Abstract
Minimally invasive delivery of peptide and protein molecules represents a significant opportunity for product differentiation and value creation versus standard injectable routes of administration. One such technology utilizes microneedle (MN) patches and it has made considerable clinical advances in systemic delivery of potent macromolecules and vaccines. A sub-class of this technology has focused on preparation of solid dense MN arrays followed by precision formulation coating on the tips of the MN. The objective of this study was to develop a drug product using the MN technology that has similar bioperformance when compared to subcutaneous route of delivery and can provide improved stability under storage. Therapeutic peptide (Peptide A, Merck & Co., Inc., Kenilworth, NJ, USA) is being developed as a subcutaneous injection for chronic dosing with a submilligram estimated therapeutic dose. Peptide A has chemical and physical stability challenges in solution and this led to exploration of a viable drug product which could provide therapeutic dosages while overcoming the stability issues seen with the compound. This work focused on developing a coated solid microstructure transdermal system (sMTS) for Peptide A followed by detailed in vitro and preclinical evaluation for two different coating formulations. Based on initial assessment, ~250 μg of Peptide A could be coated with precision on a 1.27cm2 patch which contained 316 MN’s. The delivery from these systems was achieved with absolute bioavailability being similar to the subcutaneous delivery (88% and 74% for coated sMTS 1 & 2 and 75% for subcutaneous delivery). Stability of Peptide A was also found to be significantly improved when coated on the sMTS system with minimal degradation recorded at room temperature storage as compared to the subcutaneous liquid formulation. Additionally, skin irritation (on pig skin) was also measured in this study and it was found to be minimal and self-resolving. This evaluation provided a viable option for developing a drug product with improved stability and successful delivery of the investigated molecule.

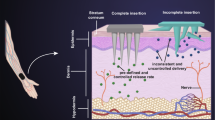
Schematic showing uncoated sMTS, resulting product with coated peptide, successful skin penetration with high delivery efficiency and bioavailability.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
J.F. Jin, L. Zhu, M. Chen, H.M. Xu, H.F. Wang, X.Q. Feng, X.P. Zhu, Q. Zhou, The optimal choice of medication administration route regarding intravenous, intramuscular, and subcutaneous injection. Patient Prefer Adherence 9, 923–942 (2015)
E. Larrañeta, M.T. McCrudden, A.J. Courtenay, R.F. Donnelly, Microneedles: A new frontier in Nanomedicine delivery. Pharm. Res. 33, 1055–1073 (2016)
M. Milewski, K. Manser, B.P. Nissley, A. Mitra, Analysis of the absorption kinetics of macromolecules following intradermal and subcutaneous administration. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 89, 134–144 (2015)
K. Ita, Transdermal delivery of drugs with microneedles-potential and challenges. Pharmaceutics 7, 90–105 (2015)
A.K. Banga, Microporation applications for enhancing drug delivery. Expert Opin. Drug Deliv. 6, 343–354 (2009)
S.H. Bariya, M.C. Gohel, T.A. Mehta, O.P. Sharma, Microneedles: an emerging transdermal drug delivery system. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 64, 11–29 (2012)
J. Vandervoort, A. Ludwig, Microneedles for transdermal drug delivery: A minireview. Front. Biosci. 13, 1711–1715 (2008)
A. S. Determan, O. R. Johnson, J. T. Moseman, R. T. Woldt, K. J. Hansen, Aqueous formulations for coating microneedle array, U.S. Patent 9,693,950 (2011)
Y. Chen, B.Z. Chen, Q.L. Wang, X. Jin, X.D. Guo, Fabrication of coated polymer microneedles for transdermal drug delivery. J. Control. Release 265, 14–21 (2017)
H.S. Gill, M.R. Prausnitz, Coated microneedles for transdermal delivery. J. Control. Release 117, 227–237 (2007)
S.J. Kim, J.H. Shin, J.Y. Noh, C.S. Song, Y.C. Kim, Development of the novel coating formulations for skin vaccination using stainless steel microneedle. Drug Deliv. Transl. Res. 6, 486–497 (2016)
Y. Ma, H.S. Gill, Coating solid dispersions on microneedles via a molten dip-coating method: Development and in vitro evaluation for transdermal delivery of a water-insoluble drug. J. Pharm. Sci. 103, 3621–3630 (2014)
M. Ameri, S.C. Fan, Y.F. Maa, Parathyroid hormone PTH(1-34) formulation that enables uniform coating on a novel transdermal microprojection delivery system. Pharm. Res. 27, 303–313 (2010a)
M. Ameri, X. Wang, Y.F. Maa, Effect of irradiation on parathyroid hormone PTH(1-34) coated on a novel transdermal microprojection delivery system to produce a sterile product--adhesive compatibility. J. Pharm. Sci. 99, 2123–2134 (2010b)
A. Vrdoljak, M.G. McGrath, J.B. Carey, S.J. Draper, A.V. Hill, C. O'Mahony, A.M. Crean, A.C. Moore, Coated microneedle arrays for transcutaneous delivery of live virus vaccines. J. Control Release 159, 34–42 (2012)
P.R. Johnson, M.R. Emery, J.T. Wolter, J.E. Raeder-Devens, D.C. Duan, M.M. David, H. Choi, Masking method for coating a microneedle array. U. S. Patent 7, 846,488 (2005)
S. Tokumoto, T. Matsudo, T. Kuwahara, Method of coating microneedle. U. S. Patent 8, 771,781 (2007)
R. Haj-Ahmad, H. Khan, M.S. Arshad, M. Rasekh, A. Hussain, S. Walsh, X. Li, M.W. Chang, Z. Ahmad, Microneedle coating techniques for transdermal drug delivery. Pharmaceutics 7, 486–502 (2015)
R. Ingrole, H. Gill, Microneedle Coating Methods: A Review with a Perspective, the Journal of Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics, 371 (2019)
Y. Zhang, K. Brown, K. Siebenaler, A. Determan, D. Dohmeier, K. Hansen, Development of lidocaine-coated microneedle product for rapid, safe, and prolonged local analgesic action. Pharm. Res. 29, 170–177 (2012a)
Y. Zhang, K. Siebenaler, K. Brown, D. Dohmeier, K. Hansen, Adjuvants to prolong the local anesthetic effects of coated microneedle products. Int. J. Pharm. 439, 187–192 (2012b)
J. Zhang, X. Mao, W. Xu, Fibril nucleation kinetics of a pharmaceutical peptide: The role of conformation stability, formulation factors and temperature effect. Mol. Pharm. 15, 5591–5601 (2018)
A.J. Harvey, S.A. Kaestner, D.E. Sutter, N.G. Harvey, J.A. Mikszta, R.J. Pettis, Microneedle-based intradermal delivery enables rapid lymphatic uptake and distribution of protein drugs. Pharm. Res. 1, 107–116 (2012)
Acknowledgements
We would like to thank Henry Wu, Preclinical Development at Merck & Co., Inc., Kenilworth, NJ, USA, for his insightful comments and guidance in this work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 114 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kapoor, Y., Milewski, M., Dick, L. et al. Coated microneedles for transdermal delivery of a potent pharmaceutical peptide. Biomed Microdevices 22, 7 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10544-019-0462-1
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10544-019-0462-1