Abstract
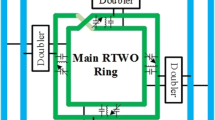
This paper presents an accurate analysis for deriving transient oscillation amplitude of Rotary Traveling Wave Oscillators (RTWOs) as a transmission-line based and high frequency circuit. The procedure of the paper is based on considering the nonlinear behavior of negative transconductors that are used for loss compensation of the transmission line. Finally, a closed-form expression for the time-domain amplitude of the RTWOs is obtained. The proposed useful and accurate expression could be used for designing the RTWOs for high performance-high speed systems. Also, it enables us to analyze and synthesize the oscillators with the desired transient behavior. This aspect of the RTWOs is not studied in previous works. The proposed theoretical results are then compared with accurate simulations. Simulations have been done in 0.18 μm CMOS technology with 1.8 V supply voltage. Results show less than 10% difference in steady state oscillation amplitude of theoretical expression and simulations. Considering the nonlinear equation of the RTWOs amplitude, complicated type of solving, simplifications and its numerical solution, the proposed derived expression has a good agreement with simulations.















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lee, J., & Razavi, B. (2003). A 40 Gb/S clock and data recovery circuit in 0.18 μm cmos technology. IEEE Journal of Solid State Circuits, 38(12), 2181–2190.
Le Grand de Mercey, G. (2004). 18 GHz–36 GHz rotary traveling wave voltage controlled oscillator in a cmos technology. Ph.D. dissertation, Bundeswehr Universitat, Neubiberg.
Ben Abdeljelil, F, Tatinian, W., Carpineto, L., Jacquemod, G. (2009). Design of a cmos 12 GHz rotary travelling wave oscillator with switched capacitor tuning. IEEE Radio Frequency Integrated Circuits Symposium, pp 579–582.
Ahmadihaji, A., & Nabavi, A. (2014). Design of a 30 GHz rotary traveling wave oscillator with improved frequency tuning range in 0.18 µm cmos technology. International Journal of Electronics and Communications, 68(11), 1053–1057.
Bai, Z., Zhou, X., Mason, R. D., & Allan, G. (2015). Low-phase noise clock distribution network using rotary traveling-wave oscillators and built-in self-test phase tuning technique. IEEE Transactions On Circuits And Systems—II: Express Briefs, 62(1), 41–45.
O’Mahony, F., Yue, C. P., Horowitz, M. A., & Wong, S. S. (2003). A 10-GHz global clock distribution using coupled standing-wave oscillators. IEEE Journal of Solid-State Circuits, 38(11), 1813–1820.
Moroni, A., Genesi, R., & Manstretta, D. (2014). Analysis and design of a 54 GHz distributed “hybrid” wave oscillator array with quadrature outputs. IEEE Journal of Solid-State Circuits, 49(5), 1158–1172.
Pontón, M., Suárez, A., & Stevenson Kenney, J. (2014). Rotary traveling-wave oscillator with differential nonlinear transmission lines. IEEE Transactions on Microwave Theory and Techniques, 62(5), 1149–1161.
Nouri, N., & Buckwalter, J. F. (2011). A 45-GHz rotary-wave voltage-controlled oscillator. IEEE Transactions on Microwave Theory and Techniques, 59(2), 383–392.
Takinami, K., Walsworth, R., Osman, S., & Beccue, S. (2010). Phase-noise analysis in rotary traveling-wave oscillators using simple physical model. IEEE Transactions on Microwave Theory and Techniques, 58(6), 1465–1474.
Zhang, C., Wang, Z., Zhao, Y., & Park, S. M. (2012). A 15 GHz, -182 dBc/Hz/mW FOM, rotary traveling wave vco in 90 nm cmos. IEEE Microwave and Wireless Components Letters, 22(4), 206–208.
Chien, J.-C., & Liang-Hung, L. (2007). A 32-GHz rotary traveling-wave voltage controlled oscillator in 0.18 μm cmos. IEEE Microwave and Wireless Components Letters, 17(10), 724–726.
Takinami, K., & Walsworth, R. (2010). Phase error calibration technique for rotary traveling wave oscillators. IEEE Journal of Solid-State Circuits, 45(11), 2433–2444.
Chen, Y., & Pedrotti, K. D. (2011). Rotary traveling-wave oscillators, analysis and simulation. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems I: Regular Papers, 58(1), 77–87.
Wood, J., Edwards, T. C., & Lipa, S. (2001). Rotary traveling-wave oscillator arrays: A new clock technology. IEEE Journal of Solid-State Circuits, 36(11), 1654–1665.
Sridhar, R. (1960). A general method for deriving the describing functions for a certain class of nonlinearities. IRE Transactions on Automatic Control, 5(2), 135–141.
Tsividis, Y. P. (1987). Operation and modeling of the mos transistor (pp. 141–148). New York: McGraw-Hill.
Ebrahimi, A., Naimi, H. M., & Adrang, H. (2011). Remarks on transient amplitude analysis of mos cross-coupled oscillators. IEICE Transactions on Electronics, 94, 231–239.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Abbasalizadeh, S., Miar-Naimi, H. Analytical formulation of transient oscillation amplitude in rotary traveling wave oscillators. Analog Integr Circ Sig Process 90, 669–679 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10470-016-0877-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10470-016-0877-z