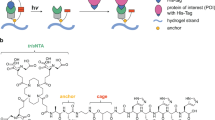
Abstract
Hydrogel materials have become a versatile platform for in vitro cell culture due to their ability to simulate many aspects of native tissues. However, precise spatiotemporal presentation of peptides and other biomolecules has remained challenging. Here we report the use of light-sensing proteins (LSPs), more commonly used in optogenetics research, as light-activated reversible binding sites within synthetic poly(ethylene glycol) (PEG) hydrogels. We used LOVTRAP, a two component LSP system consisting of LOV2, a protein domain that can cycle reversibly between “light” and “dark” conformations in response to blue light, and a z-affibody, Zdark (Zdk), that binds the dark state of LOV2, to spatiotemporally control the presentation of a recombinant protein within PEG hydrogels. By immobilizing LOV2 within PEG gels, we were able to capture a recombinant fluorescent protein (used as a model biomolecule) containing a Zdk domain, and then release the Zdk fusion protein using blue light. Zdk was removed from LOV2-containing PEG gels using focused blue light, resulting in a 30% reduction of fluorescence compared to unexposed regions of the gel. Additionally, the reversible binding capability of LOVTRAP was observed in our system, enabling our LOV2 gels to capture and release Zdk at least three times. By adding a Zdk domain to a recombinant peptide or protein, dynamic, spatially constrained displays of non-diffusing ligands within a PEG gel could feasibly be achieved using LOV2.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ai, H. W., J. N. Henderson, S. J. Remington, and R. E. Campbell. Directed evolution of a monomeric, bright and photostable version of Clavularia cyan fluorescent protein: structural characterization and applications in fluorescence imaging. Biochem. J. 400:531–540, 2006.
Alcantar, N. A., E. S. Aydil, and J. N. Israelachvili. Polyethylene glycol-coated biocompatible surfaces. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 51:343–351, 2000.
Beamish, J. A., J. M. Zhu, K. Kottke-Marchant, and R. E. Marchant. The effects of monoacrylated poly(ethylene glycol) on the properties of poly(ethylene glycol) diacrylate hydrogels used for tissue engineering. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. A 92a:441–450, 2010.
Bellucci, J. J., M. Amiram, J. Bhattacharyya, D. McCafferty, and A. Chilkoti. Three-in-one chromatography-free purification, tag removal, and site-specific modification of recombinant fusion proteins using sortase A and elastin-like polypeptides. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 52:3703–3708, 2013.
Beyer, H. M., O. S. Thomas, N. Riegel, M. D. Zurbriggen, W. Weber, and M. Horner. Generic and reversible opto-trapping of biomolecules. Acta Biomater. 79:276–282, 2018.
Boyden, E. S., F. Zhang, E. Bamberg, G. Nagel, and K. Deisseroth. Millisecond-timescale, genetically targeted optical control of neural activity. Nat. Neurosci. 8:1263–1268, 2005.
Dagliyan, O., M. Tarnawski, P. H. Chu, D. Shirvanyants, I. Schlichting, N. V. Dokholyan, and K. M. Hahn. Engineering extrinsic disorder to control protein activity in living cells. Science 354:1441–1444, 2016.
Gibson, D. G., G. A. Benders, C. Andrews-Pfannkoch, E. A. Denisova, H. Baden-Tillson, J. Zaveri, T. B. Stockwell, A. Brownley, D. W. Thomas, M. A. Algire, C. Merryman, L. Young, V. N. Noskov, J. I. Glass, J. C. Venter, C. A. Hutchison, 3rd, and H. O. Smith. Complete chemical synthesis, assembly, and cloning of a Mycoplasma genitalium genome. Science 319:1215–1220, 2008.
Guigas, G., C. Kalla, and M. Weiss. Probing the nanoscale viscoelasticity of intracellular fluids in living cells. Biophys. J . 93:316–323, 2007.
Hahn, K. M., and B. Kuhlman. Hold me tightly LOV. Nat. Methods 7:595–597, 2010.
Hahn, M. S., M. K. McHale, E. Wang, R. H. Schmedlen, and J. L. West. Physiologic pulsatile flow bioreactor conditioning of poly(ethylene glycol)-based tissue engineered vascular grafts. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 35:190–200, 2007.
Hahn, M. S., J. S. Miller, and J. L. West. Three-dimensional biochemical and biomechanical patterning of hydrogels for guiding cell behavior. Adv. Mater. 18:2679–2684, 2006.
Hammer, J. A., A. Ruta, A. M. Therien, and J. L. West. Cell compatible, site-specific covalent modification of hydrogel scaffolds enables user-defined control over cell-material interactions. Biomacromolecules 20:2486, 2019.
Hammer, J. A., and J. L. West. Dynamic ligand presentation in biomaterials. Bioconjug. Chem. 29:2140–2149, 2018.
Hayashi-Takagi, A., S. Yagishita, M. Nakamura, F. Shirai, Y. I. Wu, A. L. Loshbaugh, B. Kuhlman, K. M. Hahn, and H. Kasai. Labelling and optical erasure of synaptic memory traces in the motor cortex. Nature 525:333, 2015.
Homans, R. J., R. U. Khan, M. B. Andrews, A. E. Kjeldsen, L. S. Natrajan, S. Marsden, E. A. McKenzie, J. M. Christie, and A. R. Jones. Two photon spectroscopy and microscopy of the fluorescent flavoprotein, iLOV. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 20:16949–16955, 2018.
Leung, D. W., C. Otomo, J. Chory, and M. K. Rosen. Genetically encoded photoswitching of actin assembly through the Cdc42-WASP-Arp2/3 complex pathway. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 105:12797–12802, 2008.
Levskaya, A., O. D. Weiner, W. A. Lim, and C. A. Voigt. Spatiotemporal control of cell signalling using a light-switchable protein interaction. Nature 461:997–1001, 2009.
Li, X., D. V. Gutierrez, M. G. Hanson, J. Han, M. D. Mark, H. Chiel, P. Hegemann, L. T. Landmesser, and S. Herlitze. Fast noninvasive activation and inhibition of neural and network activity by vertebrate rhodopsin and green algae channelrhodopsin. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 102:17816–17821, 2005.
Liu, L. M., J. A. Shadish, C. K. Arakawa, K. Shi, J. Davis, and C. A. DeForest. Cyclic stiffness modulation of cell-laden protein-polymer hydrogels in response to user-specified stimuli including light. Adv. Biosyst. 2:1800240, 2018.
Lyu, S. S., J. Fang, T. Y. Duan, L. L. Fu, J. Q. Liu, and H. B. Li. Optically controlled reversible protein hydrogels based on photoswitchable fluorescent protein Dronpa. Chem. Commun. (Camb.) 53:13375–13378, 2017.
McMurtrey, R. J. Analytic models of oxygen and nutrient diffusion, metabolism dynamics, and architecture optimization in three-dimensional tissue constructs with applications and insights in cerebral organoids. Tissue Eng. C Methods 22:221–249, 2016.
Motta-Mena, L. B., A. Reade, M. J. Mallory, S. Glantz, O. D. Weiner, K. W. Lynch, and K. H. Gardner. An optogenetic gene expression system with rapid activation and deactivation kinetics. Nat. Chem. Biol. 10:196–202, 2014.
Nagel, G., M. Brauner, J. F. Liewald, N. Adeishvili, E. Bamberg, and A. Gottschalk. Light activation of channelrhodopsin-2 in excitable cells of Caenorhabditis elegans triggers rapid behavioral responses. Curr. Biol. 15:2279–2284, 2005.
Nemir, S., H. N. Hayenga, and J. L. West. PEGDA hydrogels with patterned elasticity: novel tools for the study of cell response to substrate rigidity. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 105:636–644, 2010.
Patel, P. N., A. S. Gobin, J. L. West, and C. W. Patrick, Jr. Poly(ethylene glycol) hydrogel system supports preadipocyte viability, adhesion, and proliferation. Tissue Eng. 11:1498–1505, 2005.
Polstein, L. R., and C. A. Gersbach. Light-inducible gene regulation with engineered zinc finger proteins. Methods Mol. Biol. 1148:89–107, 2014.
Polstein, L. R., and C. A. Gersbach. A light-inducible CRISPR-Cas9 system for control of endogenous gene activation. Nat. Chem. Biol. 11:198–200, 2015.
Polstein, L. R., M. Juhas, G. Hanna, N. Bursac, and C. A. Gersbach. An engineered optogenetic switch for spatiotemporal control of gene expression, cell differentiation, and tissue morphogenesis. ACS Synth. Biol. 6:2003–2013, 2017.
Salomon, M., J. M. Christie, E. Knieb, U. Lempert, and W. R. Briggs. Photochemical and mutational analysis of the FMN-binding domains of the plant blue light receptor, phototropin. Biochemistry 39:9401–9410, 2000.
Schweller, R. M., and J. L. West. Encoding hydrogel mechanics via network cross-linking structure. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 1:335–344, 2015.
Shaner, N. C., R. E. Campbell, P. A. Steinbach, B. N. Giepmans, A. E. Palmer, and R. Y. Tsien. Improved monomeric red, orange and yellow fluorescent proteins derived from Discosoma sp. red fluorescent protein. Nat. Biotechnol. 22:1567–1572, 2004.
Shimizu-Sato, S., E. Huq, J. M. Tepperman, and P. H. Quail. A light-switchable gene promoter system. Nat. Biotechnol. 20:1041–1044, 2002.
Swartz, T. E., S. B. Corchnoy, J. M. Christie, J. W. Lewis, I. Szundi, W. R. Briggs, and R. A. Bogomolni. The photocycle of a flavin-binding domain of the blue light photoreceptor phototropin. J. Biol. Chem. 276:36493–36500, 2001.
Theile, C. S., M. D. Witte, A. E. Blom, L. Kundrat, H. L. Ploegh, and C. P. Guimaraes. Site-specific N-terminal labeling of proteins using sortase-mediated reactions. Nat. Protoc. 8:1800–1807, 2013.
Tischer, D., and O. D. Weiner. Illuminating cell signalling with optogenetic tools. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 15:551–558, 2014.
Wang, H., M. Vilela, A. Winkler, M. Tarnawski, I. Schlichting, H. Yumerefendi, B. Kuhlman, R. Liu, G. Danuser, and K. M. Hahn. LOVTRAP: an optogenetic system for photoinduced protein dissociation. Nat. Methods 13:755–758, 2016.
Wang, R., Z. Yang, J. Luo, I. M. Hsing, and F. Sun. B12-dependent photoresponsive protein hydrogels for controlled stem cell/protein release. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 114:5912–5917, 2017.
Weber, L. M., C. G. Lopez, and K. S. Anseth. Effects of PEG hydrogel crosslinking density on protein diffusion and encapsulated islet survival and function. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. A 90:720–729, 2009.
Wu, Y. I., D. Frey, O. I. Lungu, A. Jaehrig, I. Schlichting, B. Kuhlman, and K. M. Hahn. A genetically encoded photoactivatable Rac controls the motility of living cells. Nature 461:104–U111, 2009.
Wylie, R. G., and M. S. Shoichet. Two-photon micropatterning of amines within an agarose hydrogel. J. Mater. Chem. 18:2716–2721, 2008.
Yoo, S. K., Q. Deng, P. J. Cavnar, Y. I. Wu, K. M. Hahn, and A. Huttenlocher. Differential regulation of protrusion and polarity by PI3K during neutrophil motility in live zebrafish. Dev. Cell 18:226–236, 2010.
Zayner, J. P., and T. R. Sosnick. Factors that control the chemistry of the LOV domain photocycle. PLoS ONE 9:e087074, 2014.
Zeskind, B. J., C. D. Jordan, W. Timp, L. Trapani, G. Waller, V. Horodincu, D. J. Ehrlich, and P. Matsudaira. Nucleic acid and protein mass mapping by live-cell deep-ultraviolet microscopy. Nat. Methods 4:567–569, 2007.
Zhou, X. X., H. K. Chung, A. J. Lam, and M. Z. Lin. Optical control of protein activity by fluorescent protein domains. Science 338:810–814, 2012.
Acknowledgments
We would like to acknowledge the generosity of Dr. Charles Gersbach for providing the blue LED array used in this study and Dr. Ashutosh Chilkoti for providing the sortase-ELP construct used to conjugate LOV2 to PEG. This work was supported by the National Science Foundation Graduate Research Fellowship under Grant Number DGE1644868.
Conflict of interest
The authors have no conflicts of interest to report.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Associate Editor Erin Lavik oversaw the review of this article.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hammer, J.A., Ruta, A. & West, J.L. Using Tools from Optogenetics to Create Light-Responsive Biomaterials: LOVTRAP-PEG Hydrogels for Dynamic Peptide Immobilization. Ann Biomed Eng 48, 1885–1894 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10439-019-02407-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10439-019-02407-w