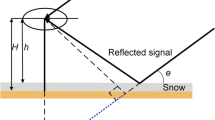
Abstract
China’s BeiDou Navigation Satellite System (BDS) is providing new opportunities for GNSS reflectometry-related applications. We give the first and comprehensive description of the feasibility and potential of using BDS signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) data to characterize land surface in terms of the volumetric soil moisture (VSM), vegetation water content (VWC) and snow depth. BDS SNR-derived interferogram metrics (phase φ, amplitude A, and effective reflector height h) are investigated, and their correlations to the corresponding land surface parameters are established. Data collected from a geodetic-quality BDS/GPS compatible receiver for approximately 300-day period were used to validate the VSM retrieval. Results show that both BDS B1 and B2 frequencies can perform well to reflect the fluctuations of the VSM. Specifically, the B2-derived phase φ exhibits a slightly higher correlation with in situ VSM than that of B1 (R = 0.83 vs. R = 0.80), and the B2-derived amplitude A also exhibits a higher correlation with MODIS NDVI than that of B1 (R = 0.49 vs. R = 0.53); whilst for snow, the B1 and B2 results indicate qualitative agreement with concurrent in situ snow depth measurements. Furthermore, similar estimation performance can be obtained by comparing the results of BDS B1 and B2 against GPS L2C and L5. Therefore, BDS could be a new and powerful data source with comparable potential as GPS for effectively characterizing high-temporal resolution land surface.












Similar content being viewed by others
Change history
14 October 2019
In the original article publication, the affiliation of co-author Yang Hong was accidentally omitted from the manuscript. The missing affiliation is given.
References
Cardellach E, Rius A, Martín-Neira M, Fabra F, Nogues-Correig O, Riboo S (2014) Consolidating the precision of interferometric GNSS-R ocean altimetry using airborne experimental data. IEEE Trans Geosci Remote Sens 52(8):4992–5004
Chen Q, Won D, Akos DM (2014) Snow depth sensing using the GPS L2C signal with a dipole antenna. EURASIP J Adv Sig Process 2014(1):106. https://doi.org/10.1186/1687-6180-2014-106
Chew CC, Small EE, Larson KM, Zavorotny VU (2014) Effects of near-surface soil moisture on GPS SNR data: development of a retrieval algorithm for soil moisture. IEEE Trans Geosci Remote Sens 52(1):537–543
Chew CC, Small EE, Larson KM (2016) An algorithm for soil moisture estimation using GPS-interferometric reflectometry for bare and vegetated soil. GPS Solut 20(3):525–537
Clarizia MP, Gommenginger C, Gleason S, Galdi C, Unwin M (2008) Global navigation satellite system-reflectometry (GNSS-R) from the UK-DMC satellite for remote sensing of the ocean surface. In: Geoscience and remote sensing symposium, 2008. IGARSS 2008, vol 1. IEEE, Boston, Mass, pp I-276–I-279
Crow WT, Zhan X (2007) Continental-scale evaluation of remotely sensed soil moisture products. IEEE Trans Geosci Remote Sens 4(3):451–455
Girolimetto D, Venturini V (2013) Water stress estimation from NDVI-Ts plot and the wet environment evapotranspiration. Adv Remote Sens 02(4):283–291
Gutmann ED, Larson KM, Williams MW, Nievinski FG, Zavorotny V (2012) Snow measurement by GPS interferometric reflectometry: an evaluation at Niwot Ridge, Colorado. Hydrol Process 26(19):2951–2961
Jackson TJ, Le Vine DM, Hsu AY, Oldak A, Starks PJ, Swift CT, Haken M (1999) Soil moisture mapping at regional scales using microwave radiometry: The Southern Great Plains Hydrology Experiment. IEEE Trans Geosci Remote Sens 37(5):2136–2151
Jackson TJ, Chen D, Cosh M, Li F, Anderson M, Walthall C, Hunt ER (2004) Vegetation water content mapping using Landsat data derived normalized difference water index for corn and soybeans. Remote Sens Environ 92(4):475–482
Jin S, Feng GP, Gleason S (2011) Remote sensing using GNSS signals: current status and future directions. Adv Space Res 47(10):1645–1653
Jin S, Qian X, Wu X (2017) Sea level change from BeiDou Navigation Satellite System-Reflectometry (BDS-R): first results and evaluation. Glob Planet Change 149:20–25
Larson KM (2016) GPS interferometric reflectometry: applications to surface soil moisture, snow depth, and vegetation water content in the western United States. WIRES Water 3(6):775–787
Larson KM, Nievinski FG (2013) GPS snow sensing: results from the EarthScope Plate Boundary Observatory. GPS Solut 17(1):41–52
Larson KM, Small EE (2016) Estimation of snow depth using L1 GPS signal-to-noise ratio data. IEEE J STARS 9(10):4802–4808
Larson KM, Small EE, Gutmann ED, Bilich AL, Braun JJ, Zavorotny VU (2008a) Use of GPS receivers as a soil moisture network for water cycle studies. Geophys Res Lett. https://doi.org/10.1029/2008GL036013
Larson KM, Small EE, Gutmann ED, Bilich AL, Axelrad P, Braun JJ (2008b) Using GPS multipath to measure soil moisture fluctuations: initial results. GPS Solut 12(3):173–177
Larson KM, Gutmann ED, Zavorotny VU, Braun JJ, Williams MW, Nievinski FG (2009) Can we measure snow depth with GPS receivers? Geophys Res Lett. https://doi.org/10.1029/2009GL039430
Larson KM, Braun JJ, Small EE, Zavorotny VU, Gutmann ED, Bilich AL (2010) GPS multipath and its relation to near-surface soil moisture content. IEEE J STARS 3(1):91–99
Larson KM, Löfgren JS, Haas R (2013) Coastal sea level measurements using a single geodetic GPS receiver. Adv Space Res 51(8):1301–1310
Li W, Yang D, Fabra F, Cao Y, Yang W (2014) Typhoon wind speed observation utilizing reflected signals from BeiDou GEO satellites. In: China satellite navigation conference (CSNC) 2014 proceedings, vol I. Springer, Berlin, pp 191–200
Martin P, Henning L, Martin S (2015) Density, specific surface area, and correlation length of snow measured by high-resolution penetrometry. J Geophys Res Earth 120(2):346–362
Masters D, Zavorotny V, Katzberg S, Emery W (2000) GPS signal scattering from land for moisture content determination. In: Geoscience and remote sensing symposium, 2000, vol 7. IEEE, Honolulu, HI, pp 3090–3092
Nievinski FG, Larson KM (2014) Forward modeling of GPS multipath for near-surface reflectometry and positioning applications. GPS Solut 18(2):309–322
Njoku EG, Entekhabi D (1996) Passive microwave remote sensing of soil moisture. J Hydrol 184(1–2):101–129
Qian X, Jin S (2016) Estimation of snow depth from GLONASS SNR and phase-based multipath reflectometry. IEEE J STARS 9(10):4817–4823
Rodriguez-Alvarez N, Camps A, Vall-Llossera M, Bosch-Lluis X, Monerris A, Ramos-Perez I, Perez-Gutierrez C (2011) Land geophysical parameters retrieval using the interference pattern GNSS-R technique. IEEE Trans Geosci Remote 49(1):71–84
Roussel N, Frappart F, Ramillien G, Darrozes J, Baup F, Lestarquit L, Ha MC (2016) Detection of soil moisture variations using GPS and GLONASS SNR data for elevation angles ranging from 2 to 70. IEEE J STARS 9(10):4781–4794
Sabia R, Caparrini M, Ruffini G (2007) Potential synergetic use of GNSS-R signals to improve the sea-state correction in the sea surface salinity estimation: application to the SMOS mission. IEEE Trans Geosci Remote 45(7):2088–2097
Siegfried MR, Medley B, Larson KM, Fricker HA, Tulaczyk S (2017) Snow accumulation variability on a West Antarctic ice stream observed with GPS reflectometry, 2007–2017. Geophys Res Lett 44:7808–7816
Tabibi S, Nievinski FG, van Dam T, Monico JF (2015) Assessment of modernized GPS L5 SNR for ground-based multipath reflectometry applications. Adv Space Res 55(4):1104–1116
Vey S, Güntner A, Wickert J, Blume T, Ramatschi M (2016) Long-term soil moisture dynamics derived from GNSS interferometric reflectometry: a case study for Sutherland, South Africa. GPS Solut 20(4):641–654
Wan W, Larson KM, Small EE, Chew CC, Braun JJ (2015) Using geodetic GPS receivers to measure vegetation water content. GPS Solut 19(2):237–248
Wang DW, Huang CL, Gu J (2016) Impact of pentration depth on L-band microwave brightness temperature in arid region based on L-MEB model. Remote Sens Technol Appl 31(3):580–589
Yan SH, Zhao F, Chen NC, Gong J (2016) Soil moisture estimation based on BeiDou B1 interference signal analysis. Sci China Earth Sci 59(12):2427–2440
Yang T, Wan W, Chen X, Chu TX, Hong Y (2017) Using BDS SNR observations to measure near-surface soil moisture fluctuations: results from low vegetated surface. IEEE Geosci Remote Sens Lett 14(8):1308–1312
Zechmeister M, Kürster M (2009) The generalised Lomb–Scargle periodogram—a new formalism for the floating-mean and Keplerian periodograms. Astron Astrophys 496(2):577–584
Acknowledgements
This study was jointly supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (NSFC) projects (Grant Nos. 41501360, 91437214, and 41401377), the Open Research Fund of Key Laboratory of Tibetan Environmental Changes and Land Surface Processes, Chinese Academy of Sciences (Grant No. TEL201503), and the Open Research Fund of State Key Laboratory of Hydroscience and Engineering, Tsinghua University (sklhse-2017-A-02).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, T., Wan, W., Chen, X. et al. Land surface characterization using BeiDou signal-to-noise ratio observations. GPS Solut 23, 32 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10291-019-0824-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10291-019-0824-4