Abstract
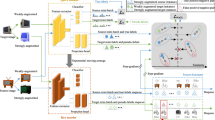
Domain adaptation learning aims to solve the classification problems of unlabeled target domain by using rich labeled samples in source domain, but there are three main problems: negative transfer, under adaptation and under fitting. Aiming at these problems, a domain adaptation network based on hypergraph regularized denoising autoencoder (DAHDA) is proposed in this paper. To better fit the data distribution, the network is built with denoising autoencoder which can extract more robust feature representation. In the last feature and classification layers, the marginal and conditional distribution matching terms between domains are obtained via maximum mean discrepancy measurement to solve the under adaptation problem. To avoid negative transfer, the hypergraph regularization term is introduced to explore the high-order relationships among data. The classification performance of the model can be improved by preserving the statistical property and geometric structure simultaneously. Experimental results of 16 cross-domain transfer tasks verify that DAHDA outperforms other state-of-the-art methods.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bellaachia A, AI-Dhelaan M (2015) Short text keyphrase extraction with hypergraphs. Prog Artif Intell 3(2):73–87
Bickel S, Brückner M, Scheffer T (2009) Discriminative learning under covariate shift. J Mach Learn Res 10:2137–2155
Bruzzone L, Marconcini M (2010) Domain adaptation problems: a DASVM classification technique and a circular validation strategy. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 32(5):770–787
Cao B, Pan SJ, Zhang Y, Yeung DY, Yang Q (2010) Adaptive transfer learning. In: AAAI, pp 407–412
Chen HY, Chien JT (2015) Deep semi-supervised learning for domain adaptation. In: MLSP, pp 1–6
Chen XJ, Zhan YZ, Ke J, Chen XB (2015) Complex video event detection via pairwise fusion of trajectory and multi-label hypergraphs. Multimedia Tools Appl 75(22):15079–15100
Chen M, Xu Z, Weinberger KQ, Sha F (2012) Marginalized denoising autoencoders for domain adaptation. In: ICML, pp 767–774
Chu WS, Torre FDL, Cohn JF (2013) Selective transfer machine for personalized facial action unit detection. In: CVPR, pp 3515–3522
Dai W, Yang Q, Xue GR, Yu Y (2007) Boosting for transfer learning. In: ICML, pp 193–200
Donahue J, Jia Y, Vinyals O, Hoffman J, Zhang N, Tzeng E, Darrell T (2014) DeCAF: a deep convolutional activation feature for generic visual recognition. In: ICML, pp 988–996
Friedman J, Hastie T, Tibshirani R (2010) Regularization paths for generalized linear models via coordinate descent. J Stat Softw 33(1):1–22
Ganin Y, Lempitsky V (2015) Unsupervised domain adaptation by backpropatation. In: ICML
Gong BQ, Shi Y, Sha F, Grauman K (2012) Geodesic flow kernel for unsupervised domain adaptation. In: CVPR, pp 2066–2073
Gretton A, Borgwardt KM, Rasch M, Schölkopf B, CSmola AJ (2006) A kernel method for the two-sample-problem. In: NIPS, pp 513–520
Huang J, Smola AJ, Gretton A, Borgwardt KM, Schölkopf B (2006) Correcting sample selection bias by unlabeled data. In: NIPS, pp 601–608
Lee SI, Chatalbashev V, Vickrey D, Koller D (2007) Learning a meta-level prior for feature relevance from multiple related tasks. In: ICML, pp 489–496
Long MS, Cao Y, Wang JM, Jordan MI (2015) Learning transferable features with deep adaptation networks. In: ICML, pp 97–105
Long MS, Wang JM, Ding GG, Sun JJ, Yu PS (2013) Transfer feature learning with joint distribution adaptation. In: ICCV, pp 2200–2207
Long MS, Wang JM, Ding GG, Sun JJ, Yu PS (2014a) Transfer joint matching for unsupervised domain adaptation. In: CVPR, pp 1410–1417
Long MS, Wang JM, Ding GG, Shen D, Yang Q (2014b) Transfer learning with graph co-regularization. IEEE Trans Knowl Data Eng 26(7):1805–1818
Lore KG, Akintayo A, Sarkar S (2016) LLNet: a deep autoencoder approach to natural low-light image enhancement. Pattern Recognit 61:650–662
Lv L, Zhao DB, Deng QQ (2016) A semi-supervised predictive sparse decomposition based on the task-driven dictionary learning. Cogn Comput. doi:10.1007/s12559-016-9438-0
Pan SJ, Yang Q (2010) A survey on transfer learning. IEEE Trans Knowl Data Eng 22(10):1345–1359
Pan SJ, Tsang IW, Kwok JT, Yang Q (2011) Domain adaptation via transfer component analysis. IEEE Trans Neural Netw 22(2):199–210
Peng Y, Wang SH, Long XZ, Lu BL (2015) Discriminative graph regularized extreme learning machine and its application to face recognition. Neurocomputing 149:340–353
Raina R, Battle A, Lee H, Packer B, Ng AY (2007) Self-taught learning: transfer learning from unlabeled data. In: ICML, pp 759–766
Raina R, Ng AY, Koller D (2006) Constructing informative priors using transfer learning. In: ICML, pp 713–720
Schwaighofer A, Tresp V, Yu K (2004) Learning Gaussian process kernels via hierarchical Bayes. In: NIPS, pp 1209–1216
Sugiyama M, Nakajima S, Kashima H, Von BP, Kawanabe M (2008) Direct importance estimation with model selection and its application to covariate shift adaptation. In: NIPS, pp 1433–1440
Sun BC, Feng JS, Saenko K (2016a) Return of frustratingly easy domain adaptation. In: AAAI, pp 2058–2065
Sun BC, Saenko K (2016b) Deep CORAL: correlation alignment for deep domain adaptaion. In: ECCV, pp 443–450
Tsai YHH, Yeh YR, Wang YCF (2016) Learning cross-domain landmarks for heterogeneous domain adaptation. In: CVPR, pp 5081–5090
Van DML, Hinton G (2008) Visualizing data using t-SNE. J Mach Learn Res 9:2579–2605
Vincent P, Larochelle H, Lajoie I, Bengio Y, Mangozal PA (2010) Stacked denoising autoencoders: learning useful representations in a deep network with a local denoising criterion. J Mach Learn Res 11:3371–3408
Vincent P, Larochelle H, Bengio Y, Mangozal PA (2008) Extracting and composing robust features with denoising autoencoders. In: ICML, pp 1096–1103
Yang B, Chen SC (2010) Sample-dependent graph construction with application to dimensionality reduction. Neurocomputing 74(1–3):301–314
Yu J, Tao D, Wang M (2012a) Adaptive hypergraph learning and its application in image classification. IEEE Trans Image Process 21(7):3262–3272
Yu J, Wang M, Tao D (2012b) Semisupervised multiview distance metric learning for cartoon synthesis. IEEE Trans Image Process 21(11):4636–4648
Yu J, Rui Y, Tao D (2014) Click prediction for web image reranking using multimodal sparse coding. IEEE Trans Image Process 23(5):2019–2032
Yuan H, Tang YY (2015) Learning with hypergraph for hyperspectral image feature extraction. IEEE Trans Geosci Remote Sens Lett 12(8):1695–1699
Zhan Y, Sun J, Niu D, Mao Q, Fan J (2015) A semi-supervised incremental learning method based on adaptive probabilistic hypergraph for video semantic detection. Multimedia Tools AppI 74(15):5513–5531
Zhang X, Yu XF, Wang SJ, Chang SF (2015) Deep transfer network: unsupervised domain adaptation. arXiv Preprint arXiv:1503.00591
Zhao DB, Zhang QC, Wang D, Zhu YH (2016) Experience replay for optimal control of nonzero-sum game systems with unknown dynamics. IEEE Trans Cybern 46(3):1–12
Zhou DY, Huang JY, Schölkopf B (2006) Learning with hypergraphs: clustering, classification, and embedding. In: NIPS, pp 1601–1608
Zhuang FZ, Cheng XH, Luo P, Pan SJ, He Q (2015) Supervised representation learning: transfer learning with deep autoencoders. In: IJCAI, pp 4119–4125
Acknowledgements
This work is supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China under Grants 61273143 and 61472424.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, X., Ma, Y. & Cheng, Y. Domain adaptation network based on hypergraph regularized denoising autoencoder. Artif Intell Rev 52, 2061–2079 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10462-017-9576-0
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10462-017-9576-0