Abstract
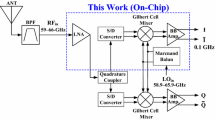
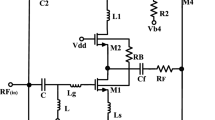
This paper provides an overview of target applications and design aspects for emerging radio frequency front-end circuits with subthreshold biasing to reduce power consumption. Design methods are described to linearize a subthreshold pseudo-differential common-source cascode low-noise amplifier (LNA) and a subthreshold active mixer. The linearization techniques can improve the third-order intermodulation intercept point (IIP3) through the use of passive components, which implies that they do not require auxiliary amplifiers to suppress third-order distortion components, and therefore do not incur any extra power consumption. A 1.95 GHz receiver front-end chip with a narrowband LNA and down-conversion mixer was designed and fabricated in 110 nm CMOS technology. Measurement results show that the linearized low-power front-end has a 20.6 dB voltage gain, a 9.5 dB double sideband noise figure, and a − 10.8 dBm IIP3 with a power consumption of 0.9 mW.



















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Oh, N.-J., & Lee, S.-G. (2005). Building a 2.4-GHz radio transceiver using IEEE 802.15.4. IEEE Circuits and Devices Magazine, 21(6), 43–51.
Contaldo, M., Banerjee, B., Ruffueux, D., Chabloz, J., Roux, E. L., & Enz, C. C. (2010). A 2.4-GHz BAW-based transceiver for wireless body area networks. IEEE Transactions on Biomedical Circuits and Systems, 4(6), 391–399.
Wong, A. C. W., Dawkins, M., Devita, G., Kasparidis, N., Katsiamis, A., King, O., et al. (2013). A 1 V 5 mA multimode IEEE 802.15.6/Bluetooth low-energy WBAN transceiver for biotelemetry applications. IEEE Journal of Solid-State Circuits, 48(1), 186–198.
Leong, C. Y., Ong, K. C., Tan, K. K., & Gan, O. P. (2006). Near field communication and Bluetooth bridge system for mobile commerce. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Industrial Informatics (pp. 50–55).
Heiberg, A. C., Brown, T. W., Fiez, T. S., & Mayaram, K. (2011). A 250 mV, 352 μW GPS receiver RF front-end in 130 nm CMOS. IEEE Journal of Solid-State Circuits, 46(4), 938–949.
Rhee, W., Xu, N., Zhou, B., & Wang, Z. (2010). Low power, non invasive UWB systems for WBAN and biomedical applications. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Information and Communication Technology Convergence (ICTC) (pp. 35–40).
Ameen, M. A., Liu, J., Ullah, S., & Kwak, K. S. (2011). A power efficient MAC protocol for implant device communication in wireless body area networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE Consumer Communications and Networking Conference (CCNC) (pp. 1155–1160).
Roberts, N. E., Oh, S., & Wentzloff, D. D. (2012). Exploiting channel periodicity in body sensor networks. IEEE Transactions on Emerging and Selected Topics in Circuits and Systems, 2(1), 4–13.
Nguyen, T.-K., Oh, N.-J., Le, V.-H., & Lee, S.-G. (2006). A low-power CMOS direct conversion receiver with 3-dB NF and 30-kHz flicker-noise corner for 915-MHz band IEEE 802.15.4 ZigBee standard. IEEE Transactions on Microwave Theory and Techniques, 54(2), 735–741.
Do, A. V., Boon, C. C., Do, M. A., Yeo, K. S., & Cabuk, A. (2008). A subthreshold low-noise amplifier optimized for ultra-low-power applications in the ISM band. IEEE Transactions on Microwave Theory and Techniques, 56(2), 286–292.
Lee, H., & Mohammadi, S. (2006). A 3 GHz subthreshold CMOS low noise amplifier. In Proceedings of the Radio Frequency Integrated Circuits (RFIC) Symposium.
Taris, T., Begueret, J., & Deval, Y. (2011). A 60 μW LNA for 2.4 GHz wireless sensors network applications. In Proceedings of the Radio Frequency Integrated Circuits (RFIC) Symposium.
Parvizi, M., Allidina, K., & El-Gamal, M. N. (2016). Short channel output conductance enhancement through forward body biasing to realize 0.5 V 250 μW 0.6–4.2 GHz current-reuse CMOS LNA. IEEE Journal of Solid-State Circuits, 51(3), 574–586.
Rahman, M., & Harjani, R. (2016). A sub-1-V 194-μW 31-dB FOM 2.3–2.5-GHz mixer-first receiver frontend for WBAN with mutual noise cancellation. IEEE Transactions on Microwave Theory and Techniques, 64(4), 1102–1109.
Chang, C.-H., Xu, L., & Onabajo, M. (2016). A low-power RF receiver front-end chip designed with methods to reduce third-order intermodulation distortion. In Proceedings of the IEEE Dallas Circuits and Systems Conference (DCAS).
Chang, C.-H., & Onabajo, M. (2013). Linearization of subthreshold low-noise amplifiers. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Symposium on Circuits and Systems (ISCAS) (pp. 377–380).
Chang, C.-H., & Onabajo, M. (2013). IIP3 enhancement of subthreshold active mixers. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems II: Express Briefs, 60(11), 731–735.
Xu, L., Wang, K., Chang, C.-H., & Onabajo, M. (2015). Inductorless linearization of low-power active mixers. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Symposium on Circuits and Systems (ISCAS) (pp. 2213–2216).
Razavi, B. (2001). Design of analog CMOS integrated circuits (1st ed.). New York: McGraw-Hill.
Weiner, D. D., & Spina, J. F. (1980). Sinusoidal analysis and modeling of weakly nonlinear circuits. New York: Van Nostrand Reinhold.
Zhang, H., & Sánchez-Sinencio, E. (2011). Linearization techniques for CMOS low noise amplifiers: A tutorial. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems I: Regular Papers, 58(1), 22–36.
Soer, M. C. M., Klumperink, E. A. M., Ru, Z., van Vliet, F. E., & Nauta, B. (2009). A 0.2-to-2.0 GHz 65 nm CMOS receiver without LNA achieving > 11 dBm IIP3 and < 6.5 dB NF. In International Solid-State Circuits Conference Technical Digest (ISSCC) (pp. 222–223).
Andrews, C., & Molnar, A. C. (2010). A passive-mixer-first receiver with baseband-controlled RF impedance matching, < 6 dB NF, and > 27dBm wideband IIP3. In International Solid-State Circuits Conference Technical Digest (ISSCC) (pp. 46–47).
Aparin, V., & Larson, L. E. (2005). Modified derivative superposition method for linearizing FET low-noise amplifier. IEEE Transactions on Microwave Theory and Techniques, 53(2), 571–581.
Fan, X., Zhang, H., & Sánchez-Sinencio, E. (2008). A noise reduction and linearity improvement technique for a differential cascode LNA. IEEE Journal of Solid-State Circuits, 43(3), 588–599.
Yang, J., Tran, N., Bai, S., Fu, M., Skafidas, E., Halpern, M., et al. (2011). A subthreshold down converter optimized for super-low-power applications in MICS Band. In Proceedings of the IEEE Biomedical Circuits and Systems Conference (BioCAS) (pp. 189–192).
Abdelghany, M. A., Pokharel, P. K., Kanaya, H., & Yoshida, K. (2011). Low-voltage low-power combined LNA-single gate mixer for 5 GHz wireless systems. In Proceedings of the Radio Frequency Integrated Circuits (RFIC) Symposium.
Lee, S.-Y., Wang, L.-H., Chen, T.-Y., & Yu, C.-T. (2012). A low-power RF front-end with merged LNA, differential power splitter, and quadrature mixer for IEEE 802.15.4 (ZigBee) applications. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Symposium on Circuits and Systems (ISCAS) (pp. 1492–1496).
Fiorelli, R., Villegas, A., Peralias, E., Vazquez, D., & Rueda, A. (2011). 2.4-GHz single-ended input low-power-voltage active front-end for Zigbee applications in 90 nm CMOS. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Circuit Theory and Design (ECCTD) (pp. 829–832).
Selvakumar, A., Zargham, M., & Liscidini, A. (2015). Sub-mW current re-use receiver front-end for wireless sensor network applications. IEEE Journal of Solid-State Circuits, 50(12), 2965–2974.
Lin, Z., Mak, P.-I., & Martins, R. P. (2014). A 0.14-mm2 1.4-mW 59.4-dB-SFDR 2.4 GHz ZigBee/WPAN receiver exploiting a split-LNTA + 50% LO topology in 65-nm CMOS. IEEE Transactions on Microwave Theory and Techniques, 62(7), 1525–1534.
Yu, Z.-H., Yi, H., Mak, P.-I., Yin, J., & Martins, R. P. (2017). A 0.18 V 32 μW Bluetooth low-energy (BLE) receiver with 1.33nW sleep power for energy-harvesting applications in 28 nm. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Solid-State Circuits Conference Technical Digest (ISSCC) (pp. 414–416).
Pengg, F., Barras, D., Kucera, M., Scolari, N., & Vouilloz, A. (2013). A low power miniaturized 1.95 mm2 fully integrated transceiver with fast PLL mode for IEEEE 802.15.4/Bluetooth smart and proprietary 2.4 GHz applications. In Proceedings of the Radio Frequency Integrated Circuits (RFIC) Symposium (pp. 71–74).
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Science Foundation under Award No. 1451213.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chang, Ch., Xu, L. & Onabajo, M. Design techniques for mitigation of intermodulation distortion components in CMOS RF receiver front-end circuits with subthreshold operation. Analog Integr Circ Sig Process 94, 335–346 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10470-017-1060-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10470-017-1060-x