Abstract
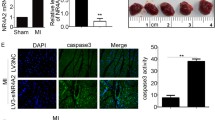
Activation of the Akt pathway has been shown to protect the heart from ischaemia/reperfusion (I/R) injury. NEDD4-1 has been shown to positively regulate nuclear trafficking of the activated form of Akt. However, the role of NEDD4-1 in cardiac I/R injury remains to be elucidated. In the present study, Lentiviral vectors were constructed to overexpress or knockdown NEDD4-1 in H9c2 cardiomyocytes subjected to I/R injury or ischemic preconditioning (IPC). The results indicated that NEDD4-1 levels were decreased after I/R and increased after IPC in rat heart tissue and in H9c2 cardiomyocytes. Overexpression of NEDD4-1 activated the Akt pathway and regulated apoptosis-related proteins in H9c2 cardiomyocytes, attenuating SI/R-induced cell apoptosis and caspase 3/7 activities. Furthermore, in vivo overexpression of NEDD4-1 attenuated myocardial apoptosis following myocardial I/R. Our results demonstrated that NEDD4-1 protects the myocardium from I/R induced apoptosis by activating PI3K/Akt signaling.





Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- DMEM:
-
Dulbecco’s modified Eagle’s medium
- FBS:
-
Fetal bovine serum
- IGF:
-
Insulin-like growth factor
- IPC:
-
Ischemic preconditioning
- I/R:
-
Ischaemia/reperfusion
- LCA:
-
Left coronary artery
- LDH:
-
Lactate dehydrogenase
- NEDD4-1:
-
Neural precursor cell expressed developmentally down-regulated 4-1
- PI:
-
Propidium iodide
- PI3K:
-
Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase
- PTEN:
-
Phosphatase and tensin homolog
- TUNEL:
-
Terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase (TdT)-mediated dUTP nick end labeling
References
Xiong J, Xue FS, Yuan YJ, Wang Q, Liao X, Wang WL (2010) Cholinergic anti-inflammatory pathway: a possible approach to protect against myocardial ischemia reperfusion injury. Chin Med J (Engl) 123:2720–2726
Hill JH, Ward PA (1971) The phlogistic role of C3 leukotactic fragments in myocardial infarcts of rats. J Exp Med 133:885–900
Pinckard RN, Olson MS, Giclas PC, Terry R, Boyer JT, O’Rourke RA (1975) Consumption of classical complement components by heart subcellular membranes in vitro and in patients after acute myocardial infarction. J Clin Invest 56:740–750
Rossen RD, Michael LH, Hawkins HK, Youker K, Dreyer WJ, Baughn RE et al (1994) Cardiolipin-protein complexes and initiation of complement activation after coronary artery occlusion. Circ Res 75:546–555
Vakeva AP, Agah A, Rollins SA, Matis LA, Li L, Stahl GL (1998) Myocardial infarction and apoptosis after myocardial ischemia and reperfusion: role of the terminal complement components and inhibition by anti-C5 therapy. Circulation 97:2259–2267
Yasojima K, Kilgore KS, Washington RA, Lucchesi BR, McGeer PL (1998) Complement gene expression by rabbit heart: upregulation by ischemia and reperfusion. Circ Res 82:1224–1230
Jolly SR, Kane WJ, Bailie MB, Abrams GD, Lucchesi BR (1984) Canine myocardial reperfusion injury. Its reduction by the combined administration of superoxide dismutase and catalase. Circ Res 54:277–285
Sack MN, Smith RM, Opie LH (2000) Tumor necrosis factor in myocardial hypertrophy and ischaemia–an anti-apoptotic perspective. Cardiovasc Res 45:688–695
Belosjorow S, Schulz R, Dorge H, Schade FU, Heusch G (1999) Endotoxin and ischemic preconditioning: TNF-alpha concentration and myocardial infarct development in rabbits. Am J Physiol 277:H2470–H2475
Jolly SR, Kane WJ, Hook BG, Abrams GD, Kunkel SL, Lucchesi BR (1986) Reduction of myocardial infarct size by neutrophil depletion: effect of duration of occlusion. Am Heart J 112:682–690
Litt MR, Jeremy RW, Weisman HF, Winkelstein JA, Becker LC (1989) Neutrophil depletion limited to reperfusion reduces myocardial infarct size after 90 min of ischemia. Evidence for neutrophil-mediated reperfusion injury. Circulation 80:1816–1827
Richard V, Murry CE, Reimer KA (1995) Healing of myocardial infarcts in dogs. Effects of late reperfusion. Circulation 92:1891–1901
Reimer KA, Vander Heide RS, Richard VJ (1993) Reperfusion in acute myocardial infarction: effect of timing and modulating factors in experimental models. Am J Cardiol 72:13G–21G
Jugdutt BI (1997) Effect of reperfusion on ventricular mass, topography, and function during healing of anterior infarction. Am J Physiol 272:H1205–H1211
Solomon A, Gersh B (1998) The open-artery hypothesis. Annu Rev Med 49:63–76
Frangogiannis NG, Mendoza LH, Lindsey ML, Ballantyne CM, Michael LH, Smith CW et al (2000) IL-10 is induced in the reperfused myocardium and may modulate the reaction to injury. J Immunol 165:2798–2808
Kajstura J, Cheng W, Reiss K, Clark WA, Sonnenblick EH, Krajewski S et al (1996) Apoptotic and necrotic myocyte cell deaths are independent contributing variables of infarct size in rats. Lab Invest 74:86–107
Fujio Y, Nguyen T, Wencker D, Kitsis RN, Walsh K (2000) Akt promotes survival of cardiomyocytes in vitro and protects against ischemia–reperfusion injury in mouse heart. Circulation 101:660–667
Wang X, Trotman LC, Koppie T, Alimonti A, Chen Z, Gao Z et al (2007) NEDD4-1 is a proto-oncogenic ubiquitin ligase for PTEN. Cell 128:129–139
Rotin D, Staub O, Haguenauer-Tsapis R (2000) Ubiquitination and endocytosis of plasma membrane proteins: role of Nedd4/Rsp5p family of ubiquitin-protein ligases. J Membr Biol 176:1–17
Ingham RJ, Gish G, Pawson T (2004) The Nedd4 family of E3 ubiquitin ligases: functional diversity within a common modular architecture. Oncogene 23:1972–1984
Staub O, Rotin D (2006) Role of ubiquitylation in cellular membrane transport. Physiol Rev 86:669–707
Staub O, Dho S, Henry P, Correa J, Ishikawa T, McGlade J et al (1996) WW domains of Nedd4 bind to the proline-rich PY motifs in the epithelial Na+ channel deleted in Liddle’s syndrome. EMBO J 15:2371–2380
Kanelis V, Rotin D, Forman-Kay JD (2001) Solution structure of a Nedd4 WW domain-ENaC peptide complex. Nat Struct Biol 8:407–412
Kanelis V, Bruce MC, Skrynnikov NR, Rotin D, Forman-Kay JD (2006) Structural determinants for high-affinity binding in a Nedd4 WW3* domain-Comm PY motif complex. Structure 14:543–553
Fouladkou F, Landry T, Kawabe H, Neeb A, Lu C, Brose N et al (2008) The ubiquitin ligase Nedd4-1 is dispensable for the regulation of PTEN stability and localization. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 105:8585–8590
Hsia HE, Kumar R, Luca R, Takeda M, Courchet J, Nakashima J et al (2014) Ubiquitin E3 ligase Nedd4-1 acts as a downstream target of PI3K/PTEN-mTORC1 signaling to promote neurite growth. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 111:13205–13210
Fan CD, Lum MA, Xu C, Black JD, Wang X (2013) Ubiquitin-dependent regulation of phospho-AKT dynamics by the ubiquitin E3 ligase, NEDD4-1, in the insulin-like growth factor-1 response. J Biol Chem 288:1674–1684
Fouladkou F, Lu C, Jiang C, Zhou L, She Y, Walls JR et al (2010) The ubiquitin ligase Nedd4-1 is required for heart development and is a suppressor of thrombospondin-1. J Biol Chem 285:6770–6780
Kim HK, Kang SW, Jeong SH, Kim N, Ko JH, Bang H et al (2012) Identification of potential target genes of cardioprotection against ischemia–reperfusion injury by express sequence tags analysis in rat hearts. J Cardiol 60:98–110
Meng XY, Yu HL, Zhang WC, Wang TH, Mai X, Liu HT et al (2014) ZFP580, a novel zinc-finger transcription factor, is involved in cardioprotection of intermittent high-altitude hypoxia against myocardial ischemia–reperfusion injury. PLoS One 9:e94635
Cantley LC (2002) The phosphoinositide 3-kinase pathway. Science 296:1655–1657
Kumar S, Tomooka Y, Noda M (1992) Identification of a set of genes with developmentally down-regulated expression in the mouse brain. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 185:1155–1161
Drinjakovic J, Jung H, Campbell DS, Strochlic L, Dwivedy A, Holt CE. E3 ligase Nedd4 promotes axon branching by downregulating PTEN. Neuron 65:341–357
Kawabe H, Neeb A, Dimova K, Young SM Jr, Takeda M, Katsurabayashi S et al (2010) Regulation of Rap2A by the ubiquitin ligase Nedd4-1 controls neurite development. Neuron 65:358–372
Bellet MM, Piobbico D, Bartoli D, Castelli M, Pieroni S, Brunacci C et al (2014) NEDD4 controls the expression of GUCD1, a protein upregulated in proliferating liver cells. Cell Cycle 13:1902–1911
Liu Y, Oppenheim RW, Sugiura Y, Lin W (2009) Abnormal development of the neuromuscular junction in Nedd4-deficient mice. Dev Biol 330:153–166
Amodio N, Scrima M, Palaia L, Salman AN, Quintiero A, Franco R et al (2010) Oncogenic role of the E3 ubiquitin ligase NEDD4-1, a PTEN negative regulator, in non-small-cell lung carcinomas. Am J Pathol 177:2622–2634
Kim SS, Yoo NJ, Jeong EG, Kim MS, Lee SH (2008) Expression of NEDD4-1, a PTEN regulator, in gastric and colorectal carcinomas. APMIS 116:779–784
Murry CE, Jennings RB, Reimer KA (1986) Preconditioning with ischemia: a delay of lethal cell injury in ischemic myocardium. Circulation 74:1124–1136
Kwak YD, Wang B, Li JJ, Wang R, Deng Q, Diao S et al (2012) Upregulation of the E3 ligase NEDD4-1 by oxidative stress degrades IGF-1 receptor protein in neurodegeneration. J Neurosci 32:10971–10981
Acknowledgements
W.H. designed the study, participated in data analysis, and wrote the article. P.Z. performed the experiments, participated in data analysis, and wrote the article. J.G., Q.Y., and D.Z. performed the experiments, data acquisition. This study was supported by the Shanghai Medical Key Specialty Construction Projects (Class A, No. ZK2012A24 and ZK2015A10), the Key Project from the Shanghai Municipal Commission of Health and Family Planning (No. 201640029), and the Min Hang District Science and Technology Committee (No. 2016MHZ70).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hu, W., Zhang, P., Gu, J. et al. NEDD4-1 protects against ischaemia/reperfusion-induced cardiomyocyte apoptosis via the PI3K/Akt pathway. Apoptosis 22, 437–448 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10495-016-1326-2
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10495-016-1326-2