Abstract
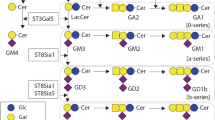
Gangliosides are a diverse group of sialic acid containing glycosphigolipids that are abundantly present in an outer plasma membrane of some cells. Biological roles of gangliosides and other lipids in cell fate regulation are being extensively studied. Gangliosides are well known to be involved in interactions between cells and in signal transduction to regulate growth, adhesion and motility. Moreover, many gangliosides are tumor-associated antigens over-expressed on several tumor types. As a result, monoclonal antibodies binding gangliosides can be used to diagnose, monitor and to treat cancer patients. In the review, we gather and discuss data of various research groups on direct cytotoxic effects elicited by several ganglioside-specific antibodies, which bind to GM2, N-acetyl-GM2, N-glycolyl-GM2, GM3, GD3, GD2, O-acetyl-GD2, without involvement of immunological mechanisms. Thus, in cultures of numerous human and mouse cancer cell lines, the antibodies were reported to cause morphological changes, aggregation and detachment of cells, inhibition of proliferation and cell death involving necrosis, apoptosis and oncosis-like mechanisms. Additionally, data on proteome alterations were reviewed that encompass, among others, changes in kinome (P38, JNK, c-MET, ERK1/2, PI3K, AKT, FAK, aurora A, B, C), protein levels of transcription factors (P53, MYCN, HSF1) and pro-apoptotic proteins (caspase 3, BAX). Next, we collected data on application of the antibodies to enhance cytotoxicity of chemotherapeutic drugs and small molecule inhibitors. Finally, further research perspectives on the topic are discussed.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Yu RK, Tsai YT, Ariga T, Yanagisawa M (2011) Structures, biosynthesis, and functions of gangliosides-an overview. J Oleo Sci 60:537–544
Tettamanti G (2004) Ganglioside/glycosphingolipid turnover: new concepts. Glycoconj J 20:301–317
Flangea C, Serb A, Sisu E, Zamfir AD (2011) Chip-based nanoelectrospray mass spectrometry of brain gangliosides. Biochim Biophys Acta 1811:513–535. doi:10.1016/j.bbalip.2011.06.008
Ghiulai RM, Sarbu M, Vukelić Ž, Ilie C, Zamfir AD (2014) Early stage fetal neocortex exhibits a complex ganglioside profile as revealed by high resolution tandem mass spectrometry. Glycoconj J 31:231–245
Willison HJ, Yuki N (2002) Peripheral neuropathies and anti-glycolipid antibodies. Brain 125:2591–2625
Ariga T, McDonald MP, Yu RK (2008) Role of ganglioside metabolism in the pathogenesis of Alzheimer’s disease—a review. J Lipid Res 49:1157–1175. doi:10.1194/jlr.R800007-JLR200
Sandhoff K, Harzer K (2013) Gangliosides and gangliosidoses: principles of molecular and metabolic pathogenesis. J Neurosci 33:10195–10208. doi:10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0822-13.2013
Ryan JM, Rice GE, Mitchell MD (2013) The role of gangliosides in brain development and the potential benefits of perinatal supplementation. Nutr Res 33:877–887. doi:10.1016/j.nutres.2013.07.021
Furukawa K, Ohmi Y, Ohkawa Y, Tokuda N, Kondo Y, Tajima O, Furukawa K (2011) Regulatory mechanisms of nervous systems with glycosphingolipids. Neurochem Res 36:1578–1586. doi:10.1007/s11064-011-0494-2
Ohmi Y, Tajima O, Ohkawa Y, Yamauchi Y, Sugiura Y, Furukawa K, Furukawa K (2011) Gangliosides are essential in the protection of inflammation and neurodegeneration via maintenance of lipid rafts: elucidation by a series of ganglioside-deficient mutant mice. J Neurochem 116:926–935. doi:10.1111/j.1471-4159.2010.07067.x
Prinetti A, Loberto N, Chigorno V, Sonnino S (2009) Glycosphingolipid behaviour in complex membranes. Biochim Biophys Acta 1788:184–193. doi:10.1016/j.bbamem.2008.09.001
Simons K, Gerl MJ (2010) Revitalizing membrane rafts: new tools and insights. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 11:688–699. doi:10.1038/nrm2977
Janich P, Corbeil D (2007) GM1 and GM3 gangliosides highlight distinct lipid microdomains within the apical domain of epithelial cells. FEBS Lett 581:1783–1787
Todeschini AR, Dos Santos JN, Handa K, Hakomori SI (2007) Ganglioside GM2-tetraspanin CD82 complex inhibits met and its cross-talk with integrins, providing a basis for control of cell motility through glycosynapse. J Biol Chem 282:8123–8133
Lopez PH, Schnaar RL (2009) Gangliosides in cell recognition and membrane protein regulation. Curr Opin Struct Biol 19:549–557. doi:10.1016/j.sbi.2009.06.001
Sorice M, Matarrese P, Tinari A, Giammarioli AM, Garofalo T, Manganelli V, Ciarlo L, Gambardella L, Maccari G, Botta M, Misasi R, Malorni W (2009) Raft component GD3 associates with tubulin following CD95/Fas ligation. FASEB J 23:3298–3308. doi:10.1096/fj.08-128140
Matarrese P, Garofalo T, Manganelli V, Gambardella L, Marconi M, Grasso M, Tinari A, Misasi R, Malorni W, Sorice M (2014) Evidence for the involvement of GD3 ganglioside in autophagosome formation and maturation. Autophagy 10:750–765. doi:10.4161/auto.27959
Todeschini AR, Hakomori SI (2008) Functional role of glycosphingolipids and gangliosides in control of cell adhesion, motility, and growth, through glycosynaptic microdomains. Biochim Biophys Acta 1780:421–433
Pukel CS, Lloyd KO, Travassos LR, Dippold WG, Oettgen HF, Old LJ (1982) GD3, a prominent ganglioside of human melanoma. Detection and characterisation by mouse monoclonal antibody. J Exp Med 155:1133–1147
Longee DC, Wikstrand CJ, Månsson JE, He X, Fuller GN, Bigner SH, Fredman P, Svennerholm L, Bigner DD (1991) Disialoganglioside GD2 in human neuroectodermal tumor cell lines and gliomas. Acta Neuropathol 82:45–54
Livingston PO, Hood C, Krug LM, Warren N, Kris MG, Brezicka T, Ragupathi G (2005) Selection of GM2, fucosyl GM1, globo H and polysialic acid as targets on small cell lung cancers for antibody mediated immunotherapy. Cancer Immunol Immunother 54:1018–1025
Kailayangiri S, Altvater B, Meltzer J, Pscherer S, Luecke A, Dierkes C, Titze U, Leuchte K, Landmeier S, Hotfilder M, Dirksen U, Hardes J, Gosheger G, Juergens H, Rossig C (2012) The ganglioside antigen G(D2) is surface-expressed in Ewing sarcoma and allows for MHC-independent immune targeting. Br J Cancer 106:1123–1133. doi:10.1038/bjc.2012.57
Marquina G, Waki H, Fernandez LE, Kon K, Carr A, Valiente O, Perez R, Ando S (1996) Gangliosides expressed in human breast cancer. Cancer Res 56:5165–5171
Alvarez-Rueda N, Desselle A, Cochonneau D, Chaumette T, Clemenceau B, Leprieur S, Bougras G, Supiot S, Mussini JM, Barbet J, Saba J, Paris F, Aubry J, Birklé S (2011) A monoclonal antibody to O-acetyl-GD2 ganglioside and not to GD2 shows potent anti-tumor activity without peripheral nervous system cross-reactivity. PLoS ONE 6:e25220. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0025220
Hettmer S, Ladisch S, Kaucic K (2005) Low complex ganglioside expression characterizes human neuroblastoma cell lines. Cancer Lett 225:141–149
Hettmer S, McCarter R, Ladisch S, Kaucic K (2004) Alterations in neuroblastoma ganglioside synthesis by induction of GD1b synthase by retinoic acid. Br J Cancer 91:389–397
Birklé S, Zeng G, Gao L, Yu RK, Aubry J (2003) Role of tumor-associated gangliosides in cancer progression. Biochimie 85:455–463
Shibuya H, Hamamura K, Hotta H, Matsumoto Y, Nishida Y, Hattori H, Furukawa K, Ueda M, Furukawa K (2012) Enhancement of malignant properties of human osteosarcoma cells with disialyl gangliosides GD2/GD3. Cancer Sci 103:1656–1664. doi:10.1111/j.1349-7006.2012.02344.x
Yan Q, Bach DQ, Gatla N, Sun P, Liu JW, Lu JY, Paller AS, Wang XQ (2013) Deacetylated GM3 promotes uPAR-associated membrane molecular complex to activate p38 MAPK in metastatic melanoma. Mol Cancer Res 11:665–675. doi:10.1158/1541-7786.MCR-12-0270-T
Lee HC, Wondimu A, Liu Y, Ma JS, Radoja S, Ladisch S (2012) Ganglioside inhibition of CD8+ T cell cytotoxicity: interference with lytic granule trafficking and exocytosis. J Immunol 189:3521–3527
Wondimu A, Liu Y, Su Y, Bobb D, Ma JS, Chakrabarti L, Radoja S, Ladisch S (2014) Gangliosides drive the tumor infiltration and function of myeloid-derived suppressor cells. Cancer Res 74:5449–5457. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-14-0927
Liu Y, Wondimu A, Yan S, Bobb D, Ladisch S (2014) Tumor gangliosides accelerate murine tumor angiogenesis. Angiogenesis 17:563–571. doi:10.1007/s10456-013-9403-4
Cheever MA, Allison JP, Ferris AS, Finn OJ, Hastings BM, Hecht TT, Mellman I, Prindiville SA, Viner JL, Weiner LM, Matrisian LM (2009) The prioritization of cancer antigens: a national cancer institute pilot project for the acceleration of translational research. Clin Cancer Res 15:5323–5337. doi:10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-09-0737
Ahmed M, Cheung NK (2014) Engineering anti-GD2 monoclonal antibodies for cancer immunotherapy. FEBS Lett 588:288–297. doi:10.1016/j.febslet.2013.11.030
Daniotti JL, Vilcaes AA, Torres Demichelis V, Ruggiero FM, Rodriguez-Walker M (2013) Glycosylation of glycolipids in cancer: basis for development of novel therapeutic approaches. Front Oncol 3:306. doi:10.3389/fonc.2013.00306
Vázquez AM, Rodrèguez-Zhurbenko N, López AM (2012) Anti-ganglioside anti-idiotypic vaccination: more than molecular mimicry. Front Oncol 2:170. doi:10.3389/fonc.2012.00170
Horwacik I, Rokita H (2012) Application of molecular mimicry to target GD2 ganglioside. In: Shimada H (ed) Neuroblastoma—present and future, InTech, Rijeka, pp. 251–271. doi: 10.5772/30020
Esser R, Müller T, Stefes D, Kloess S, Seidel D, Gillies SD, Aperlo-Iffland C, Huston JS, Uherek C, Schönfeld K, Tonn T, Huebener N, Lode HN, Koehl U, Wels WS (2012) NK cells engineered to express a GD2 -specific antigen receptor display built-in ADCC-like activity against tumour cells of neuroectodermal origin. J Cell Mol Med 16:569–581. doi:10.1111/j.1582-4934.2011.01343.x
Bjerkvig R, Engebraaten O, Laerum OD, Fredman P, Svennerholm L, Vrionis FD, Wikstrand CJ, Bigner DD (1991) Anti-GM2 monoclonal antibodies induce necrosis in GM2-rich cultures of a human glioma cell line. Cancer Res 51:4643–4648
Nakamura K, Hanibuchi M, Yano S, Tanaka Y, Fujino I, Inoue M, Takezawa T, Shitara K, Sone S, Hanai N (1999) Apoptosis induction of human lung cancer cell line in multicellular heterospheroids with humanized antiganglioside GM2 monoclonal antibody. Cancer Res 59:5323–5330
Roque-Navarro L, Chakrabandhu K, de León J, Rodríguez S, Toledo C, Carr A, de Acosta CM, Hueber AO, Pérez R (2008) Anti-ganglioside antibody-induced tumor cell death by loss of membrane integrity. Mol Cancer Ther 7:2033–2041. doi:10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-08-0222
Dippold WG, Knuth A, Meyer zum Büschenfelde KH (1984) Inhibition of human melanoma cell growth in vitro by monoclonal anti-GD3-ganglioside antibody. Cancer Res 44:806–810
Yoshida S, Fukumoto S, Kawaguchi H, Sato S, Ueda R, Furukawa K (2001) Ganglioside G(D2) in small cell lung cancer cell lines: enhancement of cell proliferation and mediation of apoptosis. Cancer Res 61(10):4244–4252
Kowalczyk A, Gil M, Horwacik I, Odrowaz Z, Kozbor D, Rokita H (2009) The GD2-specific 14G2a monoclonal antibody induces apoptosis and enhances cytotoxicity of chemotherapeutic drugs in IMR-32 human neuroblastoma cells. Cancer Lett 281:171–182. doi:10.1016/j.canlet.2009.02.040
Horwacik I, Durbas M, Boratyn E, Węgrzyn P, Rokita H (2013) Targeting GD2 ganglioside and aurora A kinase as a dual strategy leading to cell death in cultures of human neuroblastoma cells. Cancer Lett 341:248–264. doi:10.1016/j.canlet.2013.08.018
Cochonneau D, Terme M, Michaud A, Dorvillius M, Gautier N, Frikeche J, Alvarez-Rueda N, Bougras G, Aubry J, Paris F, Birklé S (2013) Cell cycle arrest and apoptosis induced by O-acetyl-GD2-specific monoclonal antibody 8B6 inhibits tumor growth in vitro and in vivo. Cancer Lett 333:194–204. doi:10.1016/j.canlet.2013.01.032
Hedberg KM, Dellheden B, Wikstrand CJ, Fredman P (2000) Monoclonal anti-GD3 antibodies selectively inhibit the proliferation of human malignant glioma cells in vitro. Glycoconj J 17:717–726
Liu B, Wu Y, Zhou Y, Peng D (2014) Endothelin A receptor antagonism enhances inhibitory effects of anti-ganglioside GD2 monoclonal antibody on invasiveness and viability of human osteosarcoma cells. PLoS ONE 9:e93576. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0093576
Retter MW, Johnson JC, Peckham DW, Bannink JE, Bangur CS, Dresser K, Cai F, Foy TM, Fanger NA, Fanger GR, Woda B, Rock KL (2005) Characterization of a proapoptotic antiganglioside GM2 monoclonal antibody and evaluation of its therapeutic effect on melanoma and small cell lung carcinoma xenografts. Cancer Res 65:6425–6434
Doronin II, Vishnyakova PA, Kholodenko IV, Ponomarev ED, Ryazantsev DY, Molotkovskaya IM, Kholodenko RV (2014) Ganglioside GD2 in reception and transduction of cell death signal in tumor cells. BMC Cancer. doi:10.1186/1471-2407-14-295
Aixinjueluo W, Furukawa K, Zhang Q, Hamamura K, Tokuda N, Yoshida S, Ueda R, Furukawa K (2005) Mechanisms for the apoptosis of small cell lung cancer cells induced by anti-GD2 monoclonal antibodies: roles of anoikis. J Biol Chem 280:29828–29836
Cazet A, Lefebvre J, Adriaenssens E, Julien S, Bobowski M, Grigoriadis A, Tutt A, Tulasne D, Le Bourhis X, Delannoy P (2010) GD3 synthase expression enhances proliferation and tumor growth of MDA-MB-231 breast cancer cells through c-Met activation. Mol Cancer Res 8:1526–1535. doi:10.1158/1541-7786.MCR-10-0302
Cazet A, Bobowski M, Rombouts Y, Lefebvre J, Steenackers A, Popa I, Guérardel Y, Le Bourhis X, Tulasne D, Delannoy P (2012) The ganglioside G(D2) induces the constitutive activation of c-Met in MDA-MB-231 breast cancer cells expressing the G(D3) synthase. Glycobiology 22:806–816. doi:10.1093/glycob/cws049
Rahmaniyan M, Qudeimat A, Kraveka JM (2012) Bioactive sphingolipids in neuroblastoma. In: Shimada H (ed) Neuroblastoma—present and future, InTech, Rijeka, pp.153–184. doi: 10.5772/27830
Hayashida N, Inouye S, Fujimoto M, Tanaka Y, Izu H, Takaki E, Ichikawa H, Rho J, Nakai A (2006) A novel HSF1-mediated death pathway that is suppressed by heat shock proteins. EMBO J 25:4773–4783
Yoshida S, Kawaguchi H, Sato S, Ueda R, Furukawa K (2002) An anti-GD2 monoclonal antibody enhances apoptotic effects of anti-cancer drugs against small cell lung cancer cells via JNK (c-Jun terminal kinase) activation. Jpn J Cancer Res 93:816–824
Houghton AN, Mintzer D, Cordon-Cardo C, Welt S, Fliegel B, Vadhan S, Carswell E, Melamed MR, Oettgen HF, Old LJ (1985) Mouse monoclonal IgG3 antibody detecting GD3 ganglioside: a phase I trial in patients with malignant melanoma. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 82:1242–1246
Uttenreuther-Fischer MM, Huang CS, Reisfeld RA, Yu AL (1995) Pharmacokinetics of anti-ganglioside GD2 mAb 14G2a in a phase I trial in pediatric cancer patients. Cancer Immunol Immunother 41:29–36
Kushner BH, Kramer K, Modak S, Cheung NK (2011) Successful multifold dose escalation of anti-GD2 monoclonal antibody 3F8 in patients with neuroblastoma: a phase I study. J Clin Oncol 29:1168–1174. doi:10.1200/JCO.2010.28.3317
Gilman AL, Ozkaynak MF, Matthay KK, Krailo M, Yu AL, Gan J, Sternberg A, Hank JA, Seeger R, Reaman GH, Sondel PM (2009) Phase I study of ch14.18 with granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor and interleukin-2 in children with neuroblastoma after autologous bone marrow transplantation or stem-cell rescue: a report from the Children’s Oncology Group. J Clin Oncol 27:85–91. doi:10.1200/JCO.2006.10.3564
Yu AL, Gilman AL, Ozkaynak MF, London WB, Kreissman SG, Chen HX, Smith M, Anderson B, Villablanca JG, Matthay KK, Shimada H, Grupp SA, Seeger R, Reynolds CP, Buxton A, Reisfeld RA, Gillies SD, Cohn SL, Maris JM, Sondel PM; Children’s Oncology Group (2010) Anti-GD2 antibody with GM-CSF, interleukin-2, and isotretinoin for neuroblastoma. N Engl J Med 363:1324–1334. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa0911123
Hernández AM, Rodríguez N, González JE, Reyes E, Rondón T, Griñán T, Macías A, Alfonso S, Vázquez AM, Pérez R (2011) Anti-NeuGcGM3 antibodies, actively elicited by idiotypic vaccination in nonsmall cell lung cancer patients, induce tumor cell death by an oncosis-like mechanism. J Immunol 186:3735–3744. doi:10.4049/jimmunol.1000609
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by Grants no.: NCN-2012/07/B/NZ1/02808 from the Polish National Science Center (HR) and DS/8/WBBiB. Faculty of Biochemistry, Biophysics and Biotechnology is a partner of the Leading National Research Center (KNOW) supported by the Ministry of Science and Higher Education.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Horwacik, I., Rokita, H. Targeting of tumor-associated gangliosides with antibodies affects signaling pathways and leads to cell death including apoptosis. Apoptosis 20, 679–688 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10495-015-1103-7
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10495-015-1103-7