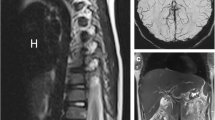
Abstract
Blood pool contrast agents such as Gadofosveset trisodium (Vasovist®, Bayer Schering Pharma AG, Berlin, Germany) are making MRA a viable first-line imaging modality for a variety of patients with venous disorders. They allow extended imaging and multiple acquisitions without loss of resolution with a single low-dose injection. The methodology is robust and can be adjusted to the patient without causing workflow problems. The emphasis of this article is on the venous applications of the blood pool contrast agent Vasovist® including venous visualisation to plan surgical and interventional procedures and venous thromboembolism, in the form of deep vein thrombosis (DVT) and pulmonary embolism (PE), where MRA with blood pool agents can help to avoid exposure to ionising radiation.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Davidson BL et al (1992) Low accuracy of color Doppler US in the detection of proximal leg vein thrombosis in asymptomatic high risk patients. Ann Intern Med 117:735–738
Turkstra F et al (1997) Diagnostic utility of ultrasonography of leg veins in patients suspected of having pulmonary embolism. Ann Intern Med 126:775–781
Kroencke T J, Taupitz M, Arnold R, et al. Three-dimensional gadolinium-enhanced magnetic resonance venography in suspected thromboocclusive disease of the central chest veins. Chest. 2001; 120:1570–1576.
Rose S C, Gomes A S, Yoon H C. MR angiography for mapping potential central venous access sites in patients with advanced venous occlusive disease. AJR. American Journal of Roentgenology. 1996; 166:1181–1187.
Prince M R, Sostman H D. MR venography: unsung and underutilized. Radiology. 2003; 226: 630–632.
Fraser D G, Moody A R, Davidson I R, et al. Deep venous thrombosis: diagnosis by using venous enhanced subtracted peak arterial MR venography versus conventional venography. Radiology. 2003; 226:812–820
Roditi G et al (1996) MR venography of left renal vein anomalies. Clin Radiol 51:861–864
Kluge A, Luboldt W, Bachmann G (2006) Acute pulmonary embolism to the subsegmental level: diagnostic accuracy of three MRI techniques compared with 16-MDCT. AJR Am J Roentgenol 187:W7–14
Parker MS, Hui FK, Camacho MA, Chung JK, Broga DW, Sethi NN (2005) Female breast radiation exposure during CT pulmonary angiography. AJR Am J Roentgenol, 185:1228–1233
Wells PS, Ginsberg JS, Anderson DR, Kearon C, Gent M, Turpie AG, Bormanis J, Weitz J, Chamberlain M, Bowie D, Barnes D, Hirsh J (1998) Use of a clinical model for safe management of patients with suspected pulmonary embolism. Ann Intern Med 129:997–1005
Fink C, Ley S, Schoenberg SO, Reiser MF, Kauczor HU. (2007) Magnetic resonance imaging of acute pulmonary embolism. Eur Radiol; 17:2546–2553
Meaney JF, Weg JG, Chenevert TL, Stafford-Johnson D, Hamilton BH, Prince MR. (1997) Diagnosis of pulmonary embolism with magnetic resonance angiography. N Engl J Med; 336:1422–1427
Gupta A, Frazer CK, Ferguson JM, et al. (1999) Acute pulmonary embolism: diagnosis with MR angiography. Radiology; 210:353–359
Oudkerk M, van Beek EJ, Wielopolski P, et al. (2002) Comparison of contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance angiography and conventional pulmonary angiography for the diagnosis of pulmonary embolism: a prospective study. Lancet; 359:1643–1647
Blum A, Bellou A, Guillemin F, Douek P, Laprevote-Heully MC, Wahl D. (2005) Performance of magnetic resonance angiography in suspected acute pulmonary embolism. Thromb Haemost; 93:503–511
Pleszewski B, Chartrand-Lefebvre C, Qanadli SD, et al. (2006) Gadolinium-enhanced pulmonary magnetic resonance angiography in the diagnosis of acute pulmonary embolism: a prospective study on 48 patients. Clin Imaging; 30:166–172
Kluge A, Luboldt W, Bachmann G. (2006) Acute pulmonary embolism to the subsegmental level: diagnostic accuracy of three MRI techniques compared with 16-MDCT. AJR Am J Roentgenol; 187:W7–14
Goyen M, Laub G, Ladd ME, et al. (2001) Dynamic 3D MR angiography of the pulmonary arteries in under four seconds. J Magn Reson Imaging; 13:372–377
Ohno Y, Higashino T, Takenaka D, et al. (2004) MR angiography with sensitivity encoding (SENSE) for suspected pulmonary embolism: comparison with MDCT and ventilation-perfusion scintigraphy. AJR Am J Roentgenol; 183:91–98
Einstein AJ, Henzlova MJ, Rajagopalan S. (2007) Estimating risk of cancer associated with radiation exposure from 64-slice computed tomography coronary angiography. Jama; 298:317–323
Parker MS, Hui FK, Camacho MA, Chung JK, Broga DW, Sethi NN. (2005) Female breast radiation exposure during CT pulmonary angiography. AJR Am J Roentgenol; 185:1228–1233
Wells PS, Ginsberg JS, Anderson DR, et al. (1998) Use of a clinical model for safe management of patients with suspected pulmonary embolism. Ann Intern Med; 129:997–1005
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Roditi, G., Fink, C. Venous MR imaging with blood pool agents. Eur Radiol Suppl 18 (Suppl 5), 3–11 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10406-009-0240-x
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10406-009-0240-x