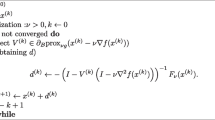Abstract
Motivated by the study of regularization for sparse problems, we propose a new regularization method for sparse vector recovery. We derive sufficient conditions on the well-posedness of the new regularization, and design an iterative algorithm, namely the iteratively reweighted algorithm (IR-algorithm), for efficiently computing the sparse solutions to the proposed regularization model. The convergence of the IR-algorithm and the setting of the regularization parameters are analyzed at length. Finally, we present numerical examples to illustrate the features of the new regularization and algorithm.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
TIKHONOV, A. N. On the solution of ill-posed problems and the method of regularization. Doklady Akademii Nauk SSSR, 151, 501–504 (1963)
BENJAMIN, S. and THORSTEN, H. Higher order convergence rates for Bregman iterated variational regularization of inverse problems. Numerische Mathematik, 141, 215–252 (2018)
ZHU, W., SHU, S., and CHENG, L. Z. An efficient proximity point algorithm for total-variation-based image restoration. Advances in Applied Mathematics and Mechanics, 6, 145–164 (2014)
CLASON, C., KRUSE, F., and KUNISH, K. Total variation regularization of multi-material topology optimization. ESAIM: Mathematical Modelling and Numerical Analysis, 52, 275–303 (2018)
ZHANG, H., CHENG, L. Z., and ZHU, W. Nuclear norm regularization with a low-rank constraint for matrix completion. Inverse Problems, 26, 115009 (2010)
DONG, J., XUE, Z. C., GUAN, J., HAN, Z. F., and WANG, W. W. Low rank matrix completion using truncated nuclear norm and sparse regularizer. Signal Processing: Image Communication, 68, 76–87 (2018)
USEVICH, K. and COMON, P. Hankel low-rank matrix completion: performance of the nuclear norm relaxation. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Signal Processing, 10, 637–646 (2017)
ZHU, W., SHU, S., and CHENG, L. Z. First-order optimality condition of basis pursuit denoise problem. Applied Mathematics and Mechanics (English Edition), 35(10), 1345–1352 (2014) https://doi.org/10.1007/s10483-014-1860-9
ZHU, W., SHU, S., and CHENG, L. Z. Proximity point algorithm for low-rank matrix recovery from sparse noise corrupted data. Applied Mathematics and Mechanics (English Edition), 35(2), 259–268 (2014) https://doi.org/10.1007/s10483-014-1788-6
BREDIES, K. and LORENZ, D. A. Regularization with non-convex separable constraints. Inverse Problem, 25, 085011 (2009)
GRASMAIR, M., HALTMEIER, M., and SCHERZER, O. Sparse regularization with lq penalty term. Inverse Problems, 24, 055020 (2008)
ENGL, H. W. and RAMLAU, R. Regularization of inverse problems. Encyclopedia of Applied and Computational Mathematics, Springer, Heidelberg (2015)
ARJOUNE, Y., KAABOUCH, N., GHAZI, H. E., and TAMTAOUI, A. Compressive sensing: performance comparison of sparse recovery algorithms. 2017 IEEE 7th Annual Computing and Communication Workshop and Conference (CCWC), IEEE, Las Vegas (2017)
DAN, W. and ZHANG, Z. Generalized sparse recovery model and its neural dynamical optimization method for compressed sensing. Circuits Systems and Signal Processing, 36, 4326–4353 (2017)
CHARTRAND, R. and STANEVA, V. Restricted isometry properties and nonconvex compressive sensing. Inverse Problems, 24, 657–682 (2008)
CHARTRAND, R. and YIN, W. T. Iteratively reweighted algorithms for compressive sensing. International Conference on Acoustics, Speech, and Signal Processing (ICASSP 2008), 3869–3872 (2008)
CHARTRAND, R. Exact reconstruction of sparse signals via nonconvex minimization. IEEE Signal Processing Letters, 14, 707–710 (2007)
GE, D., JIANG, X., and YE, Y. A note on complexity of Lp minimization. Mathematics Programming, 129, 285–299 (2011)
FOUCART, S. and LAI, M. J. Sparsest solutions of underdetermined linear systems via lq-minimization for 0 < q ≤ 1. Applied and Computational Harmonic Analysis, 26, 395–407 (2009)
FOUCART, S. A note on guaranteed sparse recovery via l1-minimization. Applied and Computational Harmonic Analysis, 29, 97–103 (2010)
CANDÈS, E. J. and PLAN, Y. A probabilistic and RIPless theory of compressed sensing. IEEE Transactions on Information Theory, 57, 7235–7254 (2010)
SUN, Q. Y. Sparse approximation property and stable recovery of sparse signals from noisy measurements. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 59, 5086–5090 (2011)
FAZEL, M. Matrix Rank Minimization with Applications, Ph.D. dissertation, Stanford University, California (2002)
CANDÈS, E. J., WAKIN, M. B., and BOYD, S. P. Enhancing sparsity by reweighted l1 minimization. Journal of Fourier Analysis and Applications, 14, 877–905 (2008)
DAUCHEBIES, I., DEVORE, R., FORNASIER, M., and GUNTURK, C. S. Iteratively reweighted least squares minimization for sparse recovery. Communications on Pure and Applied Mathematics, 63, 1–38 (2010)
MOURAD, N. and REILLY, J. F. Minimizaing nonconvex functions for sparse vector reconstruction. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 58, 3485–3496 (2010)
NEEDELL, D. Noisy signal recovery via iterative reweighted L1-minimization. 2009 Conference Record of the Forty-Third Asilomar Conference on Signals, Systems and Computers, IEEE, Pacific Grove (2009)
XU, W. Y., KHAJEHNEJAD, M. A., AVESTIMEHR, S., and HASSIBI, B. Breaking through the thresholds: an analysis for iterative reweighted l1 minimization via the Grassmann angle framework. ICASSP 2010: IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal, IEEE, Texas (2009)
CHEN, X. J., XU, F., and YE, Y. Lower bound theory of nonzero entries in solutions of l2 − lp minimization. SIAM Journal on Scientific Computing, 32, 2832–2852 (2010)
LAI, M. J. and WANG, J. An unconstrained lq minimization with 0 < q ≤ 1 for sparse solution of underdetermined linear systems. SIAM Journal on Optimization, 21, 82–101 (2011)
MOL, C. D., VITO, E. D., and ROSASCO, L. Elastic-net regularization in learning theory. Journal of Complexity, 25, 201–230 (2009)
JIN, B. T., LORENZ, D. A., and SCHIFFLER, S. Elastic-net regularization: error estimates and active set methods. Inverse Problems, 25, 115022 (2009)
ZOU, H. and HASTIE, T. Regularization and variable selection via the elastic net. Journal of the Royal Statistical Society: Series B, 67, 301–320 (2005)
CAI, J. F., OSHER, S., and SHEN, Z. W. Linearized Bregman iterations for compressed sensing. Mathematics of Computation, 78, 1515–1536 (2009)
YIN, W. Analysis and generalizations of the linearized Bregman method. SIAM Journal on Imaging Sciences, 3, 856–877 (2010)
ZHANG, H., CHENG, L. Z., and ZHU, W. A lower bound guaranteeing exact matrix completion via singular value thresholding algorithm. Applied and Computational Harmonic Analysis, 31, 454–459 (2011)
BERTSEKAS, D. P., NEDIĆC, A., and OZDAGLAR, A. E. Convex Analysis and Optimization, Athena Scietific and Tsinghua University Press, Beijing (2006)
YUAN, Z. Y. and WANG, H. X. Phase retrieval via reweighted wirtinger flow method. Applied Optics, 56, 2418–2427 (2017)
HARDY, G. H., LITTLEWOOD, J. E., and PÓLYA, G. Inequalities, Posts and Telecom Press, Beijing (2010)
FORNASIER, M. Theoretical Foundations and Numerical Methods for Sparse Recovery, De Gruyter, Berlin (2010)
Acknowledgements
Thanks to Prof.Mingjun LAI for many enlightening discussions with us on lq minimization, to Prof.Rong HUANG for his guidance during my post-doctoral research period, to Dr.Yangyang XU for his contributions to Theorem 3 and lone-term communication on sparse vector recovery with nonconvex models, and to Dr.Housen LI for his careful reading of the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Project supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 61603322) and the Research Foundation of Education Bureau of Hunan Province of China (No. 16C1542)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhu, W., Zhang, H. & Cheng, L. New regularization method and iteratively reweighted algorithm for sparse vector recovery. Appl. Math. Mech.-Engl. Ed. 41, 157–172 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10483-020-2561-6
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10483-020-2561-6