Abstract
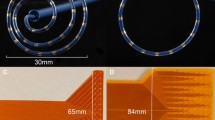
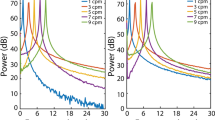
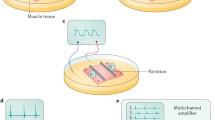
Gastric motility is governed in part by bioelectrical ‘slow waves’, and high-resolution electrical mapping has emerged as a clinical research tool with diagnostic potential. In this study, we aimed to determine the effects of electrode diameter and contact material on in vivo extracellular slow wave recordings to inform gastric mapping device design. Custom flexible-printed-circuit electrode arrays were designed with four electrode diameters (0.3, 1.8, 3.3, 4.8 mm; 4 × 8 array) and fabricated in four contact materials (gold, silver, copper, silver-chloride). The electrode arrays were placed on the gastric serosa in vivo in pigs and unipolar slow wave signals were simultaneously recorded from each electrode. Propagation, signal morphology, and noise were quantified to determine which electrodes produced signals with the highest signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) and gradient, which is a preferred metric for detection and analytical algorithms. Electrodes of diameters 0.3 and 1.8 mm recorded significantly higher signal gradients than 3.3 and 4.8 mm (p < 0.05). Silver-chloride electrodes recorded a significantly higher gradient than all other materials (p < 0.05), with no significant differences between gold, silver, and copper electrodes. Electrodes of diameters 1.8 and 3.3 mm recorded significantly higher SNR than 0.3 mm (p < 0.05). Electrodes with a diameter of 1.8 mm provided an optimal combination to maximize the signal gradient and SNR, and silver-chloride electrodes yielded the highest signal gradient. These results can now inform gastric mapping device design, particularly minimally-invasive devices where electrode size is critical.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abraham, A. C., L. K. Cheng, T. R. Angeli, S. Alighaleh, and N. Paskaranandavadivel. Dynamic slow-wave interactions in the rabbit small intestine defined using high-resolution mapping. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 31:e13670, 2019.
Alighaleh, S., L. K. Cheng, T. R. Angeli, M. Amiri, S. Sathar, G. O’Grady, and N. Paskaranandavadivel. A novel gastric pacing device to modulate slow waves and assessment by high-resolution mapping. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2019. https://doi.org/10.1109/tbme.2019.2896624.
Alvarez, W. C. The electrogastrogram and what it shows. J. Am. Med. Assoc. 78:1116–1119, 1922.
Alvarez, W. C., and L. J. Mahoney. Action currents in stomach and intestine. Am. J. Physiol. 58:476–493, 1922.
Angeli, T. R., P. Du, N. Paskaranandavadivel, P. W. M. Janssen, A. Beyder, R. G. Lentle, I. P. Bissett, L. K. Cheng, and G. O’Grady. The bioelectrical basis and validity of gastrointestinal extracellular slow wave recordings. J. Physiol. 591:4567–4579, 2013.
Angeli, T. R., G. O’Grady, N. Paskaranandavadivel, J. C. Erickson, P. Du, A. J. Pullan, I. P. Bissett, and L. K. Cheng. Experimental and automated analysis techniques for high-resolution electrical mapping of small intestine slow wave activity. J. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 19:179–191, 2013.
Angeli, T. R., L. K. Cheng, P. Du, T. H.-H. Wang, C. E. Bernard, M.-G. Vannucchi, M. S. Faussone-Pellegrini, C. Lahr, R. Vather, J. A. Windsor, G. Farrugia, T. L. Abell, and G. O’Grady. Loss of interstitial cells of Cajal and patterns of gastric dysrhythmia in patients with chronic unexplained nausea and vomiting. Gastroenterology 149:56–66.e5, 2015.
Angeli, T. R., P. Du, N. Paskaranandavadivel, A. Hall, S. J. Asirvatham, G. Farrugia, J. A. Windsor, L. K. Cheng, and G. O’Grady. High-resolution electrical mapping of porcine gastric slow-wave propagation from the mucosal surface. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 29:e13010, 2017.
Angeli, T. R., G. O’Grady, R. Vather, I. P. Bissett, and L. K. Cheng. Intra-operative high-resolution mapping of slow wave propagation in the human jejunum: feasibility and initial results. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2018. https://doi.org/10.1111/nmo.13310.
Babb, T. L., and W. Kupfer. Phagocytic and metabolic reactions to chronically implanted metal brain electrodes. Exp. Neurol. 86:171–182, 1984.
Berry, R., N. Paskaranandavadivel, P. Du, M. L. Trew, G. O’Grady, J. A. Windsor, and L. K. Cheng. A novel retractable laparoscopic device for mapping gastrointestinal slow wave propagation patterns. Surg. Endosc. 31:477–486, 2016.
Berry, R., L. K. Cheng, P. Du, N. Paskaranandavadivel, T. R. Angeli, T. Mayne, G. Beban, and G. O’Grady. Patterns of abnormal gastric pacemaking after sleeve gastrectomy defined by laparoscopic high-resolution electrical mapping. Obes. Surg. 27:1929–1937, 2017.
Bihar, E., T. Roberts, E. Ismailova, M. Saadaoui, M. Isik, A. Sanchez-Sanchez, D. Mecerreyes, T. Hervé, J. B. De Graaf, and G. G. Malliaras. Fully printed electrodes on stretchable textiles for long-term electrophysiology. Adv. Mater. Tech. 2:2–6, 2017.
Bozler, E. The action potentials of the stomach. Am. J. Physiol. 144:693–700, 1945.
Code, C. F., and J. A. Marlett. The interdigestive myo-electric complex of the stomach and small bowel of dogs. J. Physiol. 246:289–309, 1975.
Du, P., G. O’Grady, J. U. Egbuji, W. J. E. P. Lammers, D. Budgett, P. Nielsen, J. A. Windsor, A. J. Pullan, and L. K. Cheng. High-resolution mapping of in vivo gastrointestinal slow wave activity using flexible printed circuit board electrodes: methodology and validation. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 37:839–846, 2009.
Du, P., A. Hameed, T. R. Angeli, C. Lahr, T. L. Abell, L. K. Cheng, and G. O’Grady. The impact of surgical excisions on human gastric slow wave conduction, defined by high-resolution electrical mapping and in silico modeling. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 27:1409–1422, 2015.
Du, P., N. Paskaranandavadivel, T. R. Angeli, L. K. Cheng, and G. O’Grady. The virtual intestine: in silico modeling of small intestinal electrophysiology and motility and the applications. WIREs Syst. Biol. Med. 8:69–85, 2016.
Du, P., S. Calder, T. R. Angeli, S. Sathar, N. Paskaranandavadivel, G. O’Grady, and L. K. Cheng. Progress in mathematical modeling of gastrointestinal slow wave abnormalities. Front. Physiol. 8:1136, 2018.
Egbuji, J. U., G. O’Grady, P. Du, L. K. Cheng, W. J. E. P. Lammers, J. A. Windsor, and A. J. Pullan. Origin, propagation and regional characteristics of porcine gastric slow wave activity determined by high-resolution mapping. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 22:e292–e300, 2010.
Erickson, J. C., G. O’Grady, P. Du, C. Obioha, W. Qiao, W. O. Richards, L. A. Bradshaw, A. J. Pullan, and L. K. Cheng. Falling-edge, variable threshold (FEVT) method for the automated detection of gastric slow wave events in high-resolution serosal electrode recordings. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 38:1511–1529, 2010.
Hammad, F. T., B. Stephen, L. Lubbad, J. F. B. Morrison, and W. J. Lammers. Macroscopic electrical propagation in the guinea pig urinary bladder. Am. J. Physiol. Ren. Physiol. 307:F172–F182, 2014.
Hinder, R. A., and K. A. Kelly. Human gastric pacesetter potential. Site of origin, spread, and response to gastric transection and proximal gastric vagotomy. Am. J. Surg. 133:29–33, 1977.
Huizinga, J. D., and W. J. E. P. Lammers. Gut peristalsis is governed by a multitude of cooperating mechanisms. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 296:G1–G8, 2009.
Lammers, W. J. E. P., A. Al-Kais, S. Singh, K. Arafat, and T. Y. El-Sharkawy. Multielectrode mapping of slow-wave activity in the isolated rabbit duodenum. J. Appl. Phys. 74:1454–1461, 1993.
Lammers, W. J. E. P., L. Ver Donck, J. A. J. Schuurkes, and B. Stephen. Peripheral pacemakers and patterns of slow wave propagation in the canine small intestine in vivo. Can. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 83:1031–1043, 2005.
Lammers, W. J. E. P., L. Ver Donck, B. Stephen, D. Smets, and J. A. J. Schuurkes. Focal activities and re-entrant propagations as mechanisms of gastric tachyarrhythmias. Gastroenterology 135:1601–1611, 2008.
Lammers, W. J. E. P., L. Ver Donck, B. Stephen, D. Smets, and J. A. J. Schuurkes. Origin and propagation of the slow wave in the canine stomach: the outlines of a gastric conduction system. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 296:G1200–G1210, 2009.
Lammers, W. J. E. P., B. Stephen, M. A. Al-Sultan, S. B. Subramanya, and A. M. Blanks. The location of pacemakers in the uteri of pregnant guinea pigs and rats. Am. J. Physiol. Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 309:R1439–R1446, 2015.
McAdams, E. Bioelectrodes. In: Encyclopedia of Medical Devices and Instrumentation, edited by J. G. Webster. New York: Wiley, 2006, pp. 120–166.
O’Grady, G., N. Paskaranandavadivel, T. R. Angeli, P. Du, J. A. Windsor, L. K. Cheng, and A. J. Pullan. A comparison of gold versus silver electrode contacts for high-resolution gastric electrical mapping using flexible printed circuit board arrays. Physiol. Meas. 32:N13–N22, 2011.
O’Grady, G., T. R. Angeli, P. Du, C. Lahr, W. J. E. P. Lammers, J. A. Windsor, T. L. Abell, G. Farrugia, A. J. Pullan, and L. K. Cheng. Abnormal initiation and conduction of slow-wave activity in gastroparesis, defined by high-resolution electrical mapping. Gastroenterology 143(589–598):e1–e3, 2012.
O’Grady, G., T. R. Angeli, N. Paskaranandavadivel, J. C. Erickson, C. Wells, A. A. Gharibans, L. K. Cheng, and P. Du. Methods for high-resolution electrical mapping in the gastrointestinal tract. IEEE Rev. Biomed. Eng. 12:287–302, 2019.
Paskaranandavadivel, N., L. K. Cheng, P. Du, G. O’Grady, and A. J. Pullan. Improved signal processing techniques for the analysis of high resolution serosal slow wave activity in the stomach. Conf. Proc. IEEE. Eng. Med. Biol. Soc. 1:1737–1740, 2011.
Paskaranandavadivel, N., G. O’Grady, P. Du, A. J. Pullan, and L. K. Cheng. An improved method for the estimation and visualization of velocity fields from gastric high-resolution electrical mapping. IEEE. Trans. Biomed. Eng. 59:882–889, 2012.
Paskaranandavadivel, N., G. O’Grady, P. Du, and L. K. Cheng. Comparison of filtering methods for extracellular gastric slow wave recordings. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 25:79–83, 2013.
Paskaranandavadivel, N., X. Pan, P. Du, G. O’Grady, and L. K. Cheng. Detection of the recovery phase of in vivo gastric slow wave recordings. Conf. Proc. IEEE. Eng. Med. Biol. Soc. 1:6094–6097, 2015.
Putney, J., G. O’Grady, T. R. Angeli, N. Paskaranandavadivel, L. K. Cheng, J. C. Erickson, and P. Du. Determining the efficient inter-electrode distance for high-resolution mapping using a mathematical model of human gastric dysrhythmias. Conf. Proc. IEEE. Eng. Med. Biol. Soc. 1448–1451:2015, 2015.
Spach, M. S., R. C. Barr, J. W. Havstad, and E. C. Long. Skin-electrode impedance and its effect on recording cardiac potentials. Circulation 34:649–656, 1966.
Stinnett-Donnelly, J. M., N. Thompson, N. Habel, V. Petrov-Kondratov, D. D. Correa De Sa, J. H. T. Bates, and P. S. Spector. Effects of electrode size and spacing on the resolution of intracardiac electrograms. Coron. Artery Dis. 23:126–132, 2012.
Vosgueritchian, M., D. J. Lipomi, and Z. Bao. Highly conductive and transparent PEDOT:PSS films with a fluorosurfactant for stretchable and flexible transparent electrodes. Adv. Funct. Mater. 22:421–428, 2012.
Yassi, R., G. O’Grady, N. Paskaranandavadivel, P. Du, T. R. Angeli, A. J. Pullan, L. K. Cheng, and J. C. Erickson. The gastrointestinal electrical mapping suite (GEMS): software for analyzing and visualizing high-resolution (multi-electrode) recordings in spatiotemporal detail. BMC Gastroenterol. 12:60, 2012.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Dr Peng Du and Mrs Linley Nisbet for their expert assistance with this study.
Funding
This project and/or authors were supported by research grants from the Kelliher Charitable Trust, the Auckland Medical Research Foundation, the New Zealand Health Research Council (HRC), the MedTech Centre of Research Excellence New Zealand, and the Riddet Institute Centre of Research Excellence New Zealand. TRA was supported by the Edith C. Coan Postdoctoral Fellowship from the Auckland Medical Research Foundation and Rutherford Discovery Fellowship from the Royal Society of New Zealand.
Disclosure
LKC, NP, and TRA hold intellectual property in the field of gastrointestinal electrophysiology and are shareholders in FlexiMap Ltd. AAK and SA declare no conflicts of interest. No commercial financial support was provided for this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Associate Editor Xiaoxiang Zheng oversaw the review of this article.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kamat, A.A., Paskaranandavadivel, N., Alighaleh, S. et al. Effects of Electrode Diameter and Contact Material on Signal Morphology of Gastric Bioelectrical Slow Wave Recordings. Ann Biomed Eng 48, 1407–1418 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10439-020-02457-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10439-020-02457-5