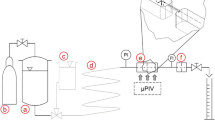
Abstract
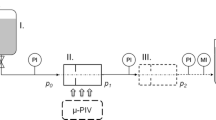
Micro-particle image velocimetry was used as an optical, non-intrusive measurement method to measure the flow pattern and visualise droplet deformation in high-pressure homogenisation disruption units of two different inlet designs (sharp-edged and conical). The flow patterns were compared either at same Reynolds numbers \({\text{(}}Re=980)\) or pressure differences (\(\Delta p=52~{\text{bar}}\)) each, to describe the influence of inlet geometry on the droplet disruption efficiency. Therefore, the shear and elongation rates were calculated from the velocity profiles and discussed regarding the visualised deformation of the emulsion droplets. For this, the viscosity ratio between the droplet and continuous phase was varied. Afterwards, the droplet size distributions (DSD) of emulsions with corresponding viscosity ratio passing the sharp-edged and the conical orifice were characterised. The inlet geometry influenced the flow pattern, shear and elongation rate profile, droplet deformation and finally droplet size distributions during the high-pressure homogenisation. On the one hand, sharp-edged inlet design resulted in higher axial velocity profiles and smaller droplets with slightly bimodal character. On the other hand, conical inlet design resulted in perfectly monomodal DSD but comparatively bigger droplets.
Graphical abstract











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adrian RJ, Westerweel J (2011) Particle image velocimetry. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Aguilar F, Köhler K, Schubert H, Schuchmann HP (2008) Herstellen von Emulsionen in einfachen und modifizierten Lochblenden: Einfluss der Geometrie auf die Effizienz der Zerkleinerung und Folgen für die Maßstabsvergrößerung. Chem Ing Tec 80(5):607–613
Ball CG, Fellouah H, Pollard A (2012) The flow field in turbulent round free jets. Prog Aerosp Sci 50:1–26
Bentley BJ, Leal LG (1986) An experimental investigation of drop deformation and breakup in steady, two-dimensional linear flows. J Fluid Mech 167(1):241
Bisten A, Schuchmann HP (2016) Optical measuring methods for the investigation of high-pressure homogenisation. Processes 4(41):1–19
Blonski S, Korczyk PM, Kowalewski TA (2007) Analysis of turbulence in a micro-channel emulsifier. Int J Therm Sci 46(11):1126–1141
Breuer MM (1985) Applications in the cosmetical industry. In: Becher P (ed) Encyclopedia of emulsion technology, volume 2: Applications. Marcel Dekker, Inc, New York
Brösel S, Schubert H (2001) Droplet disruption and coalescence in high-pressure homogenizers. In: Proceedings of the eighth international congress on engineering and food—ICEF, 8–1, pp 638–642
Budde C, Schaffner D, Walzel P (2002) Drop breakup in liquid-liquid dispersions at an orifice plate observed in a large-scale model. ChemEngTechnol 25(12):1164–1167
Cierpka C, Rossi M, Segura R, Mastrangelo F, Kähler CJ (2012) A comparative analysis of the uncertainty of astigmatism-mu PTV, stereo-mu PIV, and mu PIV. Exp Fluids 52(3):605–615
Danner T, Schubert H (2001) Coalescence processes in emulsions. In: Dickinson E, Miller R (eds), Food colloids: fundamentals of formulation, The Royal Society of Chemistry, London, pp 116–124
Davis SS, Hadgraft J, Palin KJ (1985) Medical and pharmaceutical applications of emulsions. In: Becher P (ed) Encyclopedia of emulsion technology, Volume 2: applications. Marcel Dekker, Inc, New York, pp 159–238
Floury J, Desrumaux A, LardiÞres J (2000) Effect of high-pressure homogenization on droplet size distributions and rheological properties of model oil-in-water emulsions. Innov Food Sci Emerg Technol 1(2):127–134
Gothsch T, Finke JH, Beinert S, Lesche C, Schur J, Buttgenbach S, Muller-Goymann C, Kwade A (2011) Effect of microchannel geometry on high-pressure dispersion and emulsification. ChemEngTechnol 34(3):335–343
Gothsch T, Schilcher C, Richter C, Beinert S, Dietzel A, Büttgenbach S, Kwade A (2014) High-pressure microfluidic systems (HPMS): flow and cavitation measurements in supported silicon microsystems. Microfluid Nanofluid 18(1):121–130
Gothsch T, Richter C, Beinert S, Schilcher C, Schilde C, Büttgenbach S, Kwade A (2016) Effect of cavitation on dispersion and emulsification process in high-pressure microsystems (HPMS). Chem Eng Sci 144:239–248
Grace HP (1982) Dispersion phenomena in high-viscosity immiscible fluid systems and application of static mixers as dispersion devices in such systems. Chem Eng Commun 14(3–6):225–277
Håkansson A, Fuchs L, Innings F, Revstedt J, Tragardh C, Bergenstahl B (2011) High resolution experimental measurement of turbulent flow field in a high pressure homogenizer model and its implications on turbulent drop fragmentation. ChemEngSci 66(8):1790–1801
Håkansson A, Innings F, Revstedt J, Trägårdh C, Bergenståhl B (2012) Estimation of turbulent fragmenting forces in a high-pressure homogenizer from computational fluid dynamics. Chem Eng Sci 75:309–317
Heusch R (1987) Emulsions. In: Gerhartz W, Ullmann F (eds) Ullmanns encyclopedia of industrial chemistry, 5th edn. VCH, Weinheim
Innings F, Tragardh C (2007) Analysis of the flow field in a high-pressure homogenizer. ExpThermFluid Sci 32(2):345–354
Kähler CJ, Scholz U, Ortmanns J (2006) Wall-shear-stress and near-wall turbulence measurements up to single pixel resolution by means of long-distance micro-PIV. Exp Fluids 41(2):327–341
Kähler CJ, Scharnowski S, Cierpka C (2012) On the resolution limit of digital particle image velocimetry. Exp Fluids 52(6):1629–1639
Karbstein H (1994) Untersuchungen zum Herstellen und Stabilisieren von Öl-in-Wasser-Emulsionen. Dissertation, Karlsruhe
Keane RD, Adrian RJ (1990) Optimization of particle image velocimeters. I. Double pulsed systems. Meas Sci Technol 1(11):1202–1215
Kelemen K, Crowther FE, Cierpka C, Hecht LL, Kähler CJ, Schuchmann HP (2014) Investigations on the characterization of laminar and transitional flow conditions after high pressure homogenization orifices. Microfluid Nanofluid 18(4):599–612
Kelemen K, Gepperth S, Koch R, Bauer H-J, Schuchmann HP (2015) On the visualization of droplet deformation and breakup during high-pressure homogenization. Microfluid Nanofluid 19(5):1139–1158
Kissling K, Schütz S, Piesche M (2011) Numerical investigation on the deformation of droplets in high-pressure homogenizers. In: Nagel WE, Kröner DB, Resch MM (eds) High performance computing in science and engineering ‘10. Springer, Stuttgart, pp 287–294
Köhler K, Schuchmann HP (2015) High-pressure homogenization with microstructured systems. In: Engineering aspects of food emulsification and homogenization. CRC Press, Boca Raton, pp 169–194
Kolb G, Wagner G, Ulrich J (2001) Untersuchungen zum Aufbruch von Einzeltropfen in Dispergiereinheiten zur Emulsionsherstellung. Chem Ing Tec 73:80–83
Koutsiaris AG, Mathioulakis DS, Tsangaris S (1999) Microscope PIV for velocity-field measurement of particle suspensions flowing inside glass capillaries. Meas Sci Technol 10(11):1037–1046
Lindken R, Rossi M, Grosse S, Westerweel J (2009) Micro-particle image velocimetry (microPIV): recent developments, applications, and guidelines. Lab A Chip 9(17):2551–2567
Massey BS, John W-S (1998) Mechanics of fluids. Crc Press
Meinhart CD, Wereley ST, Santiago JG (1999) PIV measurements of a microchannel flow. Exp Fluids 27(5):414–419
Merkel T, Hecht LL, Schoth A, Wagner C, Munoz-Espí R, Landfester K, Schuchmann HP (2015) Continuous preparation of polymer/inorganic composite nanoparticles via miniemulsion polymerization. In: Kind M, Peukert W, Rehage H, Schuchmann HP (eds) Colloid process engineering. Springer, Heildeberg, pp 345–370
Mielnik MM, Saetran LR (2004) Micro particle image velocimetry—an overview. Turbulence 10:83–90
Phipps LW (1975) The fragmentation of oil droplets in emulsions by a high-pressure homogenizer. JPhysD ApplPhys 8:448
Phipps LW (1982) Homogenizing valve design and its influence on milk fat globule dispersion II. High rate of flow. J Dairy Res 49:317–322
Plateau JAF (1873) Statique expérimentale et théorique des liquides soumis aux seules forces moléculaires. AcadSciBruxMem 2
Raffel M, Willert CE, Wereley ST, Kompenhans J (2007) Particle image velocimetry: a practical guide. Springer, Dordrecht
Ramamurthi K, Nandakumar K (1999) Characteristics of flow through small sharp-edged cylindrical orifices. Flow Meas Instrum 10(3):133–143
Reynolds O (1883) An experimental investigation of the circumstances which determine whether the motion of water shall be direct or sinuous, and of the law of resistance in parallel channels. Philos Trans R Soc Lond 174:935–982
Rossi M, Segura R, Cierpka C, Kähler CJ (2012) On the effect of particle image intensity and image preprocessing on the depth of correlation in micro-PIV. Exp Fluids 52(4):1063–1075
Rumscheidt FD, Mason SG (1961) Particle motions in sheared suspensions. XII. Deformation and burst of fluid drops in shear and hyperbolic flow. J Colloid Sci 16(3):238–261
Santiago JG, Wereley ST, Meinhart CD, Beebe DJ, Adrian RJ (1998) A particle image velocimetry system for microfluidics. Exp Fluids 25(4):316–319
Schlender M, Minke K, Schuchmann HP (2016) Sono-chemiluminescence (SCL) in a high-pressure double stage homogenization processes. Chem Eng Sci 142:1–11
Schuchmann HP (2016) Hydrodynamic pressure processing for enhancing emulsification and dispersion. In: Knoerzer K, Juliano P, Smithers GW (eds) Innovative food processing technologies: extraction, separation, component modification, and process intensification. Woodhead Publishing, Oxford
Stang M, Schuchmann HP, Schubert H (2001) Emulsification in high-pressure homogenizers. Eng Life Sci 1(4):151–157
Steiner H, Teppner R, Brenn G, Vankova N, Tcholakova S, Denkov N (2006) Numerical simulation and experimental study of emulsification in a narrow-gap homogenizer. ChemEngSci 61(17):5841–5855
Stone HA (1994) Dynamics of drop deformation and breakup in viscous fluids. Annu Rev Fluid Mech 26(1):65–102
Stone HA, Bentley BJ, Leal LG (1986) An experimental-study of transient effects in the breakup of viscous drops. J Fluid Mech 173:131–158
Taylor GI (1934) The formation of emulsions in definable fields of flow. Proc R Soc Lond Ser A 146(858):501–523
Tesch S, Schubert H (2001) Droplet deformation and disruption during the emulsification in a high-pressure homogenizer with an orifice valve. Chem Ing Tec 73(6):693
Tesch S, Freudig B, Schubert H (2002) Herstellen von Emulsionen in Hochdruckhomogenisatoren—Teil 1: Zerkleinern und Stabilisieren von Tropfen. Chem Ing Tec 74(6):875–880
Walstra P (1983) Formation of emulsions. In: Becher P (ed) Encyclopedia of emulsion technology, vol 1. Marcel Dekker Inc, New York, pp 57–128
Walstra P (1997) Making emulsions and foams: an overview. In: Dickinson E (ed) Food colloids: proteins, lipids and polysaccharides, papers pres. Ystad, Sweden on 24–26 April 1996, special publication/Royal society of chemistry; 192, Cambridge
Wereley ST, Meinhart CD (2010) Recent advances in micro-particle image velocimetry. Annu Rev Fluid Mech 42(1):557–576
Wibel W (2009) Untersuchungen zu laminarer, transitioneller und turbulenter Strömung in rechteckigen Mikrokanälen
Acknowledgements
The work has been carried out with financial support of the German Research Foundation (DFG) within the research project SCHU 1417/11-1.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
HPK had the principal idea for this approach; the experimental approach was first tested by KK, AB and HPK; AB and HPK conceived and designed the experiments for this paper; AB and DR performed the experiments; AB analysed the data; DS and HL from the Institute for Micro Process Engineering (Micro Apparatus Engineering—FAB) contributed to the micro manufacturing of the orifices; AB and HPK discussed and analysed the results; AB and HPK wrote the paper.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The founding sponsors had no role in the design of the study, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, and in the decision to publish the results.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Heike P. Karbstein: formerly: Schuchmann.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bisten, A., Rudolf, D. & Karbstein, H.P. Comparison of flow patterns and droplet deformations of modified sharp-edged and conical orifices during high-pressure homogenisation using µPIV. Microfluid Nanofluid 22, 57 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10404-018-2076-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10404-018-2076-y