Abstract
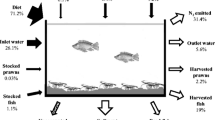
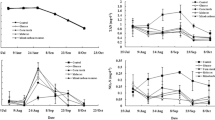
The effects of stocking density of tilapia Oreochromis niloticus with the inclusion of silver carp Hypophthalmichthys molitrix were evaluated in the C/N-CP prawn Macrobrachium rosenbergii farming system in triplicate. Management practices were same for all treatments. Bamboo side shoots were posted vertically into the pond bottoms as a periphyton substrate. A locally formulated and prepared feed containing 15.44% crude protein with a C/N ratio 15 were applied twice daily in all ponds. Maize flour was supplied in water for raising the C/N ratio 20 in all treatments. Water quality parameters, except transparency and chlorophyll a, did not differ significantly (P > 0.05) among the treatments. The periphytic abundance and biomass differed significantly (P < 0.05) among the treatments and even among different months. Although the individual harvesting weight, individual weight gain, and SGR were significantly higher (P < 0.05) in the T10000 treatment compared to T15000 and T20000 treatments, respectively, the gross and net yields of tilapia were significantly higher (P < 0.05) in the treatment T20000 followed by T15000 and T10000 treatments resulting in higher combined gross and net yield of both prawn and tilapia (16.05 and 16.92%, 32 and 33.59% from the later two treatments, respectively) with a higher economic return (BCR 0.53) during a 122-day culture period. As a whole, the study revealed that prawn, tilapia, and silver carp with a stocking density at 30,000, 20,000, and 1250 ha−1, respectively, was found to provide an optimum and sustainable production as well as economic benefit in the C/N-CP-based culture system.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahmed N, Lecouffe C, Allison EH, Muir JF (2009) The sustainable livelihoods approach to the development of freshwater prawn marketing systems in southwest Bangladesh. Aquac Econ Manag 13(3):246–269. https://doi.org/10.1080/13657300903156092
Ahmed N, Allison EH, Muir JF (2010) Rice fields to prawn farms: a blue revolution in southeast Bangladesh? Aquac Int 18(4):555–574. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10499-009-9276-0
Akand AM, Hasan MR (1992) Status of freshwater prawn (Macrobrachium spp.) culture in Bangladesh. In: Silas EG (ed) Freshwater prawns. Kerala Agricultural University, Thrissur, pp 33–41
Asaduzzaman M, Wahab MA, Verdegem MCJ, Haque S, Salam MA, Azim ME (2008) C/N ratio control and substrate addition for periphyton development jointly enhance freshwater prawn Macrobrachium rosenbergii production in ponds. Aquaculture 280(1-4):117–123. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquaculture.2008.04.019
Asaduzzaman M, Wahab MA, Verdegem MCJ, Mondal MN, Azim ME (2009a) Effects of stocking density of freshwater prawn Macrobrachium rosenbergii and addition of different levels of tilapia Oreochromis niloticus on production in C/N controlled periphyton based system. Aquaculture 286(1-2):72–79. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquaculture.2008.09.006
Asaduzzaman M, Wahab MA, Verdegem MCJ, Benerjee S, Akter T, Hasan MM, Azim ME (2009b) Effects of addition of tilapia Oreochromis niloticus and substrates for periphyton developments on pond ecology and production in C/N-controlled freshwater prawn Macrobrachium rosenbergii farming systems. Aquaculture 287(3-4):371–380. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquaculture.2008.11.011
Asaduzzaman M, Wahab MA, Verdegem MCJ, Adhikary RK, Rahman SMS, Azim ME, Verreth JAJ (2010) Effects of carbohydrate source for maintaining a high C:N ratio and fish driven re-suspension on pond ecology and production in periphyton-based freshwater prawn culture systems. Aquaculture 301(1-4):37–46. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquaculture.2010.01.025
Avnimelech Y (2007) Feeding with microbial flocs by tilapia in minimal discharge bio-flocs technology ponds. Aquaculture 264(1-4):140–147. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquaculture.2006.11.025
Azim ME (2001) The potentials of periphyton-based aquaculture production systems. Ph.D. dissertation, Institute of Animal Sciences (WIAS), Wageningen University, The Netherlands. 219 p
AzimM.E.&WahabM.A. (2005) Periphyton-based pond polyculture. In: Peiphyton, ecology, exploitation and management. (ed. by M.E. Azim, M.C.J. Verdegem, A.A. van Dam and M.C.J. Beveridge), pp. 207–222. CABI publishing, Wallingford
Azim ME, Verdegem MCJ, Rahman MM, Wahab MA, van Dam AA, Beveridge MCM (2002) Evaluation of polyculture with Indian major carps in periphyton-based pond. Aquaculture 213(1-4):131–149. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0044-8486(02)00029-7
Bowen SH (1982) Feeding digestion and growth qualitative considerations. In: Pullin RSV, Lowe-McConnel RH (eds) The biology and culture of tilapias, ICLARM Conference Proceedings 7, Manila. pp. 141–156
Boyd CE (1982) Water quality management for pond fish culture. Elsevier Sci. Publ. Co, Amsterdam 318 p
Boyd CE (1990) Water quality in ponds for aquaculture. Alabama Agricultural Experiment Station, Auburn University, Auburn 482 p
Boyd CE (1992) Water quality management for pond fish culture. Elsevier Science Publishers B. V., Amsterdam 318 p
Boyd CE (1998) Water quality for pond aquaculture. Research and development series no. 43. International center for aquaculture and aquatic environments, Alabama agricultural experiment station, Auburn University, Alabama
Cuvin-Aralar MLC (2003) Influence of three nitrogen: phosphorus ratios on growth and chemical composition of microalgae and its utilization by Nile tilapia, Oreochromisniloticus (L.). Verlag Grauer, Beuren 159 p
Dempster PW, Beveridge MCM, Baird DJ (1993) Herbivory in the tilapia Oreochromis niloticus: a comparison of feeding rates of phytoplankton and periphyton. J Fish Biol 43(3):385–392. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1095-8649.1993.tb00573.x
Dempster PW, Baird DJ, Beveridge MCM (1995) Can fish survive by filter-feeding on microparticles? Energy balance in tilapia grazing on algal suspensions. J Fish Biol 47:7–17
DoF (2011) National fish week (20–26 July). Department of Fisheries, Ministry of Fisheries and Livestock, Bangladesh 136 p
DoF (2013) Fishery statistical yearbook of Bangladesh 2011–2012. Ministry of Fisheries and Livestock, Dhaka
Garcia-Perez A, Alston DE, Cortes-Maldonado R (2000) Growth, survival, yield and size distributions of freshwater prawn Macrobrachium rosenbergii and tilapia Oreochromis niloticus in polyculture and monoculture systems in Puerto Rico. J World Aquacult Soc 31:446–451
Gomez KA, Gomez NE (1984) Statistical procedures for agricultural research, 2nd edn. John Wiley and Sons, New York 680 p
Haque MR, Islam MA, Rahman MM, Shirin MF, Wahab MA, Azim ME (2015) Effects of C/N ratio and periphyton substrates on pond ecology and production performance in giant freshwater prawn Macrobrachium rosenbergii (De Man, 1879) and tilapia Oreochromis niloticus (Linnaeus, 1758) polyculture system. Aquac Res 46(5):1139–1155. https://doi.org/10.1111/are.12270
Hari B, Kurup MB, Varghese JT, Sharma JW, Verdegem MCJ (2004) Effects of carbohydrate addition on production in extensive shrimp culture systems. Aquaculture 241(1-4):179–194. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquaculture.2004.07.002
Hepher B (1988) Nutrition of pond fishes. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, 388 p. https://doi.org/10.1017/CBO9780511735455
Hepher B, Pruginin Y (1981) Commercial fish farming—with special reference to fish culture in Israel. John Wiley and Sons, New York 261 p
Huchette SMH, Beveridge MCM, Ireland DJ (2000) The impacts of grazing by tilapias (Oreochromis niloticus L.) on periphyton communities growing on artificial substrate in cages. Aquaculture 186(1-2):45–60. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0044-8486(99)00365-8
Jiménez-Montealegre R, Verdegem M, Zamora JE, Verreth J (2002) Organic matter sedimentation and resuspension in tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) ponds during a production cycle. Aquac Eng 26(1):1–12. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0144-8609(01)00086-3
Khatrai TC (1984) Seasonal variation in the ecosystem of Lakhotia lake in Rajastan. India J Fish 3:122–129
Kunda M, Azim ME, Wahab MA, Dewan S, Roos N, Thilsted SH (2008) Potential of mixed culture of freshwater prawn (Macrobrachium rosenbergii) and self-recruiting small species mola (Amblypharyngodon mola) in rotational rice–fish/prawn culture systems in Bangladesh. Aquac Res 39(5):506–517. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2109.2008.01905.x
LoebS.L., ReuterJ.E.&GoldmanC.R. (1983) Littoral zone production of oligotrophic lakes—the contributions of phytoplankton and periphyton. In: Periphyton of freshwater ecosystems. Developments in hydrobiology, volume 17. (ed. by R.G. Wetzel), pp. 161-167. , Dr W. Junk publishers. The Hague
MacLean MH, Brown JH, Ang KJ, Jauncey K (1994) Effects of manure fertilization frequency on pond culture of the fresh water prawn, Macrobrachium rosenbergii (De Man). Aquac Fish Manag 25:601–611
Milstein A (1992) Ecological aspects of fish species interactions in polyculture ponds. Hydrobiologia 231(3):177–186. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00018201
Milstein A, Wahab MA, Rahman MM (2002) The effects of common carp, Cyprinus carpio (L.) and mrigal, Cirrhinus mirgala (Hamilton) as bottom feeders in major Indian carp polyculture. Aquac Res 33:547–556
Milstein A, Peretz Y, Harpaz S (2009) Culture of organic tilapia to market size in periphyton based ponds with reduced feed inputs. Aquac Res 40:55–59
New MB (2002) Farming freshwater prawn: a manual for the culture of giant river prawn (Macrobrachium rosenbergii). FAO Fisheries Technical Paper 428. FAO, Rome 212 p
New MB, Singholka S (1985) Freshwater prawn farming: a manual for the culture of Macrobrachium rosenbergii. FAO Fisheries Technical Paper, 225 (Rev 1). FAO, Rome
Perschbacher PW, Lorio WJ (1993) Filtration rates of catfish pond phytoplankton by Nile tilapia Oreochromis niloticus. J World Aquacult Soc 24(3):434–437. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1749-7345.1993.tb00177.x
Rahman SMS, Wahab MA, Islam MA, Kunda M, Azim ME (2010a) Effects of selective harvesting and claw ablation of all-male freshwater prawn (Macrobrachium rosenbergii) on water quality, production and economics in polyculture ponds. Aquac Res 41:404–417
Rahman SMS, Wahab MA, Kunda M, Islam MA, Azim ME (2010b) Density effects of silver carp Hypophthalmichthys molitrix and catla Catlacatla on the production system in all-male freshwater prawn–finfish polyculture ponds. Aquac Res 41:456–466
Ritvo G, Kochba M, Anvimelech Y (2004) The effects of common carp bioturbation on fishpond bottom soil. Aquaculture 242(1-4):345–356. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquaculture.2004.09.013
Shafi SM (2003) Applied fishery science. Published by Atlantic Publishers and Distributors, New Delhi-27, Volume 1, ISBN 81-269-0277-9, pp. 238–257
SheltonW.L.&PopmaT.J. (2006) Biology. In: Tilapia: biology, culture and nutrition. (ed. by C. Lim & C.D. Webster), pp. 1–49. Food Products Press, Binghamton
Smith DW (1989) The feeding selectivity of silver carp, Hypophthalmicthys molitrix. Val. J Fish Biol 34:819–828
TidwellJ.H.&BratvoldD. (2005) Utility of added substrates in shrimp culture. In: Periphyton: ecology, exploitation and management. (ed. by M.E Azim, M.C.J. Verdegem, A.A. van Dam & M.C.M. Beveridge), pp. 247–268. CABI Publishing, Wallingford
Uddin MS, Azim ME, Wahab MA, Verdegem MCJ (2006) The potential of mixed culture of genetically improved farmed tilapia (GIFT, Oreochromis niloticus) and freshwater prawn (Macrobrachium rosenbergii) in periphyton-based systems. Aquac Res 37(3):241–247. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2109.2005.01424.x
Vasquez OE, Rouse DB, Rogers WA (1989) Growth response of Macrobrachium rosenbergii to different level of hardness. J World Aquacult Soc 20(2):90–92. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1749-7345.1989.tb00528.x
Wahab MA, Ahmed ZF, Islam MA, Haq MS, Rahmatullah SM (1995) Effects of introduction of common carp, Cyprinus carpio (L), on the pond ecology and growth of fish in polyculture. Aquac Res 26(9):619–628. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2109.1995.tb00953.x
Wetzel RG, Likens GE (1991) Limnological analyses, 2nd edn. Spinger-verlag, New York. 391p. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4757-4098-1
Yasmin F, Hossain M, Islam MS, Rashid MHA (2010) Economics of fresh water prawn farming in southwest region of Bangladesh. Progress Agric 21:223–231
Acknowledgements
The authors are grateful to the field staff of Fisheries Field Laboratory, Bangladesh Agricultural University, Mymensingh, for their kind assistance during sampling and feeding of fishes and prawns.
Funding
This research was financially supported by the Ministry of Science and Technology, Bangladesh.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict on interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Haque, M.R., Islam, M.A., Khatun, Z. et al. Effects of stocking densities of tilapia Oreochromis niloticus (Linnaeus, 1758) with the inclusion of silver carp Hypophthalmichthys molitrix (Valenciennes, 1844) in C/N-CP prawn Macrobrachium rosenbergii (De Man, 1879) culture pond. Aquacult Int 26, 523–541 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10499-017-0229-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10499-017-0229-8