Abstract
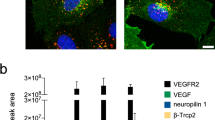
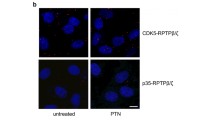
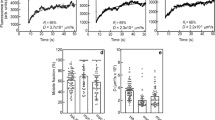
Pleiotrophin (PTN) has a moderate stimulatory effect on endothelial cell migration through ανβ3 integrin, while it decreases the stimulatory effect of vascular endothelial growth factor A (VEGFA) and inhibits cell migration in the absence of ανβ3 through unknown mechanism(s). In the present work, by using a multitude of experimental approaches, we show that PTN binds to VEGF receptor type 2 (VEGFR2) with a KD of 11.6 nM. Molecular dynamics approach suggests that PTN binds to the same VEGFR2 region with VEGFA through its N-terminal domain. PTN inhibits phosphorylation of VEGFR2 at Tyr1175 and still stimulates endothelial cell migration in the presence of a selective VEGFR2 tyrosine kinase inhibitor. VEGFR2 downregulation by siRNA or an anti-VEGFR2 antibody that binds to the ligand-binding VEGFR2 domain also induce endothelial cell migration, which is abolished by a function-blocking antibody against ανβ3 or the peptide PTN112−136 that binds ανβ3 and inhibits PTN binding. In cells that do not express ανβ3, PTN decreases both VEGFR2 Tyr1175 phosphorylation and cell migration in a VEGFR2-dependent manner. Collectively, our data identify VEGFR2 as a novel PTN receptor involved in the regulation of cell migration by PTN and contribute to the elucidation of the mechanism of activation of endothelial cell migration through the interplay between VEGFR2 and ανβ3.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kilpelainen I, Kaksonen M, Kinnunen T, Avikainen H, Fath M, Linhardt RJ, Raulo E, Rauvala H (2000) Heparin-binding growth-associated molecule contains two heparin-binding beta -sheet domains that are homologous to the thrombospondin type I repeat. J Biol Chem 275:13564–13570. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.275.18.13564
Ryan E, Shen D, Wang X (2016) Structural studies reveal an important role for the pleiotrophin C-terminus in mediating interactions with chondroitin sulfate. FEBS J 283:1488–1503. https://doi.org/10.1111/febs.13686
Papadimitriou E, Pantazaka E, Castana P, Tsalios T, Polyzos A, Beis D (2016) Pleiotrophin and its receptor protein tyrosine phosphatase beta/zeta as regulators of angiogenesis and cancer. Biochim Biophys Acta 1866:252–265. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbcan.2016.09.007
Mikelis C, Sfaelou E, Koutsioumpa M, Kieffer N, Papadimitriou E (2009) Integrin alpha(v)beta(3) is a pleiotrophin receptor required for pleiotrophin-induced endothelial cell migration through receptor protein tyrosine phosphatase beta/zeta. FASEB J 23:1459–1469. https://doi.org/10.1096/fj.08-117564
Mikelis C, Lamprou M, Koutsioumpa M, Koutsioubas AG, Spyranti Z, Zompra AA, Spiliopoulos N, Vradis AA, Katsoris P, Spyroulias GA, Cordopatis P, Courty J, Papadimitriou E (2011) A peptide corresponding to the C-terminal region of pleiotrophin inhibits angiogenesis in vivo and in vitro. J Cell Biochem 112:1532–1543. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcb.23066
Koutsioumpa M, Poimenidi E, Pantazaka E, Theodoropoulou C, Skoura A, Megalooikonomou V, Kieffer N, Courty J, Mizumoto S, Sugahara K, Papadimitriou E (2015) Receptor protein tyrosine phosphatase beta/zeta is a functional binding partner for vascular endothelial growth factor. Mol Cancer 14:19. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12943-015-0287-3
Poimenidi E, Theodoropoulou C, Koutsioumpa M, Skondra L, Droggiti E, van den Broek M, Koolwijk P, Papadimitriou E (2016) Vascular endothelial growth factor A (VEGF-A) decreases expression and secretion of pleiotrophin in a VEGF receptor-independent manner. Vasc Pharmacol 80:11–19. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.vph.2016.02.008
Héroult M, Bernard-Pierrot I, Delbé J, Hamma-Kourbali Y, Katsoris P, Barritault D, Papadimitriou E, Plouet J, Courty J (2004) Heparin affin regulatory peptide binds to vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) and inhibits VEGF-induced angiogenesis. Oncogene 23:1745–1753. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1206879
Bowler E, Oltean S (2019) Alternative splicing in angiogenesis. Int J Mol Sci 20:2067. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20092067
Simons M, Gordon E, Claesson-Welsh L (2016) Mechanisms and regulation of endothelial VEGF receptor signalling. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 17:611–625. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrm.2016.87
Peach CJ, Mignone VW, Arruda MA, Alcobia DC, Hill SJ, Kilpatrick LE, Woolard J (2018) Molecular pharmacology of VEGF-A isoforms: binding and signalling at VEGFR2. Int J Mol Sci 19:1264. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19041264
Olsson AK, Dimberg A, Kreuger J, Claesson-Welsh L (2006) VEGF receptor signalling in control of vascular function. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 7:359–371. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrm1911
Mahabeleshwar GH, Feng W, Reddy K, Plow EF, Byzova TV (2007) Mechanisms of integrin-vascular endothelial growth factor receptor cross-activation in angiogenesis. Circ Res 101:570–580. https://doi.org/10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.107.155655
West XZ, Meller N, Malinin NL, Deshmukh L, Meller J, Mahabeleshwar GH, Weber ME, Kerr BA, Vinogradova O, Byzova TV (2012) Integrin β3 crosstalk with VEGFR accommodating tyrosine phosphorylation as a regulatory switch. PLoS ONE 7:e31071. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0031071
Koutsioumpa M, Polytarchou C, Courty J, Zhang Y, Kieffer N, Mikelis C, Skandalis SS, Hellman U, Iliopoulos D, Papadimitriou E (2013) Interplay between αvβ3 integrin and nucleolin regulates human endothelial and glioma cell migration. J Biol Chem 288:343–354. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M112.387076
Brozzo MS, Bjelić S, Kisko K, Schleier T, Leppänen VM, Alitalo K, Winkler FK, Ballmer-Hofer K (2012) Thermodynamic and structural description of allosterically regulated VEGFR-2 dimerization. Blood 119:1781–1788. https://doi.org/10.1182/blood-2011-11-390922
Pettersen EF, Goddard TD, Huang CC, Couch GS, Greenblatt DM, Meng EC, Ferrin TE (2004) UCSF Chimera–a visualization system for exploratory research and analysis. J Comput Chem 25:1605–1612. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcc.20084
Case DA, Babin V, Berryman JT, Betz RM, Cai Q, Cerutti DS, Cheatham TE III, Darden TA, Duke RE, Gohlke H, Goetz AW, Gusarov S, Homeyer S, Janowski P, Kaus J, Kolossváry I, Kovalenko A, Lee TS, LeGrand S, Luchko T, Luo R, Madej B, Merz KM, Paesani F, Roe DR, Roitberg A, Sagui C, Salomon-Ferrer R, Seabra G, Simmerling CL, Smith W, Swails J, Walker RC, Wang J, Wolf RM, Wu X, Kollman PA (2014) AMBER 14. University of California, San Francisco. https://doi.org/10.13140/RG.2.2.17892.37766
Maier JA, Martinez C, Kasavajhala K, Wickstrom L, Hauser KE, Simmerling C (2015) ff14SB: Improving the accuracy of protein side chain and backbone parameters from ff99SB. J Chem Theory Comput 11:3696–3713. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jctc.5b00255
Gille H, Kowalski J, Li B, LeCouter J, Moffat B, Zioncheck TF, Pelletier N, Ferrara N (2001) Analysis of biological effects and signaling properties of Flt-1 (VEGFR-1) and KDR (VEGFR-2). A reassessment using novel receptor-specific vascular endothelial growth factor mutants. J Biol Chem 276:3222–3230. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M002016200
Clegg LW, Mac Gabhann F (2015) Site-specific phosphorylation of VEGFR2 is mediated by receptor trafficking: insights from a computational model. PLoS Comput Biol 11:e1004158. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pcbi.1004158
Somanath PR, Malinin NL, Byzova TV (2009) Cooperation between integrin alphavbeta3 and VEGFR2 in angiogenesis. Angiogenesis 12:177–185. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10456-009-9141-9
Parthymou A, Lampropoulou E, Mikelis C, Drosou G, Papadimitriou E (2008) Heparin affin regulatory peptide/pleiotrophin negatively affects diverse biological activities in C6 glioma cells. Eur J Cell Biol 87:17–29. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejcb.2007.07.007
Schuck P, Zhao H (2010) The role of mass transport limitation and surface heterogeneity in the biophysical characterization of macromolecular binding processes by SPR biosensing. Methods Mol Biol 627:15–54. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-60761-670-2_2
Jäger R, List B, Knabbe C, Souttou B, Raulais D, Zeiler T, Wellstein A, Aigner A, Neubauer A, Zugmaier G (2002) Serum levels of the angiogenic factor pleiotrophin in relation to disease stage in lung cancer patients. Br J Cancer 86:858–863. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.bjc.6600202
Hamma-Kourbali Y, Bernard-Pierrot I, Heroult M, Dalle S, Caruelle D, Milhiet PE, Fernig DG, Delbé J, Courty J (2008) Inhibition of the mitogenic, angiogenic and tumorigenic activities of pleiotrophin by a synthetic peptide corresponding to its C-thrombospondin repeat-I domain. J Cell Physiol 214:250–259. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcp.21191
Diamantopoulou Z, Bermek O, Polykratis A, Hamma-Kourbali Y, Delbé J, Courty J, Katsoris P (2010) A Pleiotrophin C-terminus peptide induces anti-cancer effects through RPTPβ/ζ. Mol Cancer 9:224. https://doi.org/10.1186/1476-4598-9-224
Elahouel R, Blanc C, Carpentier G, Frechault S, Cascone I, Destouches D, Delbé J, Courty J, Hamma-Kourbali Y (2015) Pleiotrophin exerts its migration and invasion effect through the neuropilin-1 pathway. Neoplasia 17:613–624. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neo.2015.07.007
Bernard-Pierrot I, Delbe J, Caruelle D, Barritault D, Courty J, Milhiet PE (2001) The lysine-rich C-terminal tail of heparin affin regulatory peptide is required for mitogenic and tumor formation activities. J Biol Chem 276:12228–12234. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M010913200
Zhang N, Zhong R, Perez-Pinera P, Herradon G, Ezquerra L, Wang ZY, Deuel TF (2006) Identification of the angiogenesis signaling domain in pleiotrophin defines a mechanism of the angiogenic switch. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 343:653–658. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2006.03.006
Polykratis A, Katsoris P, Courty J, Papadimitriou E (2005) Characterization of heparin affin regulatory peptide signaling in human endothelial cells. J Biol Chem 280:22454–22461. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M414407200
Atkinson SJ, Ellison TS, Steri V, Gould E, Robinson SD (2014) Redefining the role(s) of endothelial αvβ3-integrin in angiogenesis. Biochem Soc Trans 42:1590–1595. https://doi.org/10.1042/BST20140206
Reynolds AR, Reynolds LE, Nagel TE, Lively JC, Robinson SD, Hicklin DJ, Bodary SC, Hodivala-Dilke KM (2004) Elevated Flk1 (vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 2) signaling mediates enhanced angiogenesis in beta3-integrin-deficient mice. Cancer Res 64:8643–8650. https://doi.org/10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-04-2760
Robinson SD, Reynolds LE, Kostourou V, Reynolds AR, da Silva RG, Tavora B, Baker M, Marshall JF, Hodivala-Dilke KM (2009) Alphav beta3 integrin limits the contribution of neuropilin-1 to vascular endothelial growth factor-induced angiogenesis. J Biol Chem 284:33966–33981. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M109.030700
Byzova TV, Goldman CK, Pampori N, Thomas KA, Bett A, Shattil SJ, Plow EF (2000) A mechanism for modulation of cellular responses to VEGF: activation of the integrins. Mol Cell 6:851–860. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1097-2765(05)00076-6
Budd S, Byfield G, Martiniuk D, Geisen P, Hartnett ME (2009) Reduction in endothelial tip cell filopodia corresponds to reduced intravitreous but not intraretinal vascularization in a model of ROP. Exp Eye Res 89:718–727. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.exer.2009.06.011
Buharalioglu CK, Song CY, Yaghini FA, Ghafoor HU, Motiwala M, Adris T, Estes AM, Malik KU (2011) Angiotensin II-induced process of angiogenesis is mediated by spleen tyrosine kinase via VEGF receptor-1 phosphorylation. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 301:H1043–H1055. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajpheart.01018.2010
Sartori A, Corno C, De Cesare M, Scanziani E, Minoli L, Battistini L, Zanardi F, Perego P (2019) Efficacy of a selective binder of α(V)β(3) integrin linked to the tyrosine kinase inhibitor sunitinib in ovarian carcinoma preclinical models. Cancers (Basel) 11:531. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers11040531
Lee WS, Pyun BJ, Kim SW, Shim SR, Nam JR, Yoo JY, Jin Y, Jin J, Kwon YG, Yun CO, Nam DH, Oh K, Lee DS, Lee SH, Yoo JS (2015) TTAC-0001, a human monoclonal antibody targeting VEGFR-2/KDR, blocks tumor angiogenesis. MAbs 7:957–968. https://doi.org/10.1080/19420862.2015.1045168
Ding G, Chen X, Zhu J, Feng Z (2014) A murine-human chimeric IgG antibody against vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 2 inhibits angiogenesis in vitro. Cytotechnology 66:395–411. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10616-013-9587-x
Xuan ZX, Li LN, Zhang Q, Xu CW, Yang DX, Yuan Y, An YH, Wang SS, Li XW, Yuan SJ (2014) Fully human VEGFR2 monoclonal antibody BC001 attenuates tumor angiogenesis and inhibits tumor growth. Int J Oncol 45:2411–2420. https://doi.org/10.3892/ijo.2014.2690
Simmons AB, Bretz CA, Wang H, Kunz E, Hajj K, Jennedy C, Yang Z, Suwanmanee T, Kafri T, Hartnett ME (2018) Gene therapy knockdown of VEGFR2 in retinal endothelial cells to treat retinopathy. Angiogenesis 21:751–764. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10456-018-9618-5
Wragg JW, Heath VL, Bicknell R (2017) Sunitinib treatment enhances metastasis of innately drug-resistant breast tumors. Cancer Res 77:1008–1020. https://doi.org/10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-16-1982
Acknowledgements
This work has been co-financed by the Operational Program “Human Resources Development, Education and Lifelong Learning” and is co-financed by the European Union (European Social Fund) and Greek national funds, by a Marie Curie Intra European Fellowship within the 7th European Community Framework Programme (ALTangioTARGET, Grant Agreement No. 626057), Andreas Mentzelopoulos family grants scholarship for postgraduate studies at the University of Patras (to PK) and the State Scholarship Foundation in Greece (IKY) (Operational Program “Human Resources Development—Education and Lifelong Learning”, Partnership Agreement (PA) 2014–2020, scholarship to EC). We thank the Advanced Light Microscopy facility of the School of Health Sciences, University of Patras, for using the Leica SP5 confocal microscope. Synthesis of PTN16−24 and PTN112−136 was performed under the supervision of our beloved Prof. Paul Cordopatis, who is deceased.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
ML, PK, FK, ΗT, SB, MSS, MK, EP, DT and AAZ performed experiments, acquired data and tools and analyzed data; ML, TT and CMM analyzed data and critically reviewed the manuscript; EP designed the study, analyzed data and wrote the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in studies involving HUVEC were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional research committee (Bioethics Committee of the University of Patras) and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lamprou, M., Kastana, P., Kofina, F. et al. Pleiotrophin selectively binds to vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 2 and inhibits or stimulates cell migration depending on ανβ3 integrin expression. Angiogenesis 23, 621–636 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10456-020-09733-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10456-020-09733-x