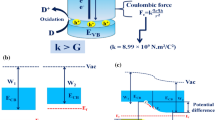
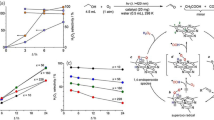
Abstract
Environmental and energy crises are a major threat to the sustainable growth of the human society, calling for greener technologies such as photocatalysis. Photocatalysis is a solar-driven approach that converts photon energy into chemical energy, yet the conversion efficacy of classical photocatalysis is usually restricted and controlled by the charge carrier’s separation and migration. Enhanced conversion requires suppressed recombination rate and superior redox abilities. From this aspect, the manipulation of heterojunction allows to overcome the drawback of classical photocatalysis. The cascade mechanism follows a dual direct charge migration route, resulting in enhanced redox abilities and efficient mineralization of pollutants. Here, we review photocatalytic material aspects in improving redox ability by cascade charge transfer. We describe the mechanisms and applications of three cascade systems: two type-II cascade systems, mediator-based cascade systems, and dual direct Z-scheme. We highlight the superiority of the direct dual cascade route with a prolonged lifetime of carriers, higher quantum yield, and enhanced redox abilities. Applications to carbon dioxide reduction, hydrogen production by water splitting and pollutant degradation are discussed.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Acar C et al (2016) Review of photocatalytic water-splitting methods for sustainable hydrogen production. Int J Energy Res 40(11):1449–1473. https://doi.org/10.1002/er.3549
Bhoi YP et al (2020) Single step combustion synthesis of novel Fe2TiO5/α-Fe2O3/TiO2 ternary photocatalyst with combined double type-II cascade charge migration processes and efficient photocatalytic activity. Appl Surf Sci 525:146571. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2020.146571
Bian J (2021) Energy platform for directed charge transfer in the cascade Z-scheme heterojunction: CO2 Photoreduction without a Cocatalyst. Angew Chem Int Ed 60(38):20906–20914. https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.202106929
Chandel N et al (2020) Magnetically separable ZnO/ZnFe2O4 and ZnO/CoFe2O4 photocatalysts supported onto nitrogen doped graphene for photocatalytic degradation of toxic dyes. Arab J Chem 13(2):4324–4340. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arabjc.2019.08.005
Chatterjee D et al (2005) Visible light induced photocatalytic degradation of organic pollutants. J Photochem Photobiol, C 6(2–3):186–205. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jphotochemrev.2005.09.001
Chnadel N et al (2020) Z-scheme photocatalytic dye degradation on AgBr/Zn (Co)Fe2O4 photocatalysts supported on nitrogen-doped graphene. Mater Today Sustain 9:100043. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arabjc.2019.08.005
Dai T et al (2021) Performance and mechanism of photocatalytic degradation of tetracycline by Z–scheme heterojunction of CdS@ LDHs. Appl Clay Sci 212:106210. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clay.2021.106210
Dutta V et al (2019) Review on augmentation in photocatalytic activity of CoFe2O4 via heterojunction formation for photocatalysis of organic pollutants in water. J Saudi Chem Soc 23(8):1119–1136. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jscs.2019.07.003
Fakhravar S et al (2020) Excellent performance of a novel dual Z-scheme Cu2S/Ag2S/BiVO4 heterostructure in metronidazole degradation in batch and continuous systems: immobilization of catalytic particles on α-Al2O3 fiber. Appl Surf Sci 505:144599. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2019.144599
Fu CF et al (2018) Nov) Material Design for Photocatalytic Water Splitting from a Theoretical Perspective. Adv Mater 30(48):e1802106. https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.201802106
Habibi-Yangjeh A et al (2020) Anchoring Bi4O5I2 and AgI nanoparticles over g-C3N4 nanosheets: Impressive visible-light-induced photocatalysts in elimination of hazardous contaminates by a cascade mechanism. Adv Powder Technol 31(7):2618–2628. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apt.2020.04.030
Hasija V et al (2019) Carbon quantum dots supported AgI/ZnO/phosphorus doped graphitic carbon nitride as Z-scheme photocatalyst for efficient photodegradation of 2, 4-dinitrophenol. J Environ Chem Eng 7(4):103272. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2019.103272
He Y et al (2020) Aug) Construction of a new cascade photogenerated charge transfer system for the efficient removal of bio-toxic levofloxacin and rhodamine B from aqueous solution: mechanism, degradation pathways and intermediates study. Environ Res 187:109647. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envres.2020.109647
Hu J et al (2020) Metal-free heterojunction of black phosphorus/oxygen-enriched porous g-C3N4 as an efficient photocatalyst for Fenton-like cascade water purification. J Mater Chem A 8(37):19484–19492. https://doi.org/10.1039/D0TA06993K
Kudo A et al (2009) Heterogeneous photocatalyst materials for water splitting. Chem Soc Rev 38(1):253–278. https://doi.org/10.1039/b800489g
Kumar A et al (2020) Perspective and status of polymeric graphitic carbon nitride based Z-scheme photocatalytic systems for sustainable photocatalytic water purification. Chem Eng J 391:123496. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2019.123496
Kumar A et al (2021) C-, N-Vacancy defect engineered polymeric carbon nitride towards photocatalysis: viewpoints and challenges. J Mater Chem A 9(1):111–153. https://doi.org/10.1039/D0TA08384D
Kumar A et al (2022a) Artificial leaf for light-driven CO2 reduction: Basic concepts, advanced structures and selective solar-to-chemical products. Chem Eng J 430:133031. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2021.133031
Kumar A et al (2022b) CO2 photoreduction into solar fuels via vacancy engineered bismuth-based photocatalysts: selectivity and mechanistic insights. Chem Eng J. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2022.135563
Li Z et al (2015) Solar fuel production: Strategies and new opportunities with nanostructures. Nano Today 10(4):468–486. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nantod.2015.06.001
Li M et al (2017) Design of a novel dual Z-scheme photocatalytic system composited of Ag2O modified Ti3+ self doped TiO2 nanocrystals with individual exposed (001) and (101) facets. Mater Charact 124:136–144. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matchar.2016.12.011
Li X et al (2018) Graphene-based heterojunction photocatalysts. Appl Surf Sci 430:53–107. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2017.08.194
Li X et al (2021) A review of material aspects in developing direct Z-scheme photocatalysts. Mater Today. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mattod.2021.02.017
Liu W et al (2018) Dual Z-scheme g-C3N4/Ag3PO4/Ag2MoO4 ternary composite photocatalyst for solar oxygen evolution from water splitting. Appl Surf Sci 456:369–378. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2018.06.156
Liu HY et al (2019) Facile assembly of g-C3N4/Ag2CO3/graphene oxide with a novel dual Z-scheme system for enhanced photocatalytic pollutant degradation. Appl Surf Sci 475:421–434. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2019.01.018
Loh JY et al (2021) Persistent CO2 photocatalysis for solar fuels in the dark. Nat Sustain 4(6):466–473. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41893-021-00681-y
Low J et al (2015) Graphene-based photocatalysts for CO2 reduction to solar fuel. J Phys Chem Lett 6(21):4244–4251. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jpclett.5b01610
Low J et al (2017) A review of direct Z-scheme photocatalysts. Small Methods 1(5):1700080. https://doi.org/10.1002/smtd.201700080
Mao J et al (2013) Recent advances in the photocatalytic CO2 reduction over semiconductors. Catal Sci Technol 3(10):2481–2498. https://doi.org/10.1039/C3CY00345K
Meng A et al (2019) Dual cocatalysts in TiO2 photocatalysis. Adv Mater 31(30):e1807660. https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.201807660
Nandal N et al (2022) A review on progress and perspective of molecular catalysis in photoelectrochemical reduction of CO2. Coord Chem Rev 451:214271. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ccr.2021.214271
Obregón S et al (2016) Cascade charge separation mechanism by ternary heterostructured BiPO4/TiO2/g-C3N4 photocatalyst. Appl Catal B 184:96–103. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2015.11.027
Ola O et al (2015) Review of material design and reactor engineering on TiO2 photocatalysis for CO2 reduction. J Photochem Photobiol, C 24:16–42. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jphotochemrev.2015.06.001
Palanisamy G et al (2021) Two-dimensional g-C3N4 nanosheets supporting Co3O4-V2O5 nanocomposite for remarkable photodegradation of mixed organic dyes based on a dual Z-scheme photocatalytic system. Diam Relat Mater 118:108540. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.diamond.2021.108540
Palanivel B et al (2020) Conversion of a type-II to a Z-scheme heterojunction by intercalation of a 0D electron mediator between the integrative NiFe2O4/g-C3N4 composite nanoparticles: boosting the radical production for photo-fenton degradation. ACS Omega 5(31):19747–19759. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsomega.0c02477
Qiao J et al (2014) A review of catalysts for the electroreduction of carbon dioxide to produce low-carbon fuels. Chem Soc Rev 43(2):631–675. https://doi.org/10.1039/c3cs60323g
Ran J et al (2014) Earth-abundant cocatalysts for semiconductor-based photocatalytic water splitting. Chem Soc Rev 43(22):7787–7812. https://doi.org/10.1039/c3cs60425j
Raza A et al (2020) Studies of Z-scheme WO3-TiO2/Cu2ZnSnS4 ternary nanocomposite with enhanced CO2 photoreduction under visible light irradiation. J CO2 Utilization 37:260–271. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcou.2019.12.020
Sharma K et al (2019) Recent advances in enhanced photocatalytic activity of bismuth oxyhalides for efficient photocatalysis of organic pollutants in water: a review. J Ind Eng Chem 78:1–20. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jiec.2019.06.022
Sharma K et al (2021) ZnS-based quantum dots as photocatalysts for water purification. J Water Process Eng 43:102217. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jwpe.2021.102217
Sharma K et al (2022) Strategies and perspectives of tailored SnS2 photocatalyst for solar driven energy applications. Sol Energy 231:546–565. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.solener.2021.11.041
Shi W et al (2020) Fabrication of ternary Ag3PO4/Co3(PO4)2/g-C3N4 heterostructure with following Type II and Z-Scheme dual pathways for enhanced visible-light photocatalytic activity. J Hazard Mater 389:121907. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2019.121907
Shit SC et al (2020) Integrated nano-architectured photocatalysts for photochemical CO2 reduction. Nanoscale 12(46):23301–23332. https://doi.org/10.1039/D0NR05884J
Singh P et al (2013) Preparation of BSA-ZnWO4 nanocomposites with enhanced adsorptional photocatalytic activity for methylene blue degradation. Int J Photoenergy. https://doi.org/10.1155/2013/726250
Tang M et al (2020) Facile synthesis of dual Z-scheme g-C3N4/Ag3PO4/AgI composite photocatalysts with enhanced performance for the degradation of a typical neonicotinoid pesticide. Appl Catal B 268:118395. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2019.118395
Tian L et al (2019) Fabrication of dual direct Z-scheme g-C3N4/MoS2/Ag3PO4 photocatalyst and its oxygen evolution performance. Appl Surf Sci 463:9–17. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2018.08.209
Tian Y et al (2021) Sep) A direct dual Z-scheme 3DOM SnS2-ZnS/ZrO2 composite with excellent photocatalytic degradation and hydrogen production performance. Chemosphere 279:130882. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2021.130882
Wageh S et al (2021) A new heterojunction in photocatalysis: S-scheme heterojunction. Chin J Catal 42(5):667. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1872-2067(20)63705-6
Wang M et al (2016) Jun) Plasmon-Mediated Solar Energy Conversion via Photocatalysis in Noble Metal/Semiconductor Composites. Adv Sci (weinh) 3(6):1600024. https://doi.org/10.1002/advs.201600024
Wang M et al (2019) Direct double Z-scheme Og-C3N4/Zn2SnO4N/ZnO ternary heterojunction photocatalyst with enhanced visible photocatalytic activity. Appl Surf Sci 492:690–702. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2019.06.260
Wang K et al (2021a) Insights into the development of Cu-based photocathodes for carbon dioxide (CO2) conversion. Green Chem 23(9):3207–3240. https://doi.org/10.1039/D0GC04417B
Wang K et al (2021b) Zinc sulfide quantum dots/zinc oxide nanospheres/bismuth-enriched bismuth oxyiodides as Z-scheme/type-II tandem heterojunctions for an efficient charge separation and boost solar-driven photocatalytic performance. J Colloid Interface Sci 592:259–270. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2021.02.051
Wang Z et al (2021c) Advances in designing heterojunction photocatalytic materials. Chin J Catal 42(5):710–730. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1872-2067(20)63698-1
Wei Z et al (2020) A review on photocatalysis in antibiotic wastewater: Pollutant degradation and hydrogen production. Chin J Catal 41(10):1440–1450. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1872-2067(19)63448-0
Xu Q et al (2018) Direct Z-scheme photocatalysts: Principles, synthesis, and applications. Mater Today 21(10):1042–1063. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mattod.2018.04.008
Xu Q et al (2020) S-Scheme Heterojunction Photocatalyst. Chem 6(7):1543–1559. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chempr.2020.06.010
Yang Y et al (2018) Efficient nanomaterials for harvesting clean fuels from electrochemical and photoelectrochemical CO2 reduction. Sustainable Energy Fuels 2(3):510–537. https://doi.org/10.1039/C7SE00371D
Yoon TP et al (2010) Visible light photocatalysis as a greener approach to photochemical synthesis. Nat Chem 2(7):527–532. https://doi.org/10.1038/nchem.687
Yu C et al (2017) One-pot facile synthesis of Bi2S3/SnS2/Bi2O3 ternary heterojunction as advanced double Z-scheme photocatalytic system for efficient dye removal under sunlight irradiation. Appl Surf Sci 420:233–242. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2017.05.147
Yu H et al (2020) Enhanced photocatalytic degradation of tetracycline under visible light by using a ternary photocatalyst of Ag3PO4/AgBr/g-C3N4 with dual Z-scheme heterojunction. Sep Purif Technol 237:116365. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2019.116365
Yuan L et al (2017) Multichannel charge transfer and mechanistic insight in metal decorated 2D–2D Bi2WO6–TiO2 cascade with enhanced photocatalytic performance. Small 13(48):1702253. https://doi.org/10.1002/smll.201702253
Yuan Y et al (2021) A review of metal oxide-based Z-scheme heterojunction photocatalysts: actualities and developments. Mater Today Energy. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mtener.2021.100829
Zhang Y et al (2015) Titanate and titania nanostructured materials for environmental and energy applications: a review. RSC Adv 5(97):79479–79510. https://doi.org/10.1039/C5RA11298B
Zhang M et al (2018) Double Z-scheme system of silver bromide@ bismuth tungstate/tungsten trioxide ternary heterojunction with enhanced visible-light photocatalytic activity. J Colloid Interface Sci 509:18–24. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2017.08.095
Zhang J et al (2020a) Synthesis of novel ternary dual Z-scheme AgBr/LaNiO3/g-C3N4 composite with boosted visible-light photodegradation of norfloxacin. Molecules 25(16):3706. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25163706
Zhang R et al (2020b) Solvothermal synthesis of a peony flower-like dual Z-scheme PANI/BiOBr/ZnFe2O4 photocatalyst with excellent photocatalytic redox activity for organic pollutant under visible-light. Sep Purif Technol 234:116098. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2019.116098
Zhao G et al (2017) Progress in catalyst exploration for heterogeneous CO2 reduction and utilization: a critical review. J Mater Chem A 5(41):21625–21649. https://doi.org/10.1039/C7TA07290B
Zhao H et al (2020) Recent advances in metal organic frame photocatalysts for environment and energy applications. Appl Mater Today 21:100821. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apmt.2020.100821
Zhao W et al (2021) A novel Z-scheme CeO2/g-C3N4 heterojunction photocatalyst for degradation of bisphenol A and hydrogen evolution and insight of the photocatalysis mechanism. J Mater Sci Technol 85:18–29. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmst.2020.12.064
Zheng Z et al (2020) Rational design of type-II nano-heterojunctions for nanoscale optoelectronics. Mater Today Phys. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mtphys.2020.100262
Zhou P et al (2014) All-solid-state Z-scheme photocatalytic systems. Adv Mater 26(29):4920–4935. https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.201400288
Zhu M et al (2017) Boosting the visible-light photoactivity of BiOCl/BiVO4/N-GQD ternary heterojunctions based on internal Z-scheme charge transfer of N-GQDs: simultaneous band gap narrowing and carrier lifetime prolonging. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 9(44):38832–38841. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.7b14412
Funding
Dr. Quyet Van Le was supported by Brain Pool Program through the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) funded by the Ministry of Science and ICT (No. 2020H1D3A1A04081409).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study conception and designed the idea for the article. Literature search, data collection, and analysis were performed by Kusum Sharma and Abhinandana Kumar. The first draft of the manuscript was written by Kusum Sharma, and all authors commented on previous versions of the manuscript. Pardeep Singh, Chuanyi Wang, Van-Huy Nguyen, and Pankaj Raizada critically revised the work. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no interests to disclose.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sharma, K., Kumar, A., Ahamad, T. et al. Improving the redox performance of photocatalytic materials by cascade-type charge transfer: a review. Environ Chem Lett 20, 2781–2795 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10311-022-01466-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10311-022-01466-1