamy, R. (2014). Targeting insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor inhibits pancreatic cancer growth and metastasis. PLoS ONE, 9(5), e97016. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0097016
Gong, J., Robbins, L. A., Lugea, A., Waldron, R. T., Jeon, C. Y., & Pandol, S. J. (2014). Diabetes, pancreatic cancer, and metformin therapy. Frontiers in Physiology, 5, 426. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphys.2014.00426
Hao, F., Xu, Q., Zhao, Y., Stevens, J. V., Young, S. H., Sinnett-Smith, J., & Rozengurt, E. (2017). Insulin Receptor and GPCR Crosstalk Stimulates YAP via PI3K and PKD in Pancreatic Cancer Cells. Molecular Cancer Research, 15(7), 929–941. https://doi.org/10.1158/1541-7786.MCR-17-0023
Rozengurt, E., Sinnett-Smith, J., & Kisfalvi, K. (2010). Crosstalk between insulin/insulin-like growth factor-1 receptors and G protein-coupled receptor signaling systems: A novel target for the antidiabetic drug metformin in pancreatic cancer. Clinical Cancer Research, 16(9), 2505–2511. https://doi.org/10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-09-2229
Liu, S. S., Ma, X. F., Zhao, J., Du, S. X., Zhang, J., Dong, M. Z., & Xin, Y. N. (2020). Association between nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and extrahepatic cancers: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Lipids in Health and Disease, 19(1), 118. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12944-020-01288-6
Chang, C. F., Tseng, Y. C., Huang, H. H., Shih, Y. L., Hsieh, T. Y., & Lin, H. H. (2018). Exploring the relationship between nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and pancreatic cancer by computed tomographic survey. Internal and Emergency Medicine, 13(2), 191–197. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11739-017-1774-x
Murphy, N., Jenab, M., & Gunter, M. J. (2018). Adiposity and gastrointestinal cancers: Epidemiology, mechanisms and future directions. Nature Reviews. Gastroenterology & Hepatology, 15(11), 659–670. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41575-018-0038-1
Maruvada, P., Leone, V., Kaplan, L. M., & Chang, E. B. (2017). The Human Microbiome and Obesity: Moving beyond Associations. Cell Host & Microbe, 22(5), 589–599. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chom.2017.10.005
Turnbaugh, P. J., Ley, R. E., Mahowald, M. A., Magrini, V., Mardis, E. R., & Gordon, J. I. (2006). An obesity-associated gut microbiome with increased capacity for energy harvest. Nature, 444(7122), 1027–1031. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature05414
He, L. (2020). Metformin and Systemic Metabolism. Trends in Pharmacological Sciences, 41(11), 868–881. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tips.2020.09.001
Forslund, K., Hildebrand, F., Nielsen, T., Falony, G., Le Chatelier, E., Sunagawa, S., Prifti, E., Vieira-Silva, S., Gudmundsdottir, V., Pedersen, H. K., Arumugam, M., Kristiansen, K., Voigt, A. Y., Vestergaard, H., Hercog, R., Costea, P. I., Kultima, J. R., Li, J., Jorgensen, T., et al. (2015). Disentangling type 2 diabetes and metformin treatment signatures in the human gut microbiota. Nature, 528(7581), 262–266. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature15766
Wu, H., Esteve, E., Tremaroli, V., Khan, M. T., Caesar, R., Manneras-Holm, L., Stahlman, M., Olsson, L. M., Serino, M., Planas-Felix, M., Xifra, G., Mercader, J. M., Torrents, D., Burcelin, R., Ricart, W., Perkins, R., Fernandez-Real, J. M., & Backhed, F. (2017). Metformin alters the gut microbiome of individuals with treatment-naive type 2 diabetes, contributing to the therapeutic effects of the drug. Nature Medicine, 23(7), 850–858. https://doi.org/10.1038/nm.4345
Shin, N. R., Lee, J. C., Lee, H. Y., Kim, M. S., Whon, T. W., Lee, M. S., & Bae, J. W. (2014). An increase in the Akkermansia spp population induced by metformin treatment improves glucose homeostasis in diet-induced obese mice. Gut, 63(5), 727–735. https://doi.org/10.1136/gutjnl-2012-303839
Riquelme, E., Zhang, Y., Zhang, L., Montiel, M., Zoltan, M., Dong, W., Quesada, P., Sahin, I., Chandra, V., San Lucas, A., Scheet, P., Xu, H., Hanash, S. M., Feng, L., Burks, J. K., Do, K. A., Peterson, C. B., Nejman, D., Tzeng, C. D., et al. (2019). Tumor Microbiome Diversity and Composition Influence Pancreatic Cancer Outcomes. Cell, 178(4), 795-806.e712. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2019.07.008
Sethi, V., Kurtom, S., Tarique, M., Lavania, S., Malchiodi, Z., Hellmund, L., Zhang, L., Sharma, U., Giri, B., Garg, B., Ferrantella, A., Vickers, S. M., Banerjee, S., Dawra, R., Roy, S., Ramakrishnan, S., Saluja, A., & Dudeja, V. (2018). Gut Microbiota Promotes Tumor Growth in Mice by Modulating Immune Response. Gastroenterology, 155(1), 33-37.e36. https://doi.org/10.1053/j.gastro.2018.04.001
Pushalkar, S., Hundeyin, M., Daley, D., Zambirinis, C. P., Kurz, E., Mishra, A., Mohan, N., Aykut, B., Usyk, M., Torres, L. E., Werba, G., Zhang, K., Guo, Y., Li, Q., Akkad, N., Lall, S., Wadowski, B., Gutierrez, J., Kochen Rossi, J. A., et al. (2018). The Pancreatic Cancer Microbiome Promotes Oncogenesis by Induction of Innate and Adaptive Immune Suppression. Cancer Discovery, 8(4), 403–416. https://doi.org/10.1158/2159-8290.CD-17-1134
Mannucci, E., Tesi, F., Bardini, G., Ognibene, A., Petracca, M. G., Ciani, S., Pezzatini, A., Brogi, M., Dicembrini, I., Cremasco, F., Messeri, G., & Rotella, C. M. (2004). Effects of metformin on glucagon-like peptide-1 levels in obese patients with and without Type 2 diabetes. Diabetes, Nutrition & Metabolism, 17(6), 336–342.
Napolitano, A., Miller, S., Nicholls, A. W., Baker, D., Van Horn, S., Thomas, E., Rajpal, D., Spivak, A., Brown, J. R., & Nunez, D. J. (2014). Novel gut-based pharmacology of metformin in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. PLoS ONE, 9(7), e100778. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0100778
Duca, F. A., Bauer, P. V., Hamr, S. C., & Lam, T. K. (2015). Glucoregulatory Relevance of Small Intestinal Nutrient Sensing in Physiology, Bariatric Surgery, and Pharmacology. Cell Metabolism, 22(3), 367–380. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cmet.2015.07.003
Yang, M., Darwish, T., Larraufie, P., Rimmington, D., Cimino, I., Goldspink, D. A., Jenkins, B., Koulman, A., Brighton, C. A., Ma, M., Lam, B. Y. H., Coll, A. P., O’Rahilly, S., Reimann, F., & Gribble, F. M. (2021). Inhibition of mitochondrial function by metformin increases glucose uptake, glycolysis and GDF-15 release from intestinal cells. Science and Reports, 11(1), 2529. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-021-81349-7
Funding
Guido Eibl is supported by the National Institutes of Health, National Cancer Institute (P01CA236585), and the Hirshberg Foundation for Pancreatic Cancer Research. Enrique Rozengurt is supported by the National Institutes of Health, National Cancer Institute (P01CA236585), National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases (R21AI156592), the Veterans Administration (I01BX003801), and the Hirshberg Foundation for Pancreatic Cancer Research.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Eibl, G., Rozengurt, E. Metformin: review of epidemiology and mechanisms of action in pancreatic cancer. Cancer Metastasis Rev 40, 865–878 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10555-021-09977-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10555-021-09977-z