Abstract
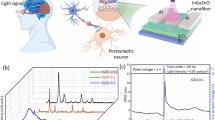
This article reports on the development, i.e., the design, fabrication, and validation of an implantable optical neural probes designed for in vivo experiments relying on optogenetics. The probes comprise an array of ten bare light-emitting diode (LED) chips emitting at a wavelength of 460 nm and integrated along a flexible polyimide-based substrate stiffened using a micromachined ladder-like silicon structure. The resulting mechanical stiffness of the slender, 250-μm-wide, 65-μm-thick, and 5- and 8-mm-long probe shank facilitates its implantation into neural tissue. The LEDs are encapsulated by a fluropolymer coating protecting the implant against the physiological conditions in the brain. The electrical interface to the external control unit is provided by 10-μm-thick, highly flexible polyimide cables making the probes suitable for both acute and chronic in vivo experiments. Optical and electrical properties of the probes are reported, as well as their in vivo validation in acute optogenetic studies in transgenic mice. The depth-dependent optical stimulation of both excitatory and inhibitory neurons is demonstrated by altering the brain activity in the cortex and the thalamus. Local network responses elicited by 20-ms-long light pulses of different optical power (20 μW and 1 mW), as well as local modulation of single unit neuronal activity to 1-s-long light pulses with low optical intensity (17 μW) are presented. The ability to modulate neural activity makes these devices suitable for a broad variety of optogenetic experiments.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
A.P. Alivisatos, A.M. Andrews, E.S. Boyden, et al., ACS Nano 7, 1850 (2013)
M.T. Alt, E. Fiedler, L. Rudmann, J.S. Ordonez, P. Ruther, T. Stieglitz, Proc. IEEE 105, 101 (2017)
S. Ayub, M. Schwaerzle, O. Paul, and P. Ruther, in Procedia Eng. (Elsevier B.V., 2015), pp. 472–475.
S. Ayub, C. Gossler, M. Schwaerzle, E. Klein, O. Paul, U. T. Schwarz, and P. Ruther, in 29th IEEE Int. Conf. Micro Electro Mech. Syst. (IEEE, 2016), pp. 379–382
E.S. Boyden, F. Zhang, E. Bamberg, G. Nagel, K. Deisseroth, Nat. Neurosci. 8, 1263 (2005)
H. Cao, L. Gu, S.K. Mohanty, J.-C. Chiao, IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 60, 225 (2013)
F.H.C. Crick, Sci. Am. 241, 219 (1979)
L.J. Gentet, M. Avermann, F. Matyas, J.F. Staiger, C.C.H. Petersen, Neuron 65, 422 (2010)
C. Goßler, C. Bierbrauer, R. Moser, M. Kunzer, K. Holc, W. Pletschen, K. Köhler, J. Wagner, M. Schwaerzle, P. Ruther, O. Paul, J. Neef, D. Keppeler, G. Hoch, T. Moser, U.T. Schwarz, J. Phys. D. Appl. Phys. 47, 205401 (2014)
V. Gradinaru, F. Zhang, C. Ramakrishnan, J. Mattis, R. Prakash, I. Diester, I. Goshen, K.R. Thompson, K. Deisseroth, Cell 141, 154 (2010)
M.M. Halassa, J.H. Siegle, J.T. Ritt, J.T. Ting, G. Feng, C.I. Moore, Nat. Neurosci. 14, 1118 (2011)
T. Hanson, N. Fitzsimmons, and J. O’Doherty, in Methods Neural Ensemble Rec., 2nd ed. (CRC Press, 2007), pp. 47–55.
K.D. Harris, D.A. Henze, J. Csicsvari, H. Hirase, G. Buzsáki, J. Neurophysiol. 84, 401 (2000)
S. Herwik, S. Kisban, A.A.A. Aarts, K. Seidl, G. Girardeau, K. Benchenane, M.B. Zugaro, S.I. Wiener, O. Paul, H.P. Neves, P. Ruther, J. Micromech. Microeng. 19, 74008 (2009)
S. Herwik, O. Paul, P. Ruther, J. Microelectromech. Syst. 20, 791 (2011)
K. Kampasi, E. Stark, J. Seymour, K. Na, H.G. Winful, G. Buzsáki, K.D. Wise, E. Yoon, Sci. Rep. 6, 30961 (2016)
T.-i. Kim, J.G. McCall, Y.H. Jung, X. Huang, E.R. Siuda, Y. Li, J. Song, Y.M. Song, H.A. Pao, R.-H. Kim, C. Lu, S.D. Lee, I.-S. Song, G. Shin, R. Al-Hasani, S. Kim, M.P. Tan, Y. Huang, F.G. Omenetto, J.A. Rogers, M.R. Bruchas, Science 340(80), 211 (2013)
S. Kisban, J. Kenntner, P. Janssen, R. V. Metzen, S. Herwik, U. Bartsch, T. Stieglitz, O. Paul, and P. Ruther, in IFMBE Proc. (2009), pp. 107–110.
G. Nagel, T. Szellas, W. Huhn, S. Kateriya, N. Adeishvili, P. Berthold, D. Ollig, P. Hegemann, E. Bamberg, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 100, 13940 (2003)
G.T. Neske, Front. Neural Circuits 9, 88 (2016)
HyungDal Park, Hyun-Joon Shin, Il-Joo Cho, Eui-sung Yoon, J.-K. F. Suh, Maesoon Im, Euisik Yoon, Yong-Jun Kim, and Jinseok Kim, in Annual Int. Conf. IEEE Eng. Med. Biol. Soc. (IEEE, 2011), pp. 2961–2964.
G. Paxinos and K. B. J. Franklin, The Mouse Brain in Stereotaxic Coordinates, 2nd ed. (Academic Press, 2001).
F. Pisanello, L. Sileo, I.A. Oldenburg, M. Pisanello, L. Martiradonna, J.A. Assad, B.L. Sabatini, M. De Vittorio, Neuron 82, 1245 (2014)
S. Ramaswamy, H. Markram, Front. Cell. Neurosci. 9, 233 (2015)
R. Raz, M. Schwaerzle, O. Paul, and P. Ruther, in Optogen B. Abstr. (2016), p. 50.
P. Ruther, O. Paul, Curr. Opin. Neurobiol. 32, 31 (2015)
R. Scharf, T. Tsunematsu, N. McAlinden, M.D. Dawson, S. Sakata, K. Mathieson, Sci. Rep. 6, 28381 (2016)
M. Schwaerzle, P. Elmlinger, O. Paul, and P. Ruther, in 28th IEEE Int. Conf. Micro Electro Mech. Syst. (IEEE, 2015), pp. 162–165.
M. Schwaerzle, O. Paul, and P. Ruther, J. Micromech. Microeng. 27, 65004 (2017)
T. Stieglitz, M. Schuetter, K.P. Koch, IEEE Eng. Med. Biol. Mag. 24, 58 (2005)
M. Wiest, J. Meloy, and E. Thomson, in Methods Neural Ensemble Rec., 2nd ed. (CRC Press, 2007), pp. 97–124.
K. D. Wise, A. M. Sodagar, Ying Yao, M. N. Gulari, G. E. Perlin, and K. Najafi, Proc. IEEE 96, 1184 (2008).
F. Wu, E. Stark, P.-C. Ku, K.D. Wise, G. Buzsáki, E. Yoon, Neuron 88, 1136 (2015)
O. Yizhar, L.E. Fenno, T.J. Davidson, M. Mogri, K. Deisseroth, Neuron 71, 9 (2011)
F. Zhang, L.-P. Wang, M. Brauner, J.F. Liewald, K. Kay, N. Watzke, P.G. Wood, E. Bamberg, G. Nagel, A. Gottschalk, K. Deisseroth, Nature 446, 633 (2007)
Acknowledgements
The research leading to these results received funding from the European Union’s 7th Framework Program (FP7/2007-2013) under grant agreement n°600925 (NeuroSeeker), the BrainLinks-BrainTools Cluster of Excellence funded by the German Research Foundation (DFG, grant no. EXC 1086), and the Hungarian Brain Research Program (Grant Nos. KTIA-13-NAP-A-IV/1-4,6).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ayub, S., Gentet, L.J., Fiáth, R. et al. Hybrid intracerebral probe with integrated bare LED chips for optogenetic studies. Biomed Microdevices 19, 49 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10544-017-0190-3
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10544-017-0190-3