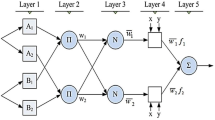
Abstract
We propose using the generalized regression neural network (GRNN) method for spatio-temporal modeling of ionosphere total electron content (TEC). The GRNN model uses radial basis functions in the pattern layer. Therefore, the accuracy and convergence speed to the optimal solution of this model are higher compared to the other machine learning models. The efficiency of the new model has been evaluated using observations of 30 global navigation satellite system (GNSS) stations in central Europe at 2015. It should be noted that the training of the GRNN model is done using the latitude and longitude of GNSS station, day of year, hours, AP, KP and DST geomagnetic indices and solar activity index (F10.7). Also, the vertical TEC corresponding to these input parameters is desirable output. The results of the new model have been compared with the results of the artificial neural network, adaptive neuro-fuzzy inference system, support vector regression, ordinary Kriging, global ionosphere map and the international reference ionosphere 2016 (IRI2016) empirical model as well as precise point positioning (PPP) method. The obtained results show that in both high and low geomagnetic and solar activities, the GRNN model has a higher accuracy with respect to the other models. The analysis of the PPP method shows an improvement of 37 mm in the coordinate components using GRNN model. The results show that the GRNN model can be considered as an alternative to global and empirical ionosphere models. The GRNN model is a high-precision regional ionosphere model.









Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
By contacting the corresponding author, all data can be provided to the readers. The IGS Rinex files can be downloaded from the ftp://cddis.gsfc.nasa.gov/pub/gps/data/daily. Also, IONEX files (GIM-TEC) have been downloaded from ftp://igs.ensg.ign.fr/pub/igs/products/ionosphere/.
References
Abe OE, Rabiu AB, Bolaji OS, Oyeyemi EO (2018) Modeling African equatorial ionosphere using ordinary Kriging interpolation technique for GNSS applications. Astrophys Space Sci 363:168
Akyilmaz O, Arslan N (2008) An experiment of predicting total electron content (TEC) by fuzzy inference systems. Earth Planets Space 60(9):967–972. https://doi.org/10.1186/BF03352852
Amerian Y, Voosoghi B, Hossainali MM (2013) Regional Ionosphere modeling in support of IRI and wavelet using GPS observations. Acta Geophys 61(5):1246–1261. https://doi.org/10.2478/s11600-013-0121-5
Ansari K, Kumar Panda S, Corumluoglu O (2018) Mathematical modeling of ionospheric TEC from Turkish permanent GNSS network (TPGN) observables during 2009–2017 and predictability of NeQuick and Kriging models. Astrophys Space Sci 363:42
Arikan F, Nayir H, Sezen U, Arikan O (2008) Estimation of single station interfrequency receiver bias using GPS-TEC. Radio Sci 43(4):69
Bilitza D, Reinisch BW (2008) International reference ionosphere 2007: improvements and new parameters. Adv Space Res 42(4):599–609
Cander R (1998) Artificial neural network applications in ionospheric studies, Annali di Geofisica, Vol.5–6.
Dach R, Hugentobler U, Fridez P, Meindl M (2007) Bernese GPS Software Version 5.0. Astronomical Institute, University of Bern, Bern.
Dreyfus G (2005) Neural networks methodology and applications. Springer, Berlin, p 2005
Erdogan S (2010) Modeling the spatial distribution of DEM error with geographically weighted regression: an experimental study. Comput Geosci 36:34–43
Etemadfard H, Hossainali MM (2017) Vector ionosphere modeling by vector spherical Slepian base functions. GPS solutions, 21-684-675
Feizi R, Voosoghi B, Ghaffari RMR (2020) Regional modeling of the ionosphere using adaptive neuro-fuzzy inference system in Iran. Adva Space Res 65(2020):2515–252
Ghaffari Razin MR (2015) Development and analysis of 3D ionosphere modeling using base functions and GPS data over Iran. Acta Geod Geophys 51(1):95–111
Ghaffari Razin MR, Voosoghi B (2020) Ionosphere time series modeling using adaptive neuro fuzzy inference system and principal component analysis. GPS Solut 24:51
Ghaffari Razin MR, Voosoghi B, Mohammadzadeh A (2015) Efficiency of artificial neural networks in map of total electron content over Iran. Acta Geod Geophys 51(3):541–555
Ghaffari Razin MR, Moradi AR, Moradi S (2021) Spatio-temporal analysis of TEC during solar activity periods using support vector machine. GPS Solut 25:121. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10291-021-01158-3
Ghritlahre H, Prasad R (2018) Investigation of thermal performance of unidirectional flow porous bed solar air heater using MLP, GRNN, and RBF models of ANN technique. Thermal Sci Eng Prog. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tsep.2018.04.006
Giraud A, Petit M (1978) Ionospheric techniques and phenomena. Springer, Berlin
Habarulema JB, McKinnell L-A, Opperman BDL (2009) A recurrent neural network approach to quantitatively studying solar wind effects on TEC derived from GPS; preliminary results. Ann Geophys 27(11):2111–2125
Hernández-Pajares M, Juan JM, Sanz J, Sanz J, Aragón-Àngel A, García-Rigo A, Salazar D, Escudero M (2011) The ionosphere: effects, GPS modeling and the benefits for space geodetic techniques. J Geod 85:887–907. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00190-011-0508-5
Inyurt S, Hasanpour Kashani M (2020) Sekertekin A (2020) Ionospheric TEC forecasting using Gaussian process regression (GPR) and multiple linear regression (MLR) in Turkey. Astrophys Space Sci 365:99. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10509-020-03817-2
Inyurt S, Sekertekin A (2019) Modeling and predicting seasonal ionospheric variations in Turkey using artificial neural network (ANN). Astrophys Space Sci 364(4):1–8
Joseph VR (2006) Limit Kriging. Technometrics 48(4):458–466
Kim B, Lee DW, Park KY, Choi SR, Choi S (2004) Prediction of plasma etching using a randomized generalized regression neural network. Vacuum 76(1):37–43
Komjathy A, Langley R. B (1996) An Assessment of predicted and measured ionospheric total electron content using a regional GPS Network. In: Proceedings of ION NTM 1996, Institute of Navigation, Santa Monica
Kopal I, Labaj I, Vršková J, Harniˇcárová M, Valíˇcek J, Ondrušová D, Krmela J, Polka Z (2022) A generalized regression neural network model for predicting the curing characteristics of carbon black-filled rubber blends. Polymers 14:653. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14040653
Leick A, Rapoport L, Tatarnikov D (2015) GPS satellite surveying. Wiley, Hoboken
Li J, Heap AD (2008) a review of spatial interpolation methods for environmental scientists. Geosci Aust Canberra 2:142
Liao X, Gao Y (2001) High-precision Ionospheric TEC recovery using a regional-area GPS network. Navigation 48(2):101–111
Liu Z (2004) Ionospheric tomographic modeling, UCGE reports, number 20198. University of Calgary, Calgary
Liu Z, Gao Y (2003) Ionospheric TEC predictions over a local area GPS reference network. GPS Solutions 8(1):23–29
Mallika IL, Ratnam DV, Raman S, Sivavaraprasad G (2020) A new ionospheric model for single frequency GNSS user applications using Klobuchar model driven by auto regressive moving average (SAKARMA) method over Indian region. IEEE Access 8:54535–54553. https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2020.2981365
Matheron G (1971) The theory of regionalized variables, and its applications. Centre de Geostatistique, Paris
Nava B, Coisson P, Radicella SM (2008) A new version of the NeQuick ionosphere electron density model. J Atmos Solar Terr Phys. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jastp.2008.01.015
Nematipour P, Raoofian-Naeeni M, Ghaffari Razin MR (2022) Regional application of C1 finite element interpolation method in modeling of ionosphere total electron content over Europe. Adv Space Res 2:56
Pérez Bello D, Natali MP, Meza A (2019) Comparison of adaptive neuro-fuzzy inference system and recurrent neural network in vert-cal total electron content forecasting. Neural Comput Appl 31:8411–8422. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-019-04528-8
Ratnam DV, Vindhya G, Dabbakuti JK (2017) Ionospheric forecasting model using fuzzy logic-based gradient descent method. Geod Geodyn 8:305–310
Ren X, Chen J, Li X et al (2019) Performance evaluation of real-time global ionospheric maps provided by different IGS analysis centers. GPS Solutions 23(4):113–117
Ren X, Yang P, Liu H, Chen J, Zhang X (2022) Deep Learning for global ionospheric TEC forecasting: different approaches and validation. Space Weather 20(5):e2021SW003011. https://doi.org/10.1029/2021SW003011
Saito A, Teraishi S, Ueno G, Fujita N, Tsugawa T (2007) GPS ionospheric tomography over Japan with constrained least squares method. Eos Trans AGU 88(52):1275
Schaer S (1999) Mapping and predicting the earth's ionosphere using the global positioning system. Ph.D. dissertation, Astronomical Institute, University of Berne, Switzerland
Schmidt M (2007) Wavelet modeling in support of IRI. Adv Space Res. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asr.2006.09.030
Sekido M, Kondo T, Kawai E, Imae M (2003) Evaluation of GPS based ionospheric TEC map by comparing with VLBI data. Radio Sci 38(4):1069. https://doi.org/10.1029/2000RS002620
Sivavaraprasad G, Deepika VS, SreenivasaRao D, Kumar R, Sridhar M (2020) Performance evaluation of neural network TEC forecasting models over equatorial low-latitude Indian GNSS station. Geod Geodyn 11:192–201
Specht DF (1991) A general regression neural network. IEEE Trans Neural Netw 2(6):568–576. https://doi.org/10.1109/72.97934
Strangeways HJ et al (2009) Near-earth space plasma modeling and forecasting. Ann Geophys 52(3–4):255–271
Walker JK (1989) Spherical cap harmonic modeling of high latitude magnetic activity and equivalent sources with sparse observations. J Atmos Terr Phys 51(2):67–80
Wen D, Wang Y, Norman R (2012) A new two-step algorithm for ionospheric tomography solution. GPS Solut 16(1):89–94
Wielgosz P, Brzezinska D, Kashani I (2003) Regional ionosphere mapping with Kriging and multiquadratic method. J Global Pos Syst 2:48–55
Yao Y, Chen P, Zhang S, Chen J (2013) A new ionospheric tomography model combining pixel-based and function-based models. Adv Space Res 52(4):614–621
Yao Y, Tang J, Kong J (2015) new ionosphere tomography algorithm with two-grid virtual observations constraints and three-dimensional velocity profile. IEEE Trans Geosci Remote Sens 53(5):2373–2383
Yilmaz A, Akdogan KE, Gurun M (2009) Regional TEC mapping using neural networks. Radio Sci 44(3):1–16. https://doi.org/10.1029/2008RS004049
Yin P, Mitchell CN, Spencer PSJ, Foster JC (2004) Ionospheric electron concentration imaging using GPS over the USA during the storm of July 2000. Geophys Res Lett 31:L12806
Yizengaw E, Moldwina MB, Dysonb PL, Essexb EA (2006) Using tomography of GPS TEC to routinely determine ionospheric average electron density profile. J Atmos Solar Terr Phys 69(3):314–321
Yuan Q, Xu H, Li T, Shen H, Zhang L (2020) Estimating surface soil moisture from satellite observations using a generalized regression neural network trained on sparse ground-based measurements in the continental US. J Hydrol 580:124351
Zheng D, Hu W, Nie W (2015) Multiscale ionospheric tomography. GPS Solut 19:579–588
Acknowledgements
The authors thank the reviewers for providing very valuable and scientific comments. The international GNSS service (IGS) is also thanked for providing the required data.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
SRGR initiated the study, provided the Matlab source codes for analysis, and data collected and analyzed. AR and NH analyzed part of the data and wrote the manuscript. All authors helped to shape the analysis and manuscript. All authors reviewed the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interest
The authors declare no competing interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Ghaffari-Razin, S.R., Rastbood, A. & Hooshangi, N. Regional application of generalized regression neural network in ionosphere spatio-temporal modeling and forecasting. GPS Solut 27, 51 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10291-022-01389-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10291-022-01389-y