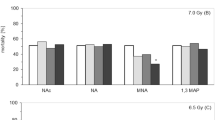
We studied the effect of human lactoferrin on cells of the hippocampal dentate gyrus of 2-2.5-month-old male C57BL/6 mice after acute gamma irradiation of the head in a dose of 8 Gy from a 60Co source. Immediately after irradiation some animals received an intraperitoneal injection of human lactoferrin (4 mg/mouse). The appearance of TUNEL+ cells in the subgranular zone 6 h after irradiation was accompanied by a corresponding decrease in the number of Ki-67- and DCX-immunoreactive cells. Administration of lactoferrin had a protective effect on mouse brain cells, which manifested in a decrease in the number of TUNEL+ cells (by 77% relative to the irradiation alone) and an increase in the number of proliferating cells (from 16 to 61% relative to control animals) and immature neurons (from 14 to 22% relative to control animals) in the dentate gyrus of the hippocampus.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Raber J, Rola R, LeFevour A, Morhardt D, Curley J, Mizumatsu S, VandenBerg SR, Fike JR. Radiation-induced cognitive impairments are associated with changes in indicators of hippocampal neurogenesis. Radiat. Res. 2004;162(1):39-47. doi: https://doi.org/10.1667/rr3206
Balentova S, Adamkov M. Molecular, cellular and functional effects of radiation-induced brain injury: a review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2015;16(11):27 796-27 815. doi: https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms161126068
Nishimura Y, Homma-Takeda S, Kim HS, Kakuta I. Radioprotection of mice by lactoferrin against irradiation with sublethal X-rays. J. Radiat. Res. 2014;55(2):277-282. doi: https://doi.org/10.1093/jrr/rrt117
Kopaeva MY, Alchinova IB, Cherepov AB, Demorzhi MS, Nesterenko MV, Zarayskaya IY, Karganov MY. New properties of a well-known antioxidant: pleiotropic effects of human lactoferrin in mice exposed to gamma irradiation in a sublethal dose. Antioxidants (Basel). 2022;11(9):1833. doi: https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox11091833
Xu SF, Zhang YH, Wang S, Pang ZQ, Fan YG, Li JY, Wang ZY, Guo C. Lactoferrin ameliorates dopaminergic neurodegeneration and motor deficits in MPTP-treated mice. Redox Biol. 2019;21:101090. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.redox.2018.101090
Kopaeva MY, Cherepov AB, Nesterenko MV, Zarayskaya IY. Pretreatment with human lactoferrin had a positive effect on the dynamics of mouse nigrostriatal system recovery after acute MPTP exposure. Biology (Basel). 2021;10(1):24. doi: https://doi.org/10.3390/biology10010024
Chen Y, Zheng Z, Zhu X, Shi Y, Tian D, Zhao F, Liu N, Hüppi PS, Troy FA 2nd, Wang B. Lactoferrin promotes early neurodevelopment and cognition in postnatal piglets by upregulating the BDNF signaling pathway and polysialylation. Mol. Neurobiol. 2015;52(1):256-269. doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-014-8856-9
Kopaeva MY, Azieva AM, Cherepov AB, Zarayskaya IY. Lactoferrin modulates induction of transcription factor c-Fos in neuronal cultures. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023;24(9):8373. doi: https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24098373
Franklin KBJ, Paxinos G. The mouse brain in stereotaxic coordinates, 3rd ed. San Diego, 2008.
Jackson SP, Bartek J. The DNA-damage response in human biology and disease. Nature. 2009;461:1071-1078. doi: https://doi.org/10.1038/nature08467
Sasaki R, Matsumoto A, Itoh K, Kawabe T, Ota Y, Yamada K, Maruta T, Soejima T, Sugimura K. Target cells of apoptosis in the adult murine dentate gyrus and O4 immunoreactivity after ionizing radiation. Neurosci. Lett. 2000;279(1):57-60. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/s0304-3940(99)00910-6
Mizumatsu S, Monje ML, Morhardt DR, Rola R, Palmer TD, Fike JR. Extreme sensitivity of adult neurogenesis to low doses of X-irradiation. Cancer Res. 2003;63(14):4021-4027.
Tada E, Parent JM, Lowenstein DH, Fike JR. X-irradiation causes a prolonged reduction in cell proliferation in the dentate gyrus of adult rats. Neuroscience. 2000;99(1):33-41. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/s0306-4522(00)00151-2
Abbott LC, Nigussie F. Adult neurogenesis in the mammalian dentate gyrus. Anat. Histol. Embryol. 2020;49(1):3-16. doi: https://doi.org/10.1111/ahe.12496
Ribeiro FF, Xapelli S. An Overview of adult neurogenesis. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2021;1331:77-94. doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-74046-7_7
Kee N, Sivalingam S, Boonstra R, Wojtowicz JM. The utility of Ki-67 and BrdU as proliferative markers of adult neurogenesis. J. Neurosci. Methods. 2002;115(1):97-105. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/s0165-0270(02)00007-9
Nacher J, Crespo C, McEwen BS. Doublecortin expression in the adult rat telencephalon. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2001;14(4):629-644. doi: https://doi.org/10.1046/j.0953-816x.2001.01683.x
Peissner W, Kocher M, Treuer H, Gillardon F. Ionizing radiation-induced apoptosis of proliferating stem cells in the dentate gyrus of the adult rat hippocampus. Brain Res. Mol. Brain Res. 1999;71(1):61-68. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/s0169-328x(99)00170-9
Seed TM. Radiation protectants: current status and future prospects. Health Phys. 2005;89(5):531-545. doi: https://doi.org/10.1097/01.hp.0000175153.19745.25
Reisz JA, Bansal N, Qian J, Zhao W, Furdui CM. Effects of ionizing radiation on biological molecules — mechanisms of damage and emerging methods of detection. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2014;21(2):260-292. doi: https://doi.org/10.1089/ars.2013.5489
Li YQ, Guo C. A review on lactoferrin and central nervous system diseases. Cells. 2021;10(7):1810. doi: https://doi.org/10.3390/cells10071810
Trentini A, Maritati M, Rosta V, Cervellati C, Manfrinato MC, Hanau S, Greco P, Bonaccorsi G, Bellini T, Contini C. Vaginal lactoferrin administration decreases oxidative stress in the amniotic fluid of pregnant women: an open-label randomized pilot study. Front. Med. (Lausanne). 2020;7:555. doi: https://doi.org/10.3389/fmed.2020.00555
Ikoma-Seki K, Nakamura K, Morishita S, Ono T, Sugiyama K, Nishino H, Hirano H, Murakoshi M. Role of LRP1 and ERK and cAMP signaling pathways in lactoferrin-induced lipolysis in mature rat adipocytes. PLoS One. 2015;10(10):e0141378. doi: https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0141378
Suzuki YA, Lopez V, Lönnerdal B. Mammalian lactoferrin receptors: structure and function. Cell Mol. Life Sci. 2005;62(22):2560-2575. doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-005-5371-1
Huang R, Ke W, Han L, Liu Y, Shao K, Jiang C, Pei Y. Lactoferrin-modified nanoparticles could mediate efficient gene delivery to the brain in vivo. Brain Res. Bull. 2010;81(6):600-604. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.brainresbull.2009.12.008
Kopaeva Y, Cherepov AB, Zarayskaya IY, Nesterenko MV. Transport of human lactoferrin into mouse brain: administration routes and distribution. Bull. Exp. Biol. Med. 2019;167(4):561-567. doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10517-019-04572-3
Ashida K, Sasaki H, Suzuki YA, Lönnerdal B. Cellular internalization of lactoferrin in intestinal epithelial cells. Biometals. 2004;17(3):311-315. doi: https://doi.org/10.1023/b:biom.0000027710.13543.3f
Liao Y, Lopez V, Shafizadeh TB, Halsted CH, Lönnerdal B. Cloning of a pig homologue of the human lactoferrin receptor: expression and localization during intestinal maturation in piglets. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. A Mol. Integr. Physiol. 2007;148(3):584-590. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cbpa.2007.08.001
Jiang R, Lopez V, Kelleher SL, Lönnerdal B. Apo- and holo-lactoferrin are both internalized by lactoferrin receptor via clathrin-mediated endocytosis but differentially affect ERK-signaling and cell proliferation in Caco-2 cells. J. Cell. Physiol. 2011;226(11):3022-3031. doi: https://doi.org/10.1002/jcp.22650
Kopaeva MYu, Alchinova IB, Nesterenko MV, Cherepov AB, Zarayskaya IYu, Karganov MYu. Lactoferrin beneficially influences the recovery of physiological and behavioral indexes in mice exposed to acute gamma-irradiation. Patogenez. 2020;18(1):29-33. Russian. doi: https://doi.org/10.25557/2310-0435.2020.01.29-33
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Translated from Kletochnye Tekhnologii v Biologii i Meditsine, No. 3, pp. 161-168, September, 2023
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Kopaeva, M.Y., Cherepov, A.B. & Zaraiskaya, I.Y. Lactoferrin Has a Protective Effect on Mouse Brain Cells after Acute Gamma Irradiation of the Head. Bull Exp Biol Med 176, 246–252 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10517-024-06004-3
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10517-024-06004-3