Abstract
Glycogen synthase kinase-3β (GSK-3β) is involved in the pathogenesis of various kidney diseases. This study was undertaken to examine the changes in GSK-3β activity in podocytes under diabetic conditions and to elucidate the functional role of GSK-3β in podocyte apoptosis. In vivo, 32 rats were injected with either diluent (n = 16, C) or with streptozotocin intraperitoneally (n = 16, DM), and 8 rats from each group were treated with 6-bromoindirubin-3′-oxime (BIO) for 3 months. In vitro, immortalized mouse podocytes were exposed to 5.6 mM glucose or 30 mM glucose (HG) with or without 10 μM BIO. Western blot analysis and TUNEL or Hoechst 33342 staining were performed to identify apoptosis. Urinary albumin excretion was significantly higher in DM rats, and this increase was significantly abrogated in DM rats by BIO treatment. The protein expression of Tyr216-phospho-GSK-3β was significantly increased in DM glomeruli and in cultured podocytes exposed to HG. Western blot analysis revealed that the protein expression of Bax and active fragments of caspase-3 were significantly increased, whereas phospho-Akt, β-catenin, and Bcl-2 protein expression were significantly decreased in DM glomeruli and HG-stimulated podocytes. Apoptosis, determined by TUNEL assay and Hoechst 33342 staining, was also significantly increased in podocytes under diabetic conditions. The changes in the expression of apoptosis-related molecules and the increase in the number of apoptotic cells in DM glomeruli as well as in HG-stimulated podocytes were significantly ameliorated by BIO. These findings suggest that enhanced GSK-3β activity within podocytes under diabetic conditions is associated with podocyte loss in diabetic nephropathy.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Frame S, Cohen P (2001) GSK3 takes centre stage more than 20 years after its discovery. Biochem J 359:1–16
Woodgett JR (1990) Molecular cloning and expression of glycogen synthase kinase-3/factor A. EMBO J 9:2431–2438
Doble BW, Woodgett JR (2003) GSK-3: tricks of the trade for a multi-tasking kinase. J Cell Sci 116:1175–1186
Ferkey DM, Kimelman D (2000) GSK-3: new thoughts on an old enzyme. Dev Biol 225:471–479
Sinha D, Wang Z, Ruchalski KL, Levine JS, Krishnan S, Lieberthal W, Schwartz JH, Borkan SC (2005) Lithium activates the Wnt and phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase Akt signaling pathways to promote cell survival in the absence of soluble survival factors. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 288:F703–F713
Pap M, Cooper GM (2002) Role of translation initiation factor 2B in control of cell survival by the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/Akt/glycogen synthase kinase 3beta signaling pathway. Mol Cell Biol 22:578–586
Sanchez JF, Sniderhan LF, Williamson AL, Fan S, Chakraborty-Sett S, Maggirwar SB (2003) Glycogen synthase kinase 3beta-mediated apoptosis of primary cortical astrocytes involves inhibition of nuclear factor kappaB signaling. Mol Cell Biol 23:4649–4662
Jacobs KM, Bhave SR, Ferraro DJ, Jaboin JJ, Hallahan DE, Thotala D (2012) GSK-3beta: a bifunctional role in cell death pathways. Int J Cell Biol 2012:930710
Gong R, Rifai A, Ge Y, Chen S, Dworkin LD (2008) Hepatocyte growth factor suppresses proinflammatory NFkappaB activation through GSK3beta inactivation in renal tubular epithelial cells. J Biol Chem 283:7401–7410
Gong R, Rifai A, Dworkin LD (2005) Activation of PI3 K-Akt-GSK3beta pathway mediates hepatocyte growth factor inhibition of RANTES expression in renal tubular epithelial cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 330:27–33
Nelson PJ, Cantley L (2010) GSK3beta plays dirty in acute kidney injury. J Am Soc Nephrol 21:199–200
Ge Y, Si J, Tian L, Zhuang S, Dworkin LD, Gong R (2011) Conditional ablation of glycogen synthase kinase 3beta in postnatal mouse kidney. Lab Invest 91:85–96
Wang Z, Havasi A, Gall J, Bonegio R, Li Z, Mao H, Schwartz JH, Borkan SC (2010) GSK3beta promotes apoptosis after renal ischemic injury. J Am Soc Nephrol 21:284–294
Lin CL, Wang JY, Huang YT, Kuo YH, Surendran K, Wang FS (2006) Wnt/beta-catenin signaling modulates survival of high glucose-stressed mesangial cells. J Am Soc Nephrol 17:2812–2820
Boini KM, Amann K, Kempe D, Alessi DR, Lang F (2009) Proteinuria in mice expressing PKB/SGK-resistant GSK3. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 296:F153–F159
George B, Vollenbroker B, Saleem MA, Huber TB, Pavenstadt H, Weide T (2011) GSK3beta inactivation in podocytes results in decreased phosphorylation of p70S6 K accompanied by cytoskeletal rearrangements and inhibited motility. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 300:F1152–F1162
Shankland SJ (2006) The podocyte’s response to injury: role in proteinuria and glomerulosclerosis. Kidney Int 69:2131–2147
Wolf G, Chen S, Ziyadeh FN (2005) From the periphery of the glomerular capillary wall toward the center of disease: podocyte injury comes of age in diabetic nephropathy. Diabetes 54:1626–1634
Li JJ, Kwak SJ, Jung DS, Kim JJ, Yoo TH, Ryu DR et al (2007) Podocyte biology in diabetic nephropathy. Kidney Int 72:S36–S42
Susztak K, Raff AC, Schiffer M, Bottinger EP (2006) Glucose-induced reactive oxygen species cause apoptosis of podocytes and podocyte depletion at the onset of diabetic nephropathy. Diabetes 55:225–233
Steffes MW, Schmidt D, McCrery R, Basgen JM (2001) Glomerular cell number in normal subjects and in type 1 diabetic patients. Kidney Int 59:2104–2113
Verzola D, Gandolfo MT, Ferrario F, Rastaldi MP, Villaggio B, Gianiorio F et al (2007) Apoptosis in the kidneys of patients with type II diabetic nephropathy. Kidney Int 72:1262–1272
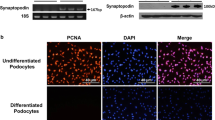
Mundel P, Reiser J, Zuniga Mejia Borja A, Pavenstadt H, Davidson GR, Kriz W, Zeller R (1997) Rearrangements of the cytoskeleton and cell contacts induce process formation during differentiation of conditionally immortalized mouse podocyte cell lines. Exp Cell Res 236:248–258
Kang SW, Adler SG, Nast CC, LaPage J, Gu JL, Nadler JL, Natarajan R (2001) 12-lipoxygenase is increased in glucose-stimulated mesangial cells and in experimental diabetic nephropathy. Kidney Int 59:1354–1362
Doublier S, Ruotsalainen V, Salvidio G, Lupia E, Biancone L, Conaldi PG, Reponen P, Tryggvason K, Camussi G (2001) Nephrin redistribution on podocytes is a potential mechanism for proteinuria in patients with primary acquired nephrotic syndrome. Am J Pathol 158:1723–1731
Sanden SK, Wiggins JE, Goyal M, Riggs LK, Wiggins RC (2003) Evaluation of a thick and thin section method for estimation of podocyte number, glomerular volume, and glomerular volume per podocyte in rat kidney with Wilms’ tumor-1 protein used as a podocyte nuclear marker. J Am Soc Nephrol 14:2484–2493
Beurel E, Jope RS (2006) The paradoxical pro- and anti-apoptotic actions of GSK3 in the intrinsic and extrinsic apoptosis signaling pathways. Prog Neurobiol 79:173–189
Linseman DA, Butts BD, Precht TA, Phelps RA, Le SS, Laessig TA, Bouchard RJ, Florez-McClure ML, Heidenreich KA (2004) Glycogen synthase kinase-3beta phosphorylates Bax and promotes its mitochondrial localization during neuronal apoptosis. J Neurosci 24:9993–10002
Maurer U, Charvet C, Wagman AS, Dejardin E, Green DR (2006) Glycogen synthase kinase-3 regulates mitochondrial outer membrane permeabilization and apoptosis by destabilization of MCL-1. Mol Cell 21:749–760
Zhao Y, Altman BJ, Coloff JL, Herman CE, Jacobs SR, Wieman HL et al (2007) Glycogen synthase kinase 3alpha and 3beta mediate a glucose-sensitive antiapoptotic signaling pathway to stabilize Mcl-1. Mol Cell Biol 27:4328–4339
Obligado SH, Ibraghimov-Beskrovnaya O, Zuk A, Meijer L, Nelson PJ (2008) CDK/GSK-3 inhibitors as therapeutic agents for parenchymal renal diseases. Kidney Int 73:684–690
Hongisto V, Smeds N, Brecht S, Herdegen T, Courtney MJ, Coffey ET (2003) Lithium blocks the c-Jun stress response and protects neurons via its action on glycogen synthase kinase 3. Mol Cell Biol 23:6027–6036
Tan J, Zhuang L, Leong HS, Iyer NG, Liu ET, Yu Q (2005) Pharmacologic modulation of glycogen synthase kinase-3beta promotes p53-dependent apoptosis through a direct Bax-mediated mitochondrial pathway in colorectal cancer cells. Cancer Res 65:9012–9020
Watcharasit P, Bijur GN, Song L, Zhu J, Chen X, Jope RS (2003) Glycogen synthase kinase-3beta (GSK3beta) binds to and promotes the actions of p53. J Biol Chem 278:48872–48879
Liao X, Zhang L, Thrasher JB, Du J, Li B (2003) Glycogen synthase kinase-3beta suppression eliminates tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand resistance in prostate cancer. Mol Cancer Ther 2:1215–1222
Song L, Zhou T, Jope RS (2004) Lithium facilitates apoptotic signaling induced by activation of the Fas death domain-containing receptor. BMC Neurosci 5:20
Lan Y, Liu X, Zhang R, Wang K, Wang Y, Hua ZC (2013) Lithium enhances TRAIL-induced apoptosis in human lung carcinoma A549 cells. Biometals 26:241–254
Kotliarova S, Pastorino S, Kovell LC, Kotliarov Y, Song H, Zhang W et al (2008) Glycogen synthase kinase-3 inhibition induces glioma cell death through c-MYC, nuclear factor-kappaB, and glucose regulation. Cancer Res 68:6643–6651
Pagtalunan ME, Miller PL, Jumping-Eagle S, Nelson RG, Myers BD, Rennke HG, Coplon NS, Sun L, Meyer TW (1997) Podocyte loss and progressive glomerular injury in type II diabetes. J Clin Invest 99:342–348
Tejada T, Catanuto P, Ijaz A, Santos JV, Xia X, Sanchez P, Sanabria N, Lenz O, Elliot SJ, Fornoni A (2008) Failure to phosphorylate AKT in podocytes from mice with early diabetic nephropathy promotes cell death. Kidney Int 73:1385–1393
Shin SY, Kim CG, Jho EH, Rho MS, Kim YS, Kim YH, Lee YH (2004) Hydrogen peroxide negatively modulates Wnt signaling through downregulation of beta-catenin. Cancer Lett 212:225–231
King TD, Jope RS (2005) Inhibition of glycogen synthase kinase-3 protects cells from intrinsic but not extrinsic oxidative stress. NeuroReport 16:597–601
Song L, De Sarno P, Jope RS (2002) Central role of glycogen synthase kinase-3beta in endoplasmic reticulum stress-induced caspase-3 activation. J Biol Chem 277:44701–44708
Kim AJ, Shi Y, Austin RC, Werstuck GH (2005) Valproate protects cells from ER stress-induced lipid accumulation and apoptosis by inhibiting glycogen synthase kinase-3. J Cell Sci 118:89–99
Lorz C, Benito-Martin A, Boucherot A, Ucero AC, Rastaldi MP, Henger A et al (2008) The death ligand TRAIL in diabetic nephropathy. J Am Soc Nephrol 19:904–914
Huang H, He X (2008) Wnt/beta-catenin signaling: new (and old) players and new insights. Curr Opin Cell Biol 20:119–125
Kaga S, Zhan L, Altaf E, Maulik N (2006) Glycogen synthase kinase-3beta/beta-catenin promotes angiogenic and anti-apoptotic signaling through the induction of VEGF, Bcl-2 and survivin expression in rat ischemic preconditioned myocardium. J Mol Cell Cardiol 40:138–147
Rao R, Hao CM, Breyer MD (2004) Hypertonic stress activates glycogen synthase kinase 3beta-mediated apoptosis of renal medullary interstitial cells, suppressing an NFkappaB-driven cyclooxygenase-2-dependent survival pathway. J Biol Chem 279:3949–3955
Dai C, Stolz DB, Kiss LP, Monga SP, Holzman LB, Liu Y (2009) Wnt/beta-catenin signaling promotes podocyte dysfunction and albuminuria. J Am Soc Nephrol 20:1997–2008
Li Z, Xu J, Xu P, Liu S, Yang Z (2013) Wnt/beta-catenin signalling pathway mediates high glucose induced cell injury through activation of TRPC6 in podocytes. Cell Prolif 46:76–85
Kato H, Gruenwald A, Suh JH, Miner JH, Barisoni-Thomas L, Taketo MM, Faul C, Millar SE, Holzman LB, Susztak K (2011) Wnt/beta-catenin pathway in podocytes integrates cell adhesion, differentiation, and survival. J Biol Chem 286:26003–26015
Kanzariya NR, Patel RK, Patel NJ (2011) Antidiabetic and vasoprotective activity of lithium: role of glycogen synthase kinase-3. Indian J Pharmacol 43:433–436
Kwon TH, Laursen UH, Marples D, Maunsbach AB, Knepper MA, Frokiaer J, Nielsen S (2000) Altered expression of renal AQPs and Na(+) transporters in rats with lithium-induced NDI. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 279:F552–F564
Meijer L, Skaltsounis AL, Magiatis P, Polychronopoulos P, Knockaert M, Leost M et al (2003) GSK-3-selective inhibitors derived from Tyrian purple indirubins. Chem Biol 10:1255–1266
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Brain Korea 21 PLUS Project for Medical Science, Yonsei University College of Medicine, the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) Grant funded by the Korea government (MSIP) (No. NRF-2011-0030086), and a grant of the Korean Health Technology R&D Project, Ministry of Health and Welfare, Republic of Korea (HI12C0646).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
J. Paeng and J. H. Chang have contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Paeng, J., Chang, J.H., Lee, S.H. et al. Enhanced glycogen synthase kinase-3β activity mediates podocyte apoptosis under diabetic conditions. Apoptosis 19, 1678–1690 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10495-014-1037-5
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10495-014-1037-5