Abstract
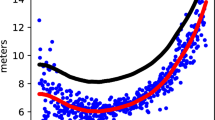
Global Navigation Satellite System (GNSS) meteorology, in which the zenith total delay (ZTD) and precipitable water vapor (PWV) are retrievable from GNSS signals, is a well-established tool for weather and climate monitoring. The real-time provision of ZTD/PWV products has always been challenging in GNSS meteorology, which is basically limited by the timely accessibility to precise satellite ephemerides. GNSS open service is based on the broadcast ephemerides. The accuracy of Galileo broadcast ephemerides has been improved to a high level, enabling real-time retrieval of ZTD/PWV using Galileo open service and being independent of network communication environments and devices. Moreover, building additional data processing systems and dense ground tracking networks is no longer necessary (excluding issues necessitating extremely accurate real-time ZTD/PWV retrievals, such as the PWV along coastal boundaries). We propose the real-time precise point positioning (PPP) technology with Galileo broadcast ephemerides to retrieve the high-accuracy ZTD/PWV. The data sets from 22 globally distributed stations spanning a year are used for analysis. Results indicate that the accuracy of real-time ZTD estimates derived from ambiguity-float solutions can reach to 2 cm after an average initialization time of 52.9 min. Taking international GNSS service (IGS) and radiosonde results as the reference, the mean bias of ZTD and PWV errors is usually less than 6 and 2 mm, respectively, while the standard deviation (STD) is 15.7 and 2.5 mm. The performance of ZTD/PWV estimates is nearly comparable to that of IGS real-time data streams, while it is worse than that of IGS post-processed precise products.














Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets at selected MGEX stations, the broadcast ephemerides, the post-processed precise products from WHU, and the ZTD products provided by IGS can be obtained from ftp://igs.gnsswhu.cn. The real-time precise products from CNES can be obtained from http://www.ppp-wizard.net/products/REAL_TIME/. The NCEP GFS forecast products can be downloaded for free at the website https://rda.ucar.edu/datasets/ds084.1/. The IGRA radiosonde data are freely accessible via the link http://www1.ncdc.noaa.gov/pub/data/igra/.
References
Baby HB, Golé P, Lavergnat J (1988) A model for the tropospheric excess path length of radio waves from surface meteorological measurements. Radio Sci 23(6):1023–1038. https://doi.org/10.1029/RS023i006p01023
Bahadur B (2022) An improved weighting strategy for tropospheric delay estimation with real-time single-frequency precise positioning. Earth Sci Inf 15(2):1267–1284. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12145-022-00814-7
Bennitt GV, Jupp A (2012) Operational assimilation of GPS zenith total delay observations into the met office numerical weather prediction models. Mon Weather Rev 140(8):2706–2719. https://doi.org/10.1175/MWR-D-11-00156.1
Bock O, Bosser P, Pacione R, Nuret M, Fourrie N, Parracho A (2016) A high-quality reprocessed ground-based GPS dataset for atmospheric process studies, radiosonde and model evaluation, and reanalysis of HyMex special observing period. Q J R Meteorol Soc 142(S1):56–71. https://doi.org/10.1002/qj.2701
Carlin L, Hauschild A, Montenbruck O (2021) Precise point positioning with GPS and Galileo broadcast ephemerides. GPS Solut 25(2):77. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10291-021-01111-4
Chen B, Liu Z (2016) A comprehensive evaluation and analysis of the performance of multiple tropospheric models in China region. IEEE Trans Geosci Remote Sens 54(2):663–678. https://doi.org/10.1109/TGRS.2015.2456099
Chen B, Yu W, Wang W, Zhang Z, Dai W (2021) A global assessment of precipitable water vapor derived from GNSS zenith tropospheric delays with ERA5, NCEP FNL, and NCEP GFS products. Earth Space Sci 8(8):e2021001796
Chen G, Wei N, Li M, Zhao Q, Zhang J (2022) BDS-3 and GPS/Galileo integrated PPP using broadcast ephemerides. GPS Solut 26(4):129. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10291-022-01311-6
Dousa J, Vaclavovic P (2014) Real-time zenith tropospheric delays in support of numerical weather prediction applications. Adv Space Res 53(9):1347–1358. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asr.2014.02.021
Gendt G, Dick G, Reigber C, Tomassini M, Liu Y, Ramatschi M (2004) Near real time GPS water vapor monitoring for numerical weather prediction in Germany. J Meteorol Soc Jpn 82(1B):361–370. https://doi.org/10.2151/jmsj.2004.361
Gradinarsky LP, Elgered G (2000) Horizontal gradients in the wet path delay derived from four years of microwave radiometer data. Geophys Res Lett 27(16):2521–2524. https://doi.org/10.1029/2000GL011427
Guerova G, Jones J, Dousa J, Dick G, Haan SD, Pottiaux E, Bock O, Pacione R, Elgered G, Vedel H, Bender M (2016) Review of the state-of-the-art and future prospects of the ground-based GNSS meteorology in Europe. Atmos Measur Tech 9(11):5385–5406. https://doi.org/10.5194/amt-9-5385-2016
Hadas T, Hobiger T (2021) Benefits of using Galileo for real-time GNSS meteorology. IEEE Geosci Remote Sens Lett 18(10):1756–1760. https://doi.org/10.1109/LGRS.2020.3007138
Hadas T, Teferle FN, Kazmierski K, Hordyniec P, Bosy J (2017) Optimum stochastic modeling for GNSS tropospheric delay estimation in real-time. GPS Solut 21(3):1069–1081. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10291-016-0595-0
Karabatic A, Weber R, Haiden T (2011) Near real-time estimation of tropospheric water vapour content from ground based GNSS data and its potential contribution to weather now-casting in Austria. Adv Space Res 47(10):1691–1703. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asr.2010.10.028
Li X, Dick G, Lu C, Ge M, Nilsson T, Ning T, Wickert J, Schuh H (2015) Multi-GNSS meteorology: Real-time retrieving of atmospheric water vapor from BeiDou, Galileo, GLONASS, and GPS observations. IEEE Trans Geosci Remote Sens 53(12):6385–6393. https://doi.org/10.1109/TGRS.2015.2438395
Li X, Tan H, Li X, Dick G, Wickert J, Schuh H (2018) Real-time sensing of precipitable water vapor from BeiDou observations: Hong Kong and CMONOC networks. J Geophys Res Atmos 123(15):7897–7909. https://doi.org/10.1029/2018JD028320
Lu C, Li X, Nilsson T, Ning T, Heinkelmann R, Ge M, Glaser S, Schuh H (2015) Real-time retrieval of precipitable water vapor from GPS and BeiDou observations. J Geodesy 89(9):843–856. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00190-015-0818-0
Lu C, Li X, Cheng J, Dick G, Ge M, Wickert J, Schuh H (2018) Real-time tropospheric delay retrieval from multi-gnss ppp ambiguity resolution: validation with final troposphere products and a numerical weather model. Remote Sens 10(3):481. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs10030481
Niell E, Coster AJ, Solheim FS, Mendes VB, Toor PC, Langley RB, Upham CA (2001) Comparison of measurements of atmospheric wet delay by radiosonde, water vapor radiometer, GPS, and VLBI. J Atmos Oceanic Tech 18(6):830–850. https://doi.org/10.1175/1520-0426(2001)018%3c0830:COMOAW%3e2.0.CO;2
Pan L, Guo F (2018) Real-time tropospheric delay retrieval with GPS, GLONASS. Galileo BDS Data Sci Rep 8:17067. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-018-35155-3
Xu Y, Ma L, Zhang F, Chen X, Yang Z (2023) Accuracy analysis of real-time precise point positioning—estimated precipitable water vapor under different meteorological conditions: a case study in Hong Kong. Atmosphere 14(4):650. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos14040650
Yuan Y, Zhang K, Rohm W, Choy S, Norman R, Wang C-S (2014) Real-time retrieval of precipitable water vapor from GPS precise point positioning. J Geophys Res Atmos 119(16):10044–10057. https://doi.org/10.1002/2014jd021486
Zhang Z, Pan L (2022) Current performance of open position service with almost fully deployed multi-GNSS constellations: GPS, GLONASS, Galileo, BDS-2, and BDS-3. Adv Space Res 69(5):1994–2019. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asr.2021.12.002
Zhao Q, Yao Y, Yao W, Li Z (2018) Real-time precise point positioning-based zenith tropospheric delay for precipitation forecasting. Sci Rep 8:7939. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-018-26299-3
Zhao Q, Yao Y, Yao W, Zhang S (2019) GNSS-derived PWV and comparison with radiosonde and ECMWF ERA-Interim data over mainland China. J Atmos Solar Terr Phys 182:85–92. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jastp.2018.11.004
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank the IGS for providing GNSS data sets and the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration for providing the IGRA radiosonde data. We also thank the National Centers for Environmental Prediction/National Weather Service/NOAA/U.S. Department of Commerce for contributing the NCEP GFS data. This research was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 41904030), and the Natural Science Foundation of Hunan Province, China (Grant No. 2020JJ5706).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study and design. LP and MD performed material preparation, data collection, and analysis. LP and BC wrote the first draft of the manuscript, and all authors commented on previous versions of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Pan, L., Deng, M. & Chen, B. Real-time GNSS meteorology: a promising alternative using real-time PPP technique based on broadcast ephemerides and the open service of Galileo. GPS Solut 28, 113 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10291-024-01659-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10291-024-01659-x