Abstract
Aim
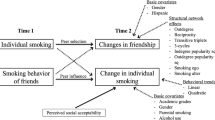
The present study aimed to examine the effects of primary social factors on the smoking behaviors according to the smoking stages—initiation and continuation—among Korean adolescents.
Subject and methods
We used the clustered logistic regression method to examine whether the primary social factors significantly influence smoking behaviors among Korean adolescents at two different stages with a cross-sectional study for 9 years.
Results
We found that primary social factors significantly influenced adolescent smoking in both stages, and peer effects for adolescent smoking were much clearer in the smoking continuation stage. In addition, adolescents initiating smoking early tend to continue their smoking with high probability.
Conclusion
The impacts of primary social factors are robust on adolescent smoking, particularly in the smoking continuation stage.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agresti A (2007) An introduction to categorical data analysis, 2nd edn. Wiley, Hoboken
Aker RL (1988) Social learning and social structure: a general theory of crime and deviance. Northeastern University Press, Boston
Alexander C, Piazza M, Mekos D et al (2001) Peers, schools, and adolescent cigarette smoking. J Adolescent Health 29:22–30
Armitage P (1955) Tests for linear trends in proportions and frequencies. Biometrics 11:375–386
Asparouhov T (2006) General multi-level modeling with sampling weights. Comm Stat Theory Methods 35:439–460
Avenevoli S, Merikangas K (2003) Familial influences on adolescent smoking. Addiction 98:1–20
Bandura A (1977) Social learning theory. Prentice Hall, Englewood Cliffs
Bauman K, Carver K, Gleiter K (2001) Trends in parents and friend influence during adolescent: the case of adolescent cigarette smoking. Addict Behav 26:349–361
Center for Disease Control and Prevention (1994) Preventing tobacco use among young people: a report of the surgeon general. Atlanta, GA
Chassin L, Presson C, Sherman S (1995) Social psychological antecedents and consequences of adolescent tobacco use. In: Wallander J, Siegel L (eds) Adolescent health problems: behavioral perspectives advances in pediatric psychology. Guilford, New York, pp 141–159
Cochran W (1954) Some methods of strengthening the common χ2 test. Biometrics 10:417–451
Cussen A, McCool J (2011) Tobacco promotion in the Pacific: the current state of tobacco promotion bans and options for accelerating progress. Asia Pac J Public Health 23:70–78
Dick B, Ferguson BJ (2015) Health for the world’s adolescents: a second chance in the second decade. J Adolesc Health 56:3–6
Duncan T, Tildesley E, Duncan S, Hops H (1995) The consistency of family and peer influences on the development of substance use in adolescence. Addiction 90:1647–1660
Eiser J, van der Pligt J (1984) Attitudinal and social factors in adolescent smoking: in search of peer group influence. J Appl Soc Psychol 14:348–363
Eiser J, Morgan M, Gammage P, Brooks N, Kirby R (1991) Adolescent health behavior and similarity-attraction: friends share smoking habits (really), but much else besides. British J Soc Psychol 30:339–348
Ezzati M, Lopez AD, Rodgers A et al (2002) Selected major risk factors and global and regional burden of disease. Lancet 360:1347–1360
Freund K, D’Agostino R, Belanger A, Kannel W, Stokes J 3rd (1992) Predictors of smoking cessation: the Framingham study. Am J Epidemiol 135:957–964
Garrow J, Webster J (1985) Quetelet’s index (W/H2) as a measure of fatness. Int J Obes 9:147–153
Godtfredsen N, Prescott E, Osler M, Vestbo J (2001) Predictors of smoking reduction and cessation in a cohort of Danish moderate and heavy smokers. Prev Med 33:46–52
Johnston L, O’Malley P, Bachman J (1995) National survey results on drug use from the monitoring the future study, 1975–1994. National Institute of Health, National Institute on Drug Abuse, Rockville, MD (Pub. No. 95-4026)
Jung M, Chung D (2012) Evidence of social contextual effects on adolescent smoking in South Korea. Asia Pac J Public Health 25:260–270
Kessler D, Witt A, Barnette P et al (1996) The food and drug administration’s regulation of tobacco products. N Engl J Med 335:988–994
Kim Y, Choi S, Chun C et al (2016) Data resource profile: the Korea youth risk behavior web-based survey (KYRBS). Int J Epidemiol 45:1076–1076e
Kobus K (2003) Peers and adolescent smoking. Addiction 98:37–55
Oetting ER, Beauvais F (1986) Peer cluster theory: drugs and the adolescent. J Counsel Dev 65:17–30
Pettitt A (1979) A non-parametric approach to the change-point problem. J Royal Stat Soc C 28:126–135
Sawyer S (2018) The age of adolescence. Lancet Child Adolescent Health 2:223–228
US Department of Health and Human Services (USDHHS) (1998) Tobacco use among high school students-United States, 1997. Morb Mortal Wkly Rep 47:229–233
Urberg K, Shyu S, Liang J (1990) Peer influence in adolescent cigarette smoking. Addict Behav 15:247–255
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
The study subjects in the present study were a part of KNHANES, which is an ongoing nationwide epidemiology study conducted by the division of Chronic Disease Control and Prevention, Ministry of Health and Welfare. All participants signed written informed consent forms, and the study was approved by institutional review board.
Conflict of interest
All authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Financial supports
No specific funding has been provided.
Authorship statement
All authors listed meet the authorship criteria according to the lastest guidelines of the international Committee of Medical Journal Editors and all authors are in agreement with the manuscript.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lee, E., Kwon, A.M. Primary social factors and smoking in Korean adolescents. J Public Health (Berl.) 30, 1251–1256 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10389-020-01400-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10389-020-01400-1