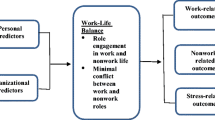
Abstract
We highlight exclusionary practices in management research, and demonstrate through example how a more inclusive management literature can address the unique contexts of persons with disabilities, a group that is disadvantaged in society, globally. Drawing from social psychology, disability, self-employment, entrepreneurship, and vocational rehabilitation literatures, we develop and test a holistic model that demonstrates how persons with disabilities might attain meaningful work and improved self-image via self-employment, thus accessing some of the economic and social-psychological benefits often unavailable to them due to organizational-employment barriers. Our longitudinal study provides evidence of the self-image value of ‘doing’ in self-employment, highlighting the potential to reduce stigma and improve generalized self-efficacy and self-esteem. Implications for self-image theory, entrepreneurship training and development, and public policy related to persons with disabilities are discussed.



Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
Considerable self-employment and entrepreneurship literature examines entrepreneurial self-efficacy, but this construct is distinct from generalized self-efficacy, and has not been shown to have the wider associations with work performance or life satisfaction of the latter construct.
References
Albrecht, G. L., & Devlieger, P. J. (1999). The disability paradox: High quality of life against all odds. Social Science & Medicine, 48(8), 977–988.
Alonso, J., Buron, A., Rojas-Farreras, S., De Graaf, R., Haro, J. M., & De Girolamo, G. … ESEMeD/MHEDEA 2000 Investigators (2009). Perceived stigma among individuals with common mental disorders. Journal of Affective Disorders, 118(1), 180–186.
Alsos, G. A., & Kolvereid, L. (1998). The business gestation process of novice, serial and parallel business founders. Entrepreneurship Theory and Practice, 22(4), 101–114.
Ameri, M., Schur, L., Adya, M., Bentley, F., McKay, P., & Kruse, D. (2018). The disability employment puzzle: Field experiment on employer hiring behavior. ILR Review, 71, 329–364.
Arns, P. G., & Linney, J. A. (1993). Work, self, and life satisfaction for persons with severe and persistent mental disorders. Psychosocial Rehabilitation Journal, 17(2), 63–79.
Ashley, D., & Graf, N. (2018). The process and experiences of self-employment among people with disabilities: A qualitative study. Rehabilitation Counseling Bulletin, 61(2), 90–100.
Audhoe, S., Hoving, J., Sluiter, J., & Frings-Dresen, M. (2010). Vocational interventions for unemployed: Effects on work participation and mental distress. A systematic review. Journal of Occupational Rehabilitation, 20(1), 1–13.
Bandura, A. (1989). Human agency in social cognitive theory. American Psychologist, 44(9), 1175.
Barclay, L. A., & Markel, K. S. (2009). Ethical fairness and human rights: The treatment of employees with psychiatric disabilities. Journal of Business Ethics, 85(3), 333–345.
Barrick, M. R., & Mount, M. K. (1991). The big five personality dimensions and job performance: A meta-analysis. Personnel Psychology, 44(1), 1–26.
Bauer, D. J., & Curran, P. J. (2005). Probing interactions in fixed and multilevel regression: Inferential and graphical techniques. Multivariate Behavioral Research, 40, 373–400.
Baum, J., Locke, E., & Smith, K. (2001). A multidimensional model of venture growth. Academy of Management Journal, 44(2), 292–303.
Baumeister, R. F., Campbell, J. D., Krueger, J. I., & Vohs, K. D. (2003). Does high self-esteem cause better performance, interpersonal success, happiness, or healthier lifestyles? Psychological Science in the Public Interest, 4, 1–44.
Becker, H. (1960). Notes on the concept of commitment. American Journal of Sociology, 32–40.
Bedini, L. A. (2000). “Just sit down so we can talk:” perceived stigma and community recreation pursuits of people with disabilities. Therapeutic Recreation Journal, 34(1), 55.
Bem, D. J. (2011). Feeling the future: Experimental evidence for anomalous retroactive influences on cognition and affect. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 100(3), 407–425.
Bond, G., Resnick, S., Drake, R., Xie, H., McHugo, G., & Bebout, R. (2001). Does competitive employment improve nonvocational outcomes for people with severe mental illness? Journal of Consulting and Clinical Psychology, 69(3), 489–501.
Bos, A. E., Pryor, J. B., Reeder, G. D., & Stutterheim, S. E. (2013). Stigma: Advances in theory and research. Basic and Applied Social Psychology, 35(1), 1–9.
Boylan, A., & Burchardt, T. (2002). Barriers to self-employment for disabled people. Report for the Small Business Services. London: Department of Trade and Industry.
Bradshaw, W., & Brekke, J. (1999). Subjective experience in schizophrenia: Factors influencing self-esteem, satisfaction with life and subjective distress. American Journal of Orthopsychiatry, 6, 254–260.
Bruton, C., & O’Mahony, C. (2009). Report on the employment of disabled people in European countries. Retrieved August 23, 2012 from http://www.disability-europe.net/countries/ireland.
Burkhauser, R. V., & Daly, M. C. (1998). Disability and work: The experiences of American and German men. Economic Review-Federal Reserve Bank of San Francisco, 2, 17.
Busenitz, L., Gomez, C., & Spencer, J. (2000). Country institutional profiles: Unlocking entrepreneurial phenomena. Academy of Management Journal, 43(5), 994–1003.
Button, P. (2017). Expanding employment discrimination protections for individuals with disabilities: Evidence from California. ILR Review, 71(2), 365–393.
Bybee, J., & Zigler, E. (1991). The self-image and guilt: A further test of the cognitive-developmental formulation. Journal of Personality, 59, 733–745.
Caldwell, K., Harris, P., S., & Renko, M. (2016). Social entrepreneurs with disabilities: Exploring motivational and attitudinal factors. Canadian Journal of Disability Studies, 5(1), 211–244.
Caplan, R., Vinokur, A., Price, R., & van Ryn, M. (1989). Job seeking, reemployment, and mental health: A randomized field experiment in coping with job loss. Journal of Applied Psychology, 74(5), 759–769.
Carlson, D., & Kacmar, K. (2000). Work-family conflict in the organization: Do life role values make a difference? Journal of Management, 2(254), 1031–1054.
Carter, N., Gartner, W., & Reynolds, P. (1996). Exploring start-up event sequences. Journal of Business Venturing, 11, 151–166.
Chaiklin, S. (2003). The zone of proximal development in Vygotsky’s analysis of learning and instruction. In A. Kosulin, B. Gindis, V. Ageyev & S. Miller (Eds.), Vygotsky’s educational theory in cultural context (pp. 39–64). New York: Cambridge University Press.
Chang, C., Ferris, D., Johnson, R., Rosen, C., & Tan, J. (2012). Core self-evaluations: A review and evaluation of the literature. Journal of Management, 38(1), 81–128.
Chen, G. (2012). Evaluating the core: Critical assessment of core self-evaluations theory. Journal of Organizational Behavior, 33(2), 153–160.
Chen, G., Gully, S. M., & Eden, D. (2001). Validation of a new general self-efficacy scale. Organizational Research Methods, 4(1), 62–83.
Chen, G., Gully, S. M., & Eden, D. (2004). General self-efficacy and self-esteem: Toward theoretical and empirical distinction between correlated self-evaluations. Journal of Organizational Behavior, 25(3), 375–395.
Cobb-Cark, D., & Schurer, S. (2013). Two economists’ musings on the stability of locus of control. The Economic Journal, 123(570), F358–F400.
Cook, J. (2006). Employment barriers for persons with psychiatric disabilities: Update of a report for the President’s commission. Psychiatr. Serv, 57(10), 1391–1405.
Corrigan, P. W., Watson, A. C., & Barr, L. (2006). The self-stigma of mental illness: Implications for self-esteem and self-efficacy. Journal of Social and Clinical Psychology, 25(8), 875–884.
Crow, S. M., & Payne, D. (1992). Affirmative action for a face only a mother could love? Journal of Business Ethics, 11(11), 869.
Daniels, T. M. (2008). Determinants of employment outcomes among persons with disabilities in public vocational rehabilitation. Dissertation Abstracts International Section A: Humanities and Social Sciences: 3294.
Davidsson, P., & Gordon, S. R. (2012). Panel studies of new venture creation: A methods-focused review and suggestions for future research. Small Business Economics, 39(4), 853–876.
Davidsson, P., & Honig, B. (2003). The role of social and human capital among nascent entrepreneurs. Journal of Business Venturing, 18(3), 301–331.
DeTienne, D. R., & Chandler, G. N. (2004). Opportunity identification and its role in the entrepreneurial classroom: A pedagogical approach and empirical test. Academy of Management Learning and Education, 3, 242–257.
Dewey, J. (2007). Experience and education. New York: Simon and Schuster.
DiStefano, C., & Motl, R. (2006). Further investigating method effects associated with negatively worded items on self-report surveys. Structural Equation Modeling, 13(3), 440–464.
Dorio, J. (2004). Tying it all together–the PASS to success: A comprehensive look at promoting job retention for workers with psychiatric disabilities in a supported employment program. Psychiatric Rehabilitation Journal, 28(1), 32–39.
Dormann, C., Fay, D., Zapf, D., & Frese, M. (2006). A state-trait analysis of job satisfaction: On the effect of core self-evaluation. Applied Psychology: An International Review, 55, 27–51.
Drake, R., McHugo, G., Bebout, R., Becker, D., Harris, M., Bond, G., & Quimby, E. (1999). A randomized clinical trial of supported employment for inner-city patients with severe mental disorders. Archives of General Psychiatry, 56(7), 627–633.
Duncan, M. C. (2001). The sociology of ability and disability in physical activity. Sociology of Sport Journal, 18(1), 1–4.
Dutta, A., Gervey, R., Chan, F., Chou, C. C., & Ditchman, N. (2008). Vocational rehabilitation services and employment outcomes for people with disabilities: A United States study. Journal of Occupational Rehabilitation, 18(4), 326–334.
Eden, D., & Aviram, A. (1993). Self-efficacy training to speed reemployment: Helping people to help themselves. Journal of Applied Psychology, 78(3), 352.
Eden, D., & Zuk, Y. (1995). Seasickness as a self-fulfilling prophecy: Raising self-efficacy to boost performance at sea. Journal of Applied Psychology, 80(5), 628–635.
Eisenhauer, J. (2007). Just looking and staring back: Challenging ableism through disability performance art. Studies in Art Education, 49(1), 7–22.
Ellison, M. L., Russinova, Z., Lyass, A., & Rogers, E. S. (2008). Professionals and managers with severe mental illnesses: Findings from a national survey. The Journal of Nervous and Mental Disease, 196(3), 179–189.
Ensminger, M., & Celentano, D. (1988). Unemployment and psychiatric distress: Social resources and coping. Social Science and Medicine, 27(3), 239–247.
Faggio, G., & Silva, O. (2014). Self-employment and entrepreneurship in urban and rural labour markets. Journal of Urban Economics, 84, 67–85.
Festinger, L. (1954). A theory of social comparison processes. Human Relations, 7, 117–140.
Finger, M. E., Escorpizo, R., Glässel, A., Gmünder, H. P., Lückenkemper, M., Chan, C., … Stucki, G. (2012). ICF core set for vocational rehabilitation: Results of an international consensus conference. Disability and Rehabilitation, 34(5), 429–438.
Gartner, W. B. (1990). What are we talking about when we talk about entrepreneurship? Journal of Business Venturing, 5(1), 15–28.
Ghormley, Y. S. (2001). E-business entrepreneurship as a career option for people with disabilities. Dissertation, Capella University.
Ginexi, E., Howe, G., & Caplan, R. (2000). Depression and control beliefs in relation to reemployment. Journal of Occupational Health Psychology, 5, 323–336.
Goffman, E. (1963). Stigma: Notes on the management of spoiled identity. Englewood Cliffs: Prentice Hall.
Goodley, D. (2014). Dis/ability studies: Theorising disablism and ableism. Routledge.
Gottlieb, A., Myhill, W. N., & Blanck, P. (2010). Employment of people with disabilities. New York, Buffalo: International Encyclopedia of Rehabilitation.
Green, S., Davis, C., Karshmer, E., Marsh, P., & Straight, B. (2005). Living stigma: The impact of labeling, stereotyping, separation, status loss, and discrimination in the lives of individuals with disabilities and their families. Sociological Inquiry, 75(2), 197–215.
Greenwood, R., Johnson, V., & Schriner, K. (1988). Employer perspectives on employment-rehabilitation partnerships. Journal of Applied Rehabilitation Counseling, 19, 8–12.
Greve, B. (2009). The labour market situation of disabled people in European countries and implementation of employment policies. Academic Network of European Disability Experts. Retrieved May 2014 from http://www.disability-europenet/theme/employment.
Guthrie, S. R., & Castelnuovo, S. (2001). Disability management among women with physical impairments: The contribution of physical activity. Sociology of Sport Journal, 18(1), 5–20.
Hales, G. (1996). Beyond disability: Towards an enabling society. London: Sage.
Hatzenbuehler, M. L., Phelan, J. C., & Link, B. G. (2013). Stigma as a fundamental cause of population health inequalities. American Journal of Public Health, 103(5), 813–821.
Hausman, J. A. (1978). Specification tests in econometrics. Econometrica, 46(6), 1251–1271.
Haynie, J., & Shepherd, D. (2011). Toward a theory of discontinuous career transition: Investigating career transitions necessitated by traumatic life events. Journal of Applied Psychology, 96, 501.
Heath, K., & Reed, D. (2013). Industry-Driven Support model to build social capital and business skills of low-income entrepreneurs with disabilities. Journal of Vocational Rehabilitation, 38(2), 139–148.
Hensley, W. E., & Roberts, M. K. (1976). Dimensions of Rosenburg's self-esteem scale. Psychological Reports, 38(2), 583–584.
Hipes, C., Lucas, J., Phelan, J., & White, R. (2016). The stigma of mental illness in the labor market. Social Science Research, 56, 16–25.
Honig, B. (2004). Entrepreneurship education: Toward a model of contingency based-business planning. Academy of Management Learning and Education, 3, 258–373.
Ipsen, C., Arnold, N., & Colling, K. (2005a). Self-employment for people with disabilities: Enhancing services through interagency linkages. Journal of Disability Policy Studies, 15(4), 231–239.
Ipsen, C., Arnold, N. L., & Colling, K. (2005b). Self-employment Policies: Changes through the decade. Journal of Disability Policy Studies, 16(2), 115–122.
Jenson, R., Petri, A., Day, A., Truman, K., & Duffy, K. (2011). Perceptions of self-efficacy among STEM students with disabilities. Journal of Postsecondary Education & Disability, 24, 269–283.
Johnson, R., Rosen, C., & Levy, P. (2008). Getting to the core of core self-evaluation: A review and recommendations. Journal of Organizational Behavior, 29, 391–413.
Jones, E., Farina, A., Hastorf, A., Markus, H., Miller, D., & Scott, R. (1984). Social Stigma: The Psychology of Marked Relationships. New York: Freeman.
Jones, G. R. (1986). Socialization tactics, self-efficacy, and newcomers’ adjustments to organizations. Academy of Management journal, 29(2), 262–279.
Jones, M.,K., & Latreille, P. L. (2011). Disability and self-employment: Evidence for the UK. Applied Economics, 43(27), 4161–4178.
Judge, T., & Bono, J. (2001). Relationship of core self-evaluations traits—self-esteem, generalized self-efficacy, locus of control, and emotional stability—with job satisfaction and job performance: A meta-analysis. Journal of Applied Psychology, 86(1), 80–920.
Judge, T., Bono, J., Erez, A., & Locke, E. (2005). Core self-evaluations and job and life satisfaction: Role of self-concordance and goal attainment. Journal of Applied Psychology, 90(2), 257–268.
Judge, T., Erez, A., & Bono, J. (1998). The power of being positive: The relation between positive self-concept and job performance. Human Performance, 11(2/3), 167–187.
Judge, T., & Hurst, C. (2008). How the rich (and happy) get richer (and happier): Relationship of core self-evaluations to trajectories in attaining work success. Journal of Applied Psychology, 93(4), 849–863.
Judge, T., Locke, E., & Durham, C. (1997). The dispositional causes of job satisfaction: A core evaluations approach. Research in Organizational Behavior, 19, 151–188.
Judge, T., Locke, E., Durham, C., & Kluger, A. (1998). Dispositional effects on job and life satisfaction: The role of core evaluations. Journal of Applied Psychology, 83(1), 17–34.
Katz, J. A. (2007). Education and training in entrepreneurship. In J. R. Baum, M. Frese & R. A. Baron (Eds.), The psychology of entrepreneurship (pp. 209–235). Mahwah: Lawrence Erlbaum.
Kinicki, A., Prussia, G., & McKee-Ryan, F. (2000). A panel study of coping with involuntary job loss. Academy of Management Journal, 43(1), 90–100.
Klein, A., & Moosbrugger, H. (2000). Maximum likelihood estimation of latent interaction effects with the LMS method. Psychometrika, 65, 457–474.
Knight, M., Wykes, T., & Hayward, P. (2006). Group treatment of perceived stigma and self-esteem in schizophrenia: A waiting list trial of efficacy. Behavioural and Cognitive Psychotherapy, 34(03), 305–318.
Kolb, D. A. (2014). Experiential learning: Experience as the source of learning and development. New York: Pearson Education.
Kolvereid, L., & Moen, Ø (1997). Entrepreneurship among business graduates: Does a major in entrepreneurship make a difference? Journal of European Industrial Training, 21(4), 154–160.
Kuhn, M. H. (1960). Self-attitudes by age, sex, and professional training. Sociological Quarterly, 1(1), 39–55.
Lai, Y. M., Hong, C. P. H., & Chee, C. Y. (2001). Stigma of mental illness. Singapore Medical Journal, 42(3), 111–114.
Lampel, J., Honig, B., & Drori, I. (2014). Organizational ingenuity: Concept, processes and strategies. Organization Studies, 35, 1–18.
Landa, C. E., & Bybee, J. A. (2007). Adaptive elements of aging: Self-image discrepancy, perfectionism, and eating problems. Developmental Psychology, 43(1), 83.
Landstrom, H. (2007). Pioneers in entrepreneurship and small business research (Vol. 8). New York: Springer.
Lannin, D. G., Vogel, D. L., Brenner, R. E., & Tucker, J. R. (2015). Predicting self-esteem and intentions to seek counseling. The Counseling Psychologist, 43(1), 64–93.
Le, A. (1999). Empirical studies of self-employment. Journal of Economic Surveys, 13(4), 381–416.
Letkemann, P. (2002). Unemployed professionals, stigma management and derivative stigmata. Work, Employment and Society, 16(3), 511–522.
Liao, J., Welsch, H., & Tan, W. (2005). Venture gestation paths of nascent entrepreneurs: Exploring temporal patterns. Journal of High Technology Management Research, 16(1), 1–22.
Lichtenstein, B., Carter, N., Dooley, K., & Gartner, W. (2007). Complexity dynamics of nascent entrepreneurship. Journal of Business Venturing, 22(2), 236–261.
Lind, P. R. (2000). President’s Committee on Employment of People with Disabilities, Getting down to Business: A Blueprint for Creating and Supporting Entrepreneurial Activities for Individuals with Disabilities. Accessed November 9, 2016 via https://eric.ed.gov/?id=ED450525.
Link, B. (1987). Understanding labeling effects in the area of mental disorders: An assessment of the effects of expectations of rejection. American Sociological Review, 52(1), 96–112.
Link, B., Cullen, F., Struening, E., Shrout, P., & Dohrenwend, B. (1989). A modified labeling theory approach to mental disorders: An empirical assessment. American Sociological Review, 400–423.
Link, B., & Phelan, J. (2001). Conceptualizing stigma. Annual Review of Sociology: 363–385.
Link, B., & Phelan, J. (2014). Stigma power. Social Science & Medicine, 103, 24–32.
Link, B., Struening, E., Neese-Todd, S., Asmussen, S., & Phelan, J. (2001). The consequences of stigma for self-esteem of people with mental illness. Psychiatric Services, 52, 1621–1626.
Loja, E., Costa, M. E., Hughes, B., & Menezes, I. (2013). Disability, embodiment and ableism: Stories of resistance. Disability & Society, 28(2), 190–203.
Loprest, P., & Maag, E. (2003). The relationship between early disability onset and education and employment. Washington: The Urban Institute.
Lyons, P. (2015). Core self-evaluation can help in making better recruitment and selection choices. Human Resource Management International Digest, 23(3), 17–19.
MacKinnon, D. P., Lockwood, C. M., & Williams, J. (2004). Confidence limits for the indirect effect: Distribution of the product and resampling methods. Multivariate Behavioral Research, 39, 99–128.
MacLean, A. (2010). The things they carry: Combat, disability, and unemployment among US men. American sociological review, 75(4), 563–585.
Mak, W., & Cheung, R. (2008). Affiliate stigma among caregivers of people with intellectual disability or mental illness. Journal of Applied Research in Intellectual Disabilities, 21, 532–545.
Maria, J. F., & Lozano, J. M. (2010). Responsible leaders for inclusive globalization: Cases in Nicaragua and Democratic Republic of the Congo. Journal of Business Ethics, 93(1), 93–111.
Markman, G., Baron, R., & Balkin, D. (2005). Are perseverance and self-efficacy costless? Assessing entrepreneurs’ regretful thinking. Journal of Organizational Behavior, 26(1), 1–19.
Martin, B., McNally, J., & Kay, M. (2013). Examining the formation of human capital in entrepreneurship: A meta-analysis of entrepreneurship education outcomes. Journal of Business Venturing, 28, 211–224.
Mavromaras, K. G., & Polidano, C. (2011). Improving the employment rates of people with disabilities through vocational education. Institute for the Study of Labor, Discussion Paper Series, No. 5548.
McFarlane, F. R. (1998). Personnel development in the field of disability with a focus on employment outcomes. Disability & Society, 13(4), 575–585.
McKee-Ryan, F., Song, Z., Wanberg, C., & Kinicki, A. J. (2005). Psychological and physical well-being during unemployment: A meta-analytic study. Journal of Applied Psychology, 90, 53–76.
McLaughlin, M. E., Bell, M. P., & Stringer, D. Y. (2004). Stigma and acceptance of persons with disabilities understudied aspects of workforce diversity. Group & Organization Management, 29(3), 302–333.
McNaughton, D., Symons, G., Light, J., & Parsons, A. (2006). My dream was to pay taxes”: The self-employment experiences of individuals who use augmentative and alternative communication. Journal of Vocational Rehabilitation, 25, 181–196.
Meacham, H., Cavanagh, J., Bartram, T., & Laing, J. (2017). Ethical management in the hotel sector: Creating an authentic work experience for workers with intellectual disabilities. Journal of Business Ethics, 1–13.
Mead, G. H. (1934). Mind, self, and society. Chicago: University of Chicago Press.
Mickelson, K., & Williams, S. (2008). Perceived stigma of poverty and depression: Examination of interpersonal & intrapersonal mediators. Journal of Social and Clinical Psychology, 27, 903–930.
Mitchell, R. K., Busenitz, L. W., Bird, B., Marie Gaglio, C., McMullen, J. S., Morse, E. A., & Smith, J. B. (2007). The central question in entrepreneurial cognition research 2007. Entrepreneurship Theory and Practice, 31(1), 1–27.
Moin, V., Duvdevany, I., & Mazor, D. (2009). Sexual identity, body image and life satisfaction among women with and without physical disability. Sexuality and Disability, 27(2), 83–95.
Nabors, L., Yanos, P., Roe, D., Hasson-Ohayon, I.… Lysaker, P. (2014). Stereotype endorsement, metacognitive capacity, and self-esteem as predictors of stigma resistance in persons with schizophrenia. Comprehensive Psychiatry, 55(4), 792–798.
Neck, H. M., & Greene, P. G. (2011). Entrepreneurship education: Known worlds and new frontiers. Journal of Small Business Management, 49(1), 55–70.
Newark, P. E., Elsässer, M., & Stieglitz, R. D. (2016). Self-esteem, self-efficacy, and resources in adults with ADHD. Journal of Attention Disorders, 20(3), 279–290.
Oosterbeek, H., van Praag, M., & Ysselstein, A. (2010). The impact of entrepreneurship education on entrepreneurship skills and motivation. European Economic Review, 54(3), 442–454.
Ostrow, L., Nemec, P., & Smith, C. (2018). Self-employment for people with psychiatric disabilities: Advantages and strategies. The Journal of Behavioral Health Services & Research, 1–11.
Ouimette, M., & Rammler, L. H. (2017). Entrepreneurship as a means to Employment First: How can it work? Journal of Vocational Rehabilitation, 46(3), 333–339.
Pagan, R. (2009). Self-employment among people with disabilities: Evidence for Europe. Disability & Society, 24(2), 217–229.
Pagán-Rodríguez, R. (2012). Transitions to and from self-employment among older people with disabilities in Europe. Journal of Disability Policy Studies, 23(2), 82–93.
Peterman, N., & Kennedy, J. (2003). Enterprise education: Influencing students’ perceptions of entrepreneurship. Entrepreneurship Theory and Practice, 28(2), 129–144.
Pettigrew, T. F., & Tropp, L. R. (2006). A meta-analytic test of intergroup contact theory. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 90(5), 751.
Philipsen, A., Richter, H., Peters, J., … van Elst, L. (2007). Structured group psychotherapy in adults with attention deficit hyperactivity disorder: Results of an open multicentre study. The Journal of Nervous and Mental Disease, 195(12), 1013–1019.
Piaget, J. (1950). The psychology of intelligence. London: Routledge and Kegan.
Piaget, J. (1953). The origins of intelligence in children. Journal of Consulting Psychology, 17, 467.
Pittaway, L., & Cope, J. (2007). Entrepreneurship education: A systematic review of the evidence. International Small Business Journal, 25(5), 479–510.
Politis, D., & Gabrielsson, J. (2009). Entrepreneurs’ attitudes towards failure: An experiential learning approach. International Journal of Entrepreneurial Behavior Research, 15, 364–383.
Pope, D., & Bambra, C. (2005). Has the Disability Discrimination Act closed the employment gap? Disability and Rehabilitation, 27(20), 1261–1266.
Raffiee, J., & Feng, J. (2014). Should I quit my day job?: A hybrid path to entrepreneurship. Academy of Management Journal, 57(4), 936–963.
Renko, M., Harris, S. P., & Caldwell, K. (2016). Entrepreneurial entry by people with disabilities. International Small Business Journal, 34(5), 555–578.
Revell, G., Smith, F., & Inge, C. (2009). An analysis of self-employment outcomes in federal/state vocational rehabilitation system. Journal of Vocational Rehabilitation, 31, 11–18.
Rich, B. L., Lepine, J. A., & Crawford, E. R. (2010). Job engagement: Antecedents and effects on job performance. Academy of Management Journal, 53(3), 617–635.
Ritsher, J., & Phelan, J. (2004). Internalized stigma predicts erosion of morale among psychiatric outpatients. Psychiatry Research, 129, 257–265.
Rocke, D. M., & Woodruff, D. L. (1996). Identification of outliers in multivariate data. Journal of the American Statistical Association, 91(435), 1047–1061.
Rogers, E. S., Anthony, W. A., Lyass, A., & Penk, W. E. (2006). A randomized clinical trial of vocational rehabilitation for people with psychiatric disabilities. Rehabilitation Counseling Bulletin, 49(3), 143–156.
Rosenberg, M. (1965). Society and the Adolescent Self-image. Princeton: Princeton University Press.
Rosenberg, M. (1979). Conceiving the Self. New York: Basic Books.
Rosenfield, S. (1997). Labeling mental illness: The effects of received services and perceived stigma on life satisfaction. American Sociological Review, 62, 660–672.
Rosenthal, D., Chan, F., Wong, D., Kundu, M., & Dutta, A. (2006). Predicting employment outcomes based on race, gender, disability, work disincentives, and vocational rehabilitation service patterns. Journal of Rehabilitation Administration, 29, 229–244.
Salancik, G. (1977). Organizational behavior in the new organizational era. In B. Straw & G. Salancik (Eds.), New directions in organizational behavior (pp. 1–53). New York: St. Clair Press.
Sarasvathy, S. (2001). Causation and effectuation: Toward a theoretical shift from economic inevitability to entrepreneurial contingency. Academy of Management Review, 26, 243–263.
Satorra, A. (2000). Scaled and adjusted restricted tests in multi-sample analysis of moment structures. In R. D. H. Heijmans, D. S. G. Pollock & A. Satorra (Eds.), Innovations in multivariate statistical analysis. A Festschrift for Heinz Neudecker (pp. 233–247). London: Kluwer Academic Publishers.
Schmitt, N. (2004). Beyond the big five: Increases in understanding and practical utility. Human Performance, 17, 347–357.
Schumacher, M., Corrigan, P., & DeJong, T. (2003). Examining cues that signal mental illness stigma. Journal of Social and Clinical Psychology, 22, 467–476.
Seekins, T., & Arnold, N. (1999). Self-employment and economic leadership as two promising perspectives on rural disability and work. Work, 12(3), 213–222.
Shahar, G., & Davidson, L. (2003). Depressive symptoms erode self-esteem in severe mental illness: A three-wave, cross-lagged study. Journal of Consulting Clinical Psychology, 71(5), 890–900.
Shane, S., & Venkataraman, S. (2000). The promise of entrepreneurship as a field of research. Academy of Management Review, 25(1), 217–226.
Shier, M., Graham, J., & Jones, M. (2009). Barriers to employment as experienced by disabled people: A qualitative analysis. Disability & Society, 24(1), 63–75.
Simsek, Z., Heavey, C., & Veiga, J. (2010). The Impact of CEO core self-evaluations on entrepreneurial orientation. Strategic Management Journal, 31, 110–119.
Sorenson, O., & Stuart, T. E. (2008). 12 Entrepreneurship: A field of dreams? Academy of Management Annals, 2(1), 517–543.
Steele, C. M., Spencer, S. J., & Lynch, M. (1993). Self-image resilience and dissonance: The role of affirmational resources. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 64(6), 885–896.
Sud, M., & VanSandt, C. V. (2015). Identity Rights: A Structural Void in Inclusive Growth. Journal of Business Ethics, 132(3), 589–601.
Szymanski, E. M. E., & Parker, R. M. (2003). Work and disability: Issues and strategies in career development and job placement. Austin: Pro-ed.
Tafarodi, R. W., & Swann, W. B. Jr. (1995). Self-liking and self-competence as dimensions of global self-esteem: Initial validation of a measure. Journal of Personality Assessment, 65(2), 322–242.
Thomson, R. G. (2017). Extraordinary bodies: Figuring physical disability in American culture and literature. Columbia: Columbia University Press.
Tierney, P., & Farmer, S. M. (2002). Creative self-efficacy: Its potential antecedents and relationship to creative performance. Academy of Management Journal, 45(6), 1137–1148.
Tipton, R. M., & Worthington, E. L. (1984). The measurement of generalized self-efficacy: A study of construct validity. Journal of Personality Assessment, 48(5), 545–548.
Turner, J. B., & Turner, R. J. (2004). Physical disability, unemployment, and mental health. Rehabilitation Psychology, 49(3), 241.
Van Brakel, W. H. (2006). Measuring health-related stigma—A literature review. Psychology, Health & Medicine, 11(3), 307–334.
Van Dongen, C. (1998). Self-esteem among persons with severe mental illness. Issues in Mental Health Nursing, 19, 29–40.
Vinokur, A., Price, R., Caplan, R., van Ryan, M., & Curran, J. (1995). The Jobs I preventive intervention for unemployed individuals. In L. Murphy, J. Hurrel, S. Sauter & G. Keita (Eds.), Job stress interventions. Washington, DC: American Psychological Association.
Vygotsky, L. S. (1980). Mind in society: The development of higher psychological processes. Cambridge: Harvard University Press.
Warr, P., & Jackson, P. (1985). Factors influencing the psychological impact of prolonged unemployment and of re-employment. Psychological Medicine, 15, 795–807.
Watson, A. C., Corrigan, P., Larson, J. E., & Sells, M. (2007). Self-stigma in people with mental illness. Schizophrenia Bulletin, 33(6), 1312–1318.
Wehman, P., Revell, W. G., & Brooke, V. (2003). Competitive employment: Has it become the “first choice” yet? Journal of Disability Policy Studies, 14(3), 163–173.
Wehmeyer, M. L. (1994). Employment status and perceptions of control of adults with cognitive and developmental disabilities. Research in Developmental Disabilities, 15(2), 119–131.
Williams, C. (2006). Disability in the Workplace. (75-001-XIE) Ottawa: Statistics Canada. Retrieved February 12, 2015 from http://goo.gl/RM8aiI.
Wolfe, M., & Patel, P. (2017). Persistent and repetitive: Obsessive-Compulsive personality disorder and self-employment. Journal of Business Venturing Insights, 8, 125–137.
World Health Organization (2011). World Report on Disability. Retrieved July 21, 2012 from http://www.who.int/disabilities/world_report/2011/report/en/.
Yamamoto, S., Unruh, D., & Bullis, M. (2011). The viability of self-employment for individuals with disabilities in the United States: A synthesis of the empirical-research literature. Journal of Vocational Rehabilitation, 35(2), 117–127.
Yamamoto, S. H., & Alverson, C. Y. (2013). Successful vocational outcomes: A multilevel analysis of self-employment through US vocational rehabilitation agencies. Journal of Vocational Rehabilitation, 38(1), 15–27.
Zhang, L., Li, W., Liu, B., & Xie, W. (2014). Self-esteem as mediator and moderator of the relationship between stigma perception and social alienation of Chinese adults with disability. Disability and Health Journal, 7(1), 119–123.
Zhao, H., Seibert, S. E., & Hills, G. E. (2005). The mediating role of self-efficacy in the development of entrepreneurial intentions. Journal of Applied Psychology, 90, 1265–1272.
Acknowledgements
We thank Dirk De Clercq and Ciaran Heavey for their input to earlier versions of this paper. We also thank the Social Sciences and Humanities Research Council of Canada for research grant and scholarship support, which helped to make this work possible.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest in undertaking this research.
Ethical Approval
All procedures performed in this research were in accordance with the ethical standards of McMaster University, Canada, and University College Dublin, Ireland, and approved by the Research Ethics Board of both universities.
Informed Consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the research.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Martin, B.C., Honig, B. Inclusive Management Research: Persons with Disabilities and Self-Employment Activity as an Exemplar. J Bus Ethics 166, 553–575 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10551-019-04122-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10551-019-04122-x