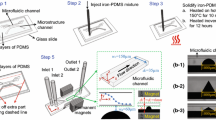
Abstract
Superconducting magnets enable the study of high magnetic fields on materials and objects, for example in material synthesis, self-assembly or levitation experiments. The setups employed often lack in precise spatial control of the object of interest within the bore of the magnet. Microfluidic technology enables accurate manipulation of fluidic surroundings and we have investigated the integration of microfluidic devices into superconducting magnets to enable controlled studies of objects in high magnetic fields. Polymeric microparticles similar in size to biological cells were manipulated via diamagnetic repulsion. The particles were suspended in an aqueous paramagnetic medium of manganese (II) chloride and pumped into a microfluidic chip, where they were repelled in continuous flow by the high magnetic field. The extent of deflection was studied as a function of increasing (1) particle size, (2) paramagnetic salt concentration, and (3) magnetic field strength. Optimizing these parameters allowed for the spatial separation of two particle populations via on-chip free-flow diamagnetophoresis. Finally, preliminary findings on the repulsion of air bubbles are shown.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Beaugnon E, Tournier R (1991) Levitation of organic materials. Nature 349(6309):470
Berry MV, Geim AK (1997) Of flying frogs and levitrons. Eur J Phys 18:307–313
Gijs MAM (2004) Magnetic bead handling on-chip: new opportunities for analytical applications. Microfluid Nanofluid 1(1):22–40
Gijs MAM, Lacharme F, Lehmann U (2010) Microfluidic applications of magnetic particles for biological analysis and catalysis. Chem Rev 110(3):1518–1563
Guevorkian K, Valles JM (2006) Swimming Paramecium in magnetically simulated enhanced, reduced, and inverted gravity environments. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 103(35):13051–13056
Hahn YK, Park JK (2011) Versatile immunoassays based on isomagnetophoresis. Lab Chip 11(12):2045–2048
Han KH, Frazier AB (2004) Continuous magnetophoretic separation of blood cells in microdevice format. J Appl Phys 96(10):5797–5802
Han KH, Frazier AB (2005) Diamagnetic capture mode magnetophoretic microseparator for blood cells. J Microelectromech Syst 14(6):1422–1431
Happel J, Brenner H (1973) Low Reynolds number hydrodynamics. 2nd revised edn. Noordhoff International Publishing, Leyden
Hirota N, Kurashige M, Iwasaka M, Ikehata M, Uetake H, Takayama T, Nakamura H, Ikezoe Y, Ueno S, Kitazawa K (2004) Magneto-Archimedes separation and its application to the separation of biological materials. Phys B 346–347:267–271
Iiguni Y, Suwa M, Watarai H (2004) High-magnetic-field electromagnetophoresis of micro-particles in a capillary flow system. J Chromatogr A 1032(1–2):165–171
Ikezoe Y, Hirota N, Nakagawa J, Kitazawa K (1998) Making water levitate. Nature 393(6687):749
Iles A, Oki A, Pamme N (2007) Bonding of soda-lime glass microchips at low temperature. Microfluid Nanofluid 3(1):119–122
Kang JH, Choi S, Lee W, Park JK (2008) Isomagnetophoresis to discriminate subtle difference in magnetic susceptibility. J Am Chem Soc 130:396–397
Kose AR, Fischer B, Mao L, Koser H (2009) Label-free cellular manipulation and sorting via biocompatible ferrofluids. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 106(51):21478–21483
Liang L, Zhu J, Xuan X (2011) Three-dimensional diamagnetic particle deflection in ferrofluid microchannel flows. Biomicrofluidics 5(3):034110
Liu Y, Zhu D-M, Strayer DM, Israelsson UE (2010) Magnetic levitation of large water droplets and mice. Adv Space Res 45(1):208–213
Lorin C, Mailfert A, Chatain D (2010) Design of a large oxygen magnetic levitation facility. Microgravity Sci Tec 22(1):71–77
McCreedy T (2001) Rapid prototyping of glass and PDMS microstructures for micro total analytical systems and micro chemical reactors by microfabrication in the general laboratory. Anal Chim Acta 427(1):39–43
Motokawa M, Hamai M, Sato T, Mogi I, Awaji S, Watanabe K, Kitamura N, Makihara M (2001) Crystal growth and materials processing in the magnetic levitation condition. J Magn Magn Mater 226–230(Part 2):2090–2093
Pamme N (2006) Magnetism and microfluidics. Lab Chip 6(1):24–38
Pamme N, Manz A (2004) On-chip free-flow magnetophoresis: continuous flow separation of magnetic particles and agglomerates. Anal Chem 76(24):7250–7256
Pamme N, Wilhelm C (2006) Continuous sorting of magnetic cells via on-chip free-flow magnetophoresis. Lab Chip 6(8):974–980
Pamme N, Eijkel JCT, Manz A (2006) On-chip free-flow magnetophoresis: separation and detection of mixtures of magnetic particles in continuous flow. J Magn Magn Mater 307(2):237–244
Park JI, Nie Z, Kumachev A, Abdelrahman AI, Binks BP, Stone HA, Kumacheva E (2009) A microfluidic approach to chemically driven assembly of colloidal particles at gas-liquid interfaces. Angew Chem Int Ed 48:5300–5303
Peyman SA, Kwan EY, Margarson O, Iles A, Pamme N (2009) Diamagnetic repulsion-A versatile tool for label-free particle handling in microfluidic devices. J Chromatogr A 1216(52):9055–9062
Quettier L, Vincent-Viry O, Mailfert A, Juster FP (2003) Micro-gravity: superconducting coils for crystal growth. Influence of the levitation force on natural convection in the fluid. Eur Phys J Appl Phys 22(1):69–73
Rodriguez-Villarreal AI, Tarn MD, Madden LA, Lutz JB, Greenman J, Samitier J, Pamme N (2011) Flow focussing of particles and cells based on their intrinsic properties using a simple diamagnetic repulsion setup. Lab Chip 11(7):1240–1248
Tagami M, Hamai M, Mogi I, Watanabe K, Motokawa M (1999) Solidification of levitating water in a gradient strong magnetic field. J Cryst Growth 203(4):594–598
Tarn MD, Hirota N, Iles A, Pamme N (2009a) On-chip diamagnetic repulsion in continuous flow. Sci Technol Adv Mater 10(1):014611
Tarn MD, Peyman SA, Robert D, Iles A, Wilhelm C, Pamme N (2009b) The importance of particle type selection and temperature control for on-chip free-flow magnetophoresis. J Magn Magn Mater 321(24):4115–4122
Valles JM, Lin K, Denegre JM, Mowry KL (1997) Stable magnetic field gradient levitation of Xenopus laevis: Toward low-gravity simulation. Biophys J 73(2):1130–1133
Watarai H, Namba M (2001) Magnetophoretic behavior of single polystyrene particles in aqueous manganese (II) chloride. Anal Sci 17(10):1233–1236
Watarai H, Namba M (2002) Capillary magnetophoresis of human blood cells and their magnetophoretic trapping in a flow system. J Chromatogr A 961(1):3–8
Watarai H, Suwa M, Iiguni Y (2004) Magnetophoresis and electromagnetophoresis of microparticles in liquids. Anal Bioanal Chem 378(7):1693–1699
Winkleman A, Gudiksen KL, Ryan D, Whitesides GM, Greenfield D, Prentiss M (2004) A magnetic trap for living cells suspended in a paramagnetic buffer. Appl Phys Lett 85(12):2411–2413
Winkleman A, Perez-Castillejos R, Gudiksen KL, Phillips ST, Prentiss M, Whitesides GM (2007) Density-based diamagnetic separation: devices for detecting binding events and for collecting unlabeled diamagnetic particles in paramagnetic solutions. Anal Chem 79(17):6542–6550
Yin DC, Lu HM, Geng LQ, Shi ZH, Luo HM, Li HS, Ye YJ, Guo WH, Shang P, Wakayama NI (2008) Growing and dissolving protein crystals in a levitated and containerless droplet. J Cryst Growth 310(6):1206–1212
Zhang K, Liang Q, Ai X, Hu P, Wang Y, Luo G (2011a) On-demand microfluidic droplet manipulation using hydrophobic ferrofluid as a continuous-phase. Lab Chip 11(7):1271–1275
Zhang K, Liang QL, Ai XN, Hu P, Wang YM, Luo GA (2011b) Comprehensive two-dimensional manipulations of picoliter microfluidic droplets sampled from nanoliter samples. Anal Chem 83(20):8029–8034
Zhu T, Marrero F, Mao L (2010) Continuous separation of non-magnetic particles inside ferrofluids. Microfluid Nanofluid 9(4):1003–1009
Zhu T, Cheng R, Mao L (2011a) Focusing microparticles in a microfluidic channel with ferrofluids. Microfluid Nanofluid 11(6):695–701
Zhu T, Lichlyter D, Haidekker M, Mao L (2011b) Analytical model of microfluidic transport of non-magnetic particles in ferrofluids under the influence of a permanent magnet. Microfluid Nanofluid 10(6):1233–1245
Zhu J, Liang L, Xuan X (2012) On-chip manipulation of nonmagnetic particles in paramagnetic solutions using embedded permanent magnets. Microfluid Nanofluid 12(1–4):65–73
Acknowledgments
The authors thank the National Institute for Materials Science (NIMS, Japan) for funding.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Vojtíšek, M., Tarn, M.D., Hirota, N. et al. Microfluidic devices in superconducting magnets: on-chip free-flow diamagnetophoresis of polymer particles and bubbles. Microfluid Nanofluid 13, 625–635 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10404-012-0979-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10404-012-0979-6