Abstract
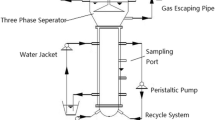
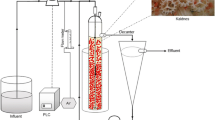
The influence of pH shocks on the trace metal dynamics and performance of methanol fed upflow anaerobic granular sludge bed (UASB) reactors was investigated. For this purpose, two UASB reactors were operated with metal pre-loaded granular sludge (1mM Co, Ni and Fe; 30°C; 96h) at an organic loading rate (OLR) of 5gCOD l reactor−1d−1. One UASB reactor (R1) was inoculated with sludge that originated from a full scale reactor treating alcohol distillery wastewater, while the other reactor (R2) was inoculated with sludge from a full scale reactor treating paper mill wastewater. A 30h pH shock (pH 5) strongly affected the metal retention dynamics within the granular sludge bed in both reactors. Iron losses in soluble form with the effluent were considerable: 2.3 and 2.9% for R1 and R2, respectively, based on initial iron content in the reactors, while losses of cobalt and nickel in soluble form were limited. Sequential extraction of the metals from the sludge showed that cobalt, nickel, iron and sulfur were translocated from the residual to the organic/sulfide fraction during the pH shock in R2, increasing 34, 47, 109 and 41% in the organic/sulfide fraction, respectively. This is likely due to the modification of the iron sulfide precipitate stability, which influences the extractability of iron and trace metals. Such a translocation was not observed for the R1 sludge during the first 30h pH shock, but a second 4day pH shock induced significant losses of cobalt (18%), iron (29%) and sulfur (29%) from the organic/sulfide fraction, likely due to iron sulfide dissolution and concomitant release of cobalt. After the 30h pH shock, VFA accumulated in the R2 effluent, whereas both VFA and methanol accumulated in R1 after the 4day pH shock. The formed VFA, mainly acetate, were not converted to methane due to the loss of methanogenic activity of the sludge on acetate. The VFA accumulation gradually disappeared, which is likely to be related to out-competition of acetogens by methanogens. Zinc, copper and manganese supply did not have a clear effect on the acetate removal and methanol conversion, but zinc may have induced the onset of methanol degradation after day 152 in R1.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alloway BJ (1990) Heavy Metals in Soils, 1st edn. (pp 7–27). Chapman and Hall.
InstitutionalAuthorNameAmerican Public Health Association (1985) Standard Methods for Examination of Water and Wastewater EditionNumber16 American Public Health Association Washington DC
A Anderko PJ Shuler (1997) ArticleTitleA computational approach to predicting the formation of iron sulfide species using stability diagrams Comp. Geosci. 23 647–658
G Billon B Oudane J Laureyns A Boughriet (2001) ArticleTitleChemistry of metal sulfides in anoxic sediments Phys. Chem. 3 3586–3592
DR Boone JAGF Menaia JE Boone RA Mah (1987) ArticleTitleEffects of hydrogen pressure during growth and effects of pregrowth with hydrogen on acetate degradation by Methanosarcina species Apl. Env. Microbiol. 53 83–87
L Florencio JA Field G Lettinga (1994) ArticleTitleThe importance of Cobalt for the individual trophic groups in an anaerobic methanol degrading consortium Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 60 227–234
G Gonzalez-Gil R Kleerebezem A van Aelst Zoutberg AI Versprille G. Lettinga (1999) ArticleTitleToxicity effects from formaldehyde on methanol degrading on methanol degrading sludge and its anaerobic conversion in biobed expanded granular sludge (EGSB) reactors Wat. Sci. Technol. 40 195–202
ED Hullebusch Particlevan MH Zandvoort PNL Lens (2003) ArticleTitleMetal immobilisation by biofilms: mechanisms and analytical tools Re/Views in Environ. Sci. Bio/tech. 2 9–33
T Jong DL Parry (2004) ArticleTitleHeavy metal speciation in solid-phase materials from a bacterial sulfate reducing bioreactor using sequential extraction procedure combined with acid volatile sulfide analyses J. Environ. Monit. 6 278–285
Lee van der J. CHESS (2000) updated for version 2.5, Technical report, LHM/RD/13, école des Mines de Paris, Fontainbleau, France
PNL Lens de D Beer CCH Cronenberg FP Houwen SPP Ottengraf WH Verstraee (1993) ArticleTitleHeterogeneous distribution of microbial activity in methanogenic aggregates: pH and Glucose microprophiles Appl.Environ. Microbiol. 59 3803–3815
G Lettinga AT Geest Particlevander S Hobma J Laan Particlevan der (1979) ArticleTitleAnaerobic treatment of methanolic wastes Water Res. 13 725–737
A Maes M Vanthuyne P Cauwenberg B Engels (2003) ArticleTitleMetal partitioning in a sulfidic canal sediment: metal solubility as a function of pH combined with EDTA extraction in anoxic conditions Sci. Total Env. 312 181–193
TK Mazumder N Nishio S Fukazaki S Nagai (1987) ArticleTitleProduction of extracellular vitamin B12 compounds from methanol by Methanosarcina barkeri Appl. Microbiol. Biotech. 26 511–516
DP Modak KP Singh H Chandra PK Ray (1992) ArticleTitleMobile and bound forms of trace metals in sediments of the lower Ganges Water Res. 26 1541–1548
JW Morse GW Luther (1999) ArticleTitleChemical influences on trace element sulfide interactions in anoxic sediments Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta. 63 3373–3378
K Sauer R Thauer (2000) ArticleTitleMethyl-coenzyme M formation in methanogenic archaea; involvement of zinc in coenzyme M activation Eur. J. Biochem. 267 2498–2504
MR Smith RA Mah (1978) ArticleTitleGrowth and methanogenesis by Methanosarcina strain 227 on acetate and methanol. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 36 870–879
A Tessier PGC Campbell M Bisson (1979) ArticleTitleSequential extraction procedure for the speciation of particulate trace metals Anal. Chem. 51 844–851
A Veeken (1998) Removal of heavy metals from biowaste. Department of Environmental Technology Wageningen University, The Netherlands
JHP Watson DC Ellwood Q Deng S Mikhalovsky CE Hayter J Evans (1995) ArticleTitleHeavy metal adsorption on bacterially produced FeS Miner. Eng. 8 1097–1108
J Weijma AJM Stams Pol LW Hulshoff G Lettinga (2000) ArticleTitleThermophilic sulfate reduction and methanogenesis with methanol in a high-rate anaerobic reactor Biotechnol. Bioeng. 67 354–363
MH Zandvoort MB Osuna R Geerts G Lettinga P Lens (2002) ArticleTitleEffect of nickel deprivation on methanol degradation in a methanogenic granular sludge reactor J. Ind. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 29 268–274
MH Zandvoort R Geerts G Lettinga PNL Lens (2003) ArticleTitleMethanol degradation in granular sludge reactors at sub-optimal metal concentrations: role of iron, nickel and cobalt Enzyme Microb. Technol. 33 190–198
MH Zandvoort J Gieteling G Lettinga PNL Lens (2004) ArticleTitleStimulation of methanol degradation in UASB reactors: in situ versus pre-loading cobalt on anaerobic granular sludge Biotechnol. Bioeng. 87 897–904
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zandvoort, M.H., van Hullebusch, E.D., Peerbolte, A. et al. Influence of pH shocks on trace metal dynamics and performance of methanol fed granular sludge bioreactors. Biodegradation 16, 549–567 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10532-004-7789-9
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10532-004-7789-9