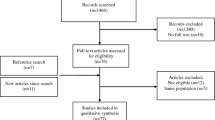
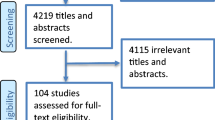
Abstract
Background
The prevalence of gout varied in different populations and it appeared to be increasing in the past decades. Gout is a serious health issue and is an independent risk factor for heart failure and metabolic. Therefore, we have used the method of meta-analysis to systematically evaluate the prevalence of gout in mainland China and have provided relevantly informative data for gout prevention and control.
Methods
Relevant articles from 2000 to 2016 October were identified by searching four electronic databases: PubMed, Chinese WanFang, CNKI, and Chongqing VIP. All of the calculations were performed using the MetaAnalyst beta 3.13 and R3.3 software.
Results
In all, 30 eligible articles (1 in English and 29 in Chinese) were included with a total sample size of 146,081. The pooled prevalence of gout was 1.1% (95% CI: 0.8%, 1.5%). Subgroup analysis showed the following results: 1.7 and 0.5% for male and female; 1.3 and 1.0% for inland and coast, respectively; 1.4, 1.0 and 0.7% for urban, city and rural areas; 1.0 and 1.6% for community and hospital; 1.2, 1.7, and 0.8% for eastern, central and western region; 1.0, 1.1 and 1.3% for 2000–2005, 2006–2009 and 2010–2016, respectively.
Conclusion
The prevalence of gout in mainland China is an ascendant trend that differs according to sex and region.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chen X-Y, Yang H-d, Yang J-Y (2009) Prevalence of hyperuricemia and gout among urban residents in Dali, Yunnan. China Prac Med 4:257–259
China Center for Disease Control and Prevention (2016) Nutritional status and alcohol intake. In: Health N, Family Planning Commission of the People’s Republic of China (eds) Report on Chinese Nutrition and Chronic Disease (2015), 1st edn. People’s Medical Publishing House, Beijing, pp 11–60
Choi HK, Atkinson K, Karlson EW, Willett W, Curhan G (2014) Purine-rich food, dairy and protein intake, and the risk of gout in men. N Engl J Med 350:1093–1103
Cui S-F, Wang X-D, Tian Z-l, Wei H-C, Tian X-J, Yin Y-S (2014) Epidemiological study on hyperuricemia and gout in community of Yu county in Hebei Province. Chin J Hemorh 24:501–515
Fang W-G, Huang X-M, Wang Y, Chen W, Zhu W-g, Chen J-l, Zeng X-J (2006) Epidemiological investigation of gout in some people in Beijing area. Basic Med Clin 26:781–985
Guang B-S, Bai X, Xu H, Zhou X-J, YI X-L, Wang Y-Q, Qiu H-B (2013) Quantitative analysis of gout and hyperuricemia in recent 10 years. Heilongjiang Med Pharma 36:51–53
Guo R-S, Li X-Y, Li Y-X, Zou Y-Y (2011) Epidemiological investigation of gout in Harbin area. Chin J Disability 19:117
Harris CM, Lloyd DC, Lewis J (1995) The prevalence and prophylaxis of gout in England. J Clin Epidemiol 48:1153–1158
Hu Y-Y, Yimamu M, Ayipaxia A (2011) Epidemiological survey of hyperuricemia and gout in Uygur population of Xinjiang. J Chin Pract Diagnosis Therapy 25:876–881
Huang J-T, Zhou B-H, Chen S-S, Dong J-B (2013) A cross-sectional study on gout and hyperuricemia in community population. Zhejiang Preventive Med J 25:8–10
Li R, Sun J, Ren L-M, Wang H-Y, Liu W-H, Zhang X-W, Chen S, Mu R, He J, Zhao Y, Long L, Liu Y-Y, Liu X, Lu X-L, Li Y-H, Wang S-Y, Pan S-S, Li C, Wang H-Y, Li Z-G (2012) Epidemiology of eight common rheumatic diseases in China: a large-scale cross-sectional survey in Beijing. Rheumatology (Oxford) 51:721–729 https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/?term=Epidemiology+rheumatic+diseases+China. Accessed 20 October 2016
Liu R, Han C, Wu D, Xia X, Gu J, Guan H, Shan Z, Teng W (2015) Prevalence of hyperuricemia and gout in Mainland China from 2000 to 2014: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Biomed Res Int 1–12. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/?term=Prevalence+Gout+China.+Biomed+Res+Int. Accessed 20 October 2016
Liu X-Q, Wang X-P, Guan L-Q, Zhe H-X, He H-R, Zhang X (2016) Prevalence and associated risk factors of hyperuricemia and gout in Han, Uygur, Kazak, Xibe of Xinjiang Ili Kazak autonomous prefecture. Chin J Gen Practice 14:1186–1192
Mao Y-S, Zhou L-N, Ye H-Y, Huang T, Chen C-X, Du J, Hong Z-L, Hu R-M (2006) Epidemiological survey on prevalences of hyperuricemia and gout in staff of a petrochemical corporation in Ningbo. Chin J Endocrinol Metab 22:338–341
Miao Z-M, Zhao S-H, Wang Y-G, Li C-G, Wang Z-C, Chen Y, Chen X-Y, Yan S-L (2006) Epidemiological survey of hyperuricemia and gout in coastal areas of Shangdong province. Chin J Endocrinol Metab 22:421–425
Nuki G, Simkin PA (2006) A concise history of gout and hyperuricemia and their treatment. Arthritis Res Ther 8:1–5
Pan P-X (2008) Epidemiological investigation of gout in Shenzhen area. Chin J Misdiagn 8:7807–7808
Shao J-H, Mo B-Q, Yu R-B, Li Z, Liu H, Xu Y-C (2003) Epidemiological study on hyperuricemia and gout in community of Nanjing. Chin J Dis Control Prev 7:305–308
Song W, Liu J-D, Chen Z-X, Huo Y, Lin A-H, Jiang Y-L (2014) Hyperuricemia and gout: a prevalence survey among over-40-year old community residents in Nanchang District. Chin Gen Practice J 17:181–184
Wallace SL, Robinson H, Masi AT, Decker JL, McCarty DJ, Yü TF (1977) Preliminary criteria for the classification of the acute arthritis of primary gout. Arthritis Rheum 20:895–900
Wang K, Fu Z-J, Li C-G, Liu S-G, Miao Z-M, Yan S-L, Wang Y-G, Meng D-M, Han L (2010) Survey of hyperuricemia and gout in two villages of Fushan township of Zhaoyuan in Shandong province. Acta Academiae Medicinae Qingdao Universitatis 46:380–383
Wang M, Jiang X, Wu W, Zhang D (2013) A meta-analysis of alcohol consumption and the risk of gout. Clin Rheumatol 32:1641–1648
Wang Q-W, Chen R, Du L-C, Zeng Q-X (2001) An epidemiological and clinical study of primary gout. Chin J Intern Med 40:313–315
Wu L-J, Song X-Y, Ku E-B, Shi Y-M, Huang C-B, Huang J, Liu A-H, Mikelayi, Teng Y-F, Gu L-N, Meng X-Y, Shan X-J, Mu Y-S, Yuan A-P, Zhang L (2012) Epidemiological study on hyperuricemia and gout in Uygur population in Turpan area Xinjiang. J Peking University (Health Sciences) 44:250–253
Wu W-R, Guo J-M, Yang W, Luo H-B (2007) Investigation on the prevalence of gout and hyperuricemia in 1482 people of physical examination in Guangzhou City. Hainan Med J 18:110–112
Wu W-R, Guo J-M, Yang W, Zhong Z-G, Liu Y-H, Luo H-B (2008) Investigation on prevalence of gout and hyperuricemia in community of Guangzhou City. Gen Practice Chin Med 6:728–729
Yan S-L, Zhao S-H, Li C-G, Wang Y-G, Wang P, Wang Z-C, Wang F, Chen Y, Wang F, Miao Z-M (2011) A five years follow up study on patients with gout and hyperuricemia. Chin J Endocrinol Metab 27:548–551
Yang J (2006) The study and redivision of China’s economic regionalization. Commercial Times 32:44–46
Yang L-H, Song J, Shi L, LV X-M, Amina, Yang S-L, Basangpichi, Meng S-Y (2015) Epidemiological survey on hyperuricemia and gout among urban population of Lhasa. Med J West China 27:1476–1478
Yao Z-L, Jiang S-J, Liu H, Wan X-Q, Ding Z-G (2007) Epidemiological study on hyperuricemia and gout in the coastal area of Qingdao city. Chin J Rheumato 11:672–675
Yu J-W, Yang T-G, Diao W-X, Cai X-Q, Li T, Zhong H, Hu D-L, Chen C-Q, Chen Z-X (2010) An epidemiological survey of hyperuricemia and gout among residents in Foshan, Guangdong Province. Chin J Epidemiol 31:860–862
Yuan S, Li X-M, Ma Y-T, Ma X, Huang Y, Fu Z-Y, Xie X, Liu F, Wang L, Pan S (2011) Epidemiological survey of hyperuricemia and gout in Xinjiang adult population. Chin J Endocrinol Metab 27:570–572
Zai F-Y, He Y-N, Ma G-S, Li Y-P, Wang Z-H, Hu Y-S, Zhao L-Y, Cui Z-H, Li Y, Yang X-G (2005) The current situation and trend of food consumption of urban and rural residents in China. Chin J Epidemiol 26:485–488
Zeng X-G, Chen B, Zeng F, Hou C-Z, He Q, Huang L, Wu J-W, Chen Q-Q (2008) Epidemiological survey of common rheumatic in Guangxi Nanning Zhuang population. J Practical Med 24:1432–1434
Zeng X-G (2005) Epidemiological investigation of hyperuricemia and gout in Nanning railway workers. Heilongjiang Med Pharma 29:876–877
Zhang L-Z, Zhou Y-X (2010) Epidemiological survey of gout and hyperuricemia among young people in the community of Tangshan City. J Shandong University (Medical Science edn.) 48:163–164
Zhang P, Zhang L, Wang C-H, Wei S-P, Qiao Q-Z (2014) Prevalence of hyperuricemia and gout among people over 30 years old in Xingtai mountainous area. Practical Preventive Med 21:1010–1012
Zhang X-S, Yu W-G, Yu L-X, Zhang L-Y, Yu Y (2006) An epidemiologic study on hyperuricaemia and gout in residents of coastal areas of Haiyang City in Shandong. Chin J Gen Pract 5:216–219
Zhao F-H (2016) Epidemiological investigation and analysis of gout in Xiping County. Health Mag 10:25
Zhou J-M, Yang J, Dong J-L, Zhang Y, Tian L, Gu Y (2011) Epidemiological survey of hyperuricemia and gout in northern Sichuan Qiang people. Contemp Med 17:12–14
Zhou K, Xia M (2015) An epidemiological survey of hyperuricemia and gout in the residents of Hong Kong. Int J Lab Med 36:707–709
Zhu Y, Pandya BJ, Choi HK (2011) Prevalence of gout and hyperuricemia in the US general population: the National Health and nutrition examination survey 2007–2008. Arthritis Rheum 63:3136–3141
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Funding
This study was not funded
Conflict of interests
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interests regarding the publication of this paper.
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Informed consent
Informed consent was not obtained from all individual participants included in the study, because it is secondary source.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, Y., Tang, Z., Huang, Z. et al. The prevalence of gout in mainland China from 2000 to 2016: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Public Health 25, 521–529 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10389-017-0812-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10389-017-0812-5