Abstract
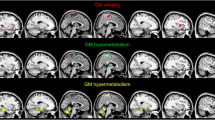
Perturbation of corticohippocampal circuits is a key step in the pathogenesis of transient global amnesia. We evaluated the spatial distribution of altered cerebral metabolism to determine the location of the corticohippocampal circuits perturbed during the acute stage of transient global amnesia. A consecutive series of 12 patients with transient global amnesia who underwent 18F-fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography within 3 days after symptom onset was identified. We used statistical parametric mapping with two contrasts to identify regions of decreased and increased brain metabolism in transient global amnesia patients compared with 25 age-matched controls. Transient global amnesia patients showed hypometabolic clusters in the left temporal and bilateral parieto-occipital regions that belong to the posterior medial network as well as, hypermetabolic clusters in the bilateral inferior frontal regions that belong to the anterior temporal network. The posterior medial and anterior temporal networks are the two main corticohippocampal circuits involved in memory-guided behavior. Decreased metabolism in the posterior medial network might explain the impairment of episodic memory observed during the acute stage of transient global amnesia. Concomitant increased metabolism within the anterior temporal network might occur as a compensatory mechanism.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baron JC, Petit-Taboué MC, Le Doze F, Desgranges B, Ravenel N, Marchal G (1994) Right frontal cortehypometabolism in transient global amnesia. A PET study. Brain 117:545–552. doi:10.1093/brain/117.3.545
Bartsch T, Butler C (2013) Transient amnesic syndromes. Nat Rev Neurol 9:86–97. doi:10.1038/nrneurol.2012.264
Bartsch T, Deuschl G (2010) Transient global amnesia: functional anatomy and clinical implications. Lancet Neurol 9:205–214. doi:10.1016/S1474-4422(09)70344-8
Burle B, Spieser L, Roger C, Casini L, Hasbroucq T, Vidal F (2015) Spatial and temporal resolutions of EEG: is it really black and white? A scalp current density view. Int J Psychophysiol 97:210–220. doi:10.1016/j.ijpsycho.2015.05.004
Burwell RD (2000) The parahippocampal region: corticocortical connectivity. Ann N Y Acad Sci 911:25–42. doi:10.1111/j.1749-6632.2000.tb06717.x
Chung YA, Jeong J, Yang DW, Kang BJ, Kim SH, Chung SK, Sohn HS, Peterson BS (2009) A Tc-99m SPECT study of regional cerebral blood flow in patients with transient global amnesia. Neuroimage 47:50–55. doi:10.1016/j.neuroimage.2008.11.011
Cohen J (1992) A power primer. Psychol Bull 112:155–159. doi:10.1037/0033-2909.112.1.155
Cohen AD, Price JC, Weissfeld LA, James J, Rosario BL, Bi W, Nebes RD, Saxton JA, Snitz BE, Aizenstein HA, Wolk DA, Dekosky ST, Mathis CA, Klunk WE (2009) Basal cerebral metabolism may modulate the cognitive effects of Abeta in mild cognitive impairment: an example of brain reserve. J Neurosci 29:14770–14778. doi:10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3669-09.2009
Eustache F, Desgranges B, Petit-Taboué MC, de la Sayette V, Piot V, Sablé C, Marchal G, Baron JC (1997) Transient global amnesia: implicit/explicit memory dissociation and PET assessment of brain perfusion and oxygen metabolism in the acute stage. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 63:357–367. doi:10.1136/jnnp.63.3.357
Förster A, Al-Zghloul M, Kerl HU, Böhme J, Mürle B, Groden C (2015) Value of dynamic susceptibility contrast perfusion MRI in the acute phase of transient global amnesia. PLoS ONE 10:e0122537. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0122537
Gonzalez-Martinez V, Comte F, de Verbizier D, Carlander B (2010) Transient global amnesia: concordant hippocampal abnormalities on positron emission tomography and magnetic resonance imaging. Arch Neurol 67:510. doi:10.1001/archneurol.2010.50
Guillery B, Desgranges B, de la Sayette V, Landeau B, Eustache F, Baron JC (2002) Transient global amnesia: concomitant episodic memory and positron emission tomography assessment in two additional patients. Neurosci Lett 325:62–66. doi:10.1016/S0304-3940(02)00233-1
Heiss WD, Pawlik G, Holthoff V, Kessler J, Szelies B (1992) PET correlates of normal and impaired memory functions. Cerebrovasc Brain Metab Rev 4:1–27
Hodges JR, Warlow CP (1990) Syndromes of transient amnesia: towards a classification. A study of 153 cases. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 53:834–843. doi:10.1136/jnnp.53.10.834
Hutchinson JB, Uncapher MR, Wagner AD (2009) Posterior parietal cortex and episodic retrieval: convergent and divergent effects of attention and memory. Learn Mem 16:343–356. doi:10.1101/lm.919109
Jang JW, Park YH, Park SY, Wang MJ, Lim JS, Kim SH, Chun IK, Yang Y, Kim S (2015) Longitudinal cerebral perfusion change in transient global amnesia related to left posterior medial network disruption. PLoS ONE 10:e0145658. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0145658
Jovin TG, Vitti RA, McCluskey LF (2000) Evolution of temporal lobe hypoperfusion in transient global amnesia: a serial single photon emission computed tomography study. J Neuroimaging 10:238–241
Kim MJ, Lee KM, Son YD, Jeon HA, Kim YB, Cho ZH (2012) Increased basal forebrain metabolism in mild cognitive impairment: an evidence for brain reserve in incipient dementia. J Alzheimers Dis 32:927–938. doi:10.3233/JAD-2012-120133
Kim J, Kwon Y, Yang Y, Jang IM, Chang Y, Park YH, Jang JW, Kim JH, Kim S (2014) Clinical experience of modified diffusion-weighted imaging protocol for lesion detection in transient global amnesia: an 8-year large-scale clinical study. J Neuroimaging 24:331–337. doi:10.1111/jon.12021
Kwon Y, Yang Y, Jang JW, Park YH, Kim J, Park SH, Kim S (2014) Left dominance of EEG abnormalities in patients with transient global amnesia. Seizure 23:825–829. doi:10.1016/j.seizure.2014.06.014
La Joie R, Landeau B, Perrotin A, Bejanin A, Egret S, Pélerin A, Mézenge F, Belliard S, de La Sayette V, Eustache F, Desgranges B, Chételat G (2014) Intrinsic connectivity identifies the hippocampus as a main crossroad between Alzheimer’s and semantic dementia-targeted networks. Neuron 81:1417–1428. doi:10.1016/j.neuron.2014.01.026
Laloux P, Brichant C, Cauwe F, Decoster P (1992) Technetium-99m HM-PAO single photon emission computed tomography imaging in transient global amnesia. Arch Neurol 49:543–546. doi:10.1001/archneur.1992.00530290131022
Lampl Y, Sadeh M, Lorberboym M (2004) Transient global amnesia—not always a benign process. Acta Neurol Scand 110:75–79. doi:10.1111/j.1600-0404.2004.00275.x
Libby LA, Ekstrom AD, Ragland JD, Ranganath C (2012) Differential connectivity of perirhinal and parahippocampal cortices within human hippocampal subregions revealed by high-resolution functional imaging. J Neurosci 32:6550–6560. doi:10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3711-11.2012
Lin KN, Liu RS, Yeh TP, Wang SJ, Liu HC (1993) Posterior ischemia during an attack of transient global amnesia. Stroke 24:1093–1095. doi:10.1161/01.STR.24.7.1093
Matsuda H, Higashi S, Tsuji S, Sumiya H, Miyauchi T, Hisada K, Yamashita J (1993) High resolution Tc-99m HMPAO SPECT in a patient with transient global amnesia. Clin Nucl Med 18:46–49. doi:10.1097/00003072-199301000-00011
Murray BD, Kensinger EA (2014) The route to an integrative associative memory is influenced by emotion. PLoS ONE 9:e82372. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0082372
Park YH, Jang JW, Yang Y, Kim JE, Kim S (2013) Reflections of two parallel pathways between the hippocampus and neocortex in transient global amnesia: a cross-sectional study using DWI and SPECT. PLoS ONE 8:e67447. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0067447
Park YH, Jeong HY, Jang JW, Park SY, Lim JS, Kim JY, Im CH, Ahn S, Park SH, Kim S (2016) Disruption of the posterior medial network during the acute stage of transient global amnesia: a preliminary study. Clin EEG Neurosci 47:69–74. doi:10.1177/1550059414543684
Ranganath C, Ritchey M (2012) Two cortical systems for memory-guided behaviour. Nat Rev Neurosci 13:713–726. doi:10.1038/nrn3338
Ryoo I, Kim JH, Kim S, Choi BS, Jung C, Hwang SI (2012) Lesion detectability on diffusion-weighted imaging in transient global amnesia: the influence of imaging timing and magnetic field strength. Neuroradiology 54:329–334. doi:10.1007/s00234-011-0889-4
Sakashita Y, Kanai M, Sugimoto T, Taki S, Takamori M (1997) Changes in cerebral blood flow and vasoreactivity in response to acetazolamide in patients with transient global amnesia. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 63:605–610. doi:10.1136/jnnp.63.5.605
Sestieri C, Shulman GL, Corbetta M (2017) The contribution of the human posterior parietal cortex to episodic memory. Nat Rev Neurosci 18:183–192. doi:10.1038/nrn.2017.6
Stern Y (2002) What is cognitive reserve? Theory and research application of the reserve concept. J Int Neuropsychol Soc 8:448–460. doi:10.1017/S1355617702813248
Stern Y, Alexander GE, Prohovnik I, Mayeux R (1992) Inverse relationship between education and parietotemporal perfusion deficit in Alzheimer’s disease. Ann Neurol 32:371–375. doi:10.1002/ana.410320311
Takeuchi R, Yonekura Y, Matsuda H, Nishimura Y, Tanaka H, Ohta H, Sakahara H, Konishi J (1998) Resting and acetazolamide-challenged technetium-99m-ECD SPECT in transient global amnesia. J Nucl Med 39:1360–1362
Wang MJ, Yi S, Han JY, Park SY, Jang JW, Chun IK, Giau VV, Bagyinszky E, Lim KT, Kang SM, An SS, Park YH, Youn YC, Kim S (2016) Analysis of cerebrospinal fluid and [11C]PIB PET biomarkers for Alzheimer’s disease with updated protocols. J Alzheimers Dis 52:1403–1413. doi:10.3233/JAD-160143
Xia M, Wang J, He Y (2013) BrainNet viewer: a network visualization tool for human brain connectomics. PLoS ONE 8:e68910. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0068910
Yang Y, Kim JS, Kim S, Kim YK, Kwak YT, Han IW (2009) Cerebellar hypoperfusion during transient global amnesia: an MRI and oculographic study. J Clin Neurol 5:74–80. doi:10.3988/jcn.2009.5.2.7
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declared no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Ethical Approval
The study protocol was approved by the Institutional Review Board of Seoul National University Bundang Hospital. Informed consent was not required due to the retrospective nature of the study and minimal risk to participants.
Additional information
SangHak Yi and Young Ho Park have contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yi, S., Park, Y.H., Jang, JW. et al. Decreased Metabolism in the Posterior Medial Network with Concomitantly Increased Metabolism in the Anterior Temporal Network During Transient Global Amnesia. Brain Topogr 31, 468–476 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10548-017-0602-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10548-017-0602-y