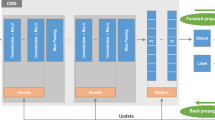
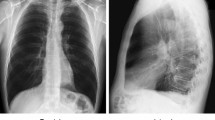
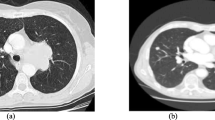
Abstract
Lung diseases represent a significant global health threat, impacting both well-being and mortality rates. Diagnostic procedures such as Computed Tomography (CT) scans and X-ray imaging play a pivotal role in identifying these conditions. X-rays, due to their easy accessibility and affordability, serve as a convenient and cost-effective option for diagnosing lung diseases. Our proposed method utilized the Contrast-Limited Adaptive Histogram Equalization (CLAHE) enhancement technique on X-ray images to highlight the key feature maps related to lung diseases using DenseNet201. We have augmented the existing Densenet201 model with a hybrid pooling and channel attention mechanism. The experimental results demonstrate the superiority of our model over well-known pre-trained models, such as VGG16, VGG19, InceptionV3, Xception, ResNet50, ResNet152, ResNet50V2, ResNet152V2, MobileNetV2, DenseNet121, DenseNet169, and DenseNet201. Our model achieves impressive accuracy, precision, recall, and F1-scores of 95.34%, 97%, 96%, and 96%, respectively. We also provide visual insights into our model’s decision-making process using Gradient-weighted Class Activation Mapping (Grad-CAM) to identify normal, pneumothorax, and atelectasis cases. The experimental results of our model in terms of heatmap may help radiologists improve their diagnostic abilities and labelling processes.











Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The dataset for the current study is available at www.kaggle.com/nih-chest-xrays/data.
References
Bhandary, A., Prabhu, G.A., Rajinikanth, V., Thanaraj, K.P., Satapathy, S.C., Robbins, D.E., Shasky, C., Zhang, Y.-D., Tavares, J.M.R., Raja, N.S.M.: Deep-learning framework to detect lung abnormality - A study with chest X-ray and lung CT scan images. Pattern Recognition Letters 129, 271–278 (2020)
Zheng, M., Marron, R.M., Sehgal, S.: Hard Metal Lung Disease and Other Rare Occupational Lung Diseases, pp. 101–109. CRC Press, Boca Raton (2023)
Tarlo, S.M.: Occupational lung diseases. Canadian Journal of Respiratory, Critical Care, and Sleep Medicine 4(sup1), 6–8 (2020)
Peroni, D., Boner, A.: Atelectasis: mechanisms, diagnosis and management. Paediatric Respiratory Reviews 1(3), 274–278 (2000)
Posner, K., Needleman, J.P.: Pneumothorax. Pediatrics in Review 29(2), 69–70 (2008)
Brenner, D.R., McLaughlin, J.R., Hung, R.J.: Previous Lung Diseases and Lung Cancer Risk: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. PloS one 6(3), 17479 (2011)
Lavine, M.: The Early Clinical X-ray in the United States: Patient Experiences and Public Perceptions. Journal of the History of Medicine and Allied Sciences 67(4), 587–625 (2012)
Ramgopal, S., Lorenz, D., Navanandan, N., Cotter, J.M., Shah, S.S., Ruddy, R.M., Ambroggio, L., Florin, T.A.: Validation of Prediction Models for Pneumonia Among Children in the Emergency Department. Pediatrics 150(1) (2022)
Wang, K., Jiang, P., Meng, J., Jiang, X.: Attention-Based DenseNet for Pneumonia Classification. IRBM 43(5), 479–485 (2022)
Islam, M.R., Nahiduzzaman, M.: Complex features extraction with deep learning model for the detection of COVID19 from CT scan images using ensemble based machine learning approach. Expert Systems with Applications 195, 116554 (2022)
Mnassri, B., Echtioui, A., Kallel, F., Ben Hamida, A., Dammak, M., Mhiri, C., Ben Mahfoudh, K.: New contrast enhancement method for multiple sclerosis lesion detection. Journal of Digital Imaging 36(2), 468–485 (2023)
Chhabra, M., Kumar, R.: An Advanced VGG16 Architecture-Based Deep Learning Model to Detect Pneumonia from Medical Images. In: Emergent Converging Technologies and Biomedical Systems: Select Proceedings of ETBS 2021, pp. 457–471 (2022)
Rajasenbagam, T., Jeyanthi, S., Pandian, J.A.: Detection of pneumonia infection in lungs from chest X-ray images using deep convolutional neural network and content-based image retrieval techniques. Journal of Ambient Intelligence and Humanized Computing, 1–8 (2021)
Gaur, P., Malaviya, V., Gupta, A., Bhatia, G., Pachori, R.B., Sharma, D.: COVID-19 disease identification from chest CT images using empirical wavelet transformation and transfer learning. Biomedical Signal Processing and Control 71, 103076 (2022)
Ferreira Junior, J.R., Cardona Cardenas, D.A., Moreno, R.A., de Sá Rebelo, M.d.F., Krieger, J.E., Gutierrez, M.A.: Novel Chest Radiographic Biomarkers for COVID-19 Using Radiomic Features Associated with Diagnostics and Outcomes. Journal of Digital Imaging 34, 297–307 (2021)
Upasana, C., Tewari, A.S., Singh, J.P.: An attention-based Pneumothorax Classification using Modified Xception Model. Procedia Computer Science 218, 74–82 (2023)
Filice, R.W., Stein, A., Wu, C.C., Arteaga, V.A., Borstelmann, S., Gaddikeri, R., Galperin-Aizenberg, M., Gill, R.R., Godoy, M.C., Hobbs, S.B., et al: Crowdsourcing pneumothorax annotations using machine learning annotations on the NIH chest X-ray dataset. Journal of Digital Imaging 33, 490–496 (2020)
Güler, O., Polat, K.: Classification performance of Deep Transfer Learning Methods for Pneumonia Detection from Chest X-Ray Images. Journal of Artificial Intelligence and Systems 4(1), 107–126 (2022)
Simonyan, K., Zisserman, A.: Very Deep Convolutional Networks for Large-Scale Image Recognition. arXiv preprint arXiv:1409.1556 (2014)
Chollet, F.: Xception: Deep learning with depthwise separable convolutions. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 1251–1258 (2017)
Sandler, M., Howard, A., Zhu, M., Zhmoginov, A., Chen, L.-C.: MobileNetV2: Inverted Residuals and Linear Bottlenecks. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 4510–4520 (2018)
He, K., Zhang, X., Ren, S., Sun, J.: Deep Residual Learning for Image Recognition. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 770–778 (2016)
Huang, G., Liu, Z., Van Der Maaten, L., Weinberger, K.Q.: Densely Connected Convolutional Networks. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 4700–4708 (2017)
Huemann, Z., Hu, J., Bradshaw, T.: ConTEXTual Net: A Multimodal Vision-Language Model for Segmentation of Pneumothorax. arXiv preprint arXiv:2303.01615 (2023)
Souid, A., Sakli, N., Sakli, H.: Classification and Predictions of Lung Diseases from Chest X-rays Using MobileNet V2. Applied Sciences 11(6), 2751 (2021)
Alaba, S.Y., Ball, J.E.: Deep Learning-Based Image 3D Object Detection for Autonomous Driving. IEEE Sensors Journal (2023)
Rahman, T., Khandakar, A., Kadir, M.A., Islam, K.R., Islam, K.F., Mazhar, R., Hamid, T., Islam, M.T., Kashem, S., Mahbub, Z.B., et al: Reliable Tuberculosis Detection Using Chest X-ray With Deep Learning, Segmentation and Visualization. IEEE Access 8, 191586–191601 (2020)
Cho, Y., Kim, J.S., Lim, T.H., Lee, I., Choi, J.: Detection of the location of pneumothorax in chest X-rays using small artificial neural networks and a simple training process. Scientific Reports 11(1), 13054 (2021)
De Vos, B.D., Berendsen, F.F., Viergever, M.A., Sokooti, H., Staring, M., Išgum, I.: A deep learning framework for unsupervised affine and deformable image registration. Medical Image Analysis 52, 128–143 (2019)
Sharma, P., Bisht, I., Sur, A.: Wavelength-Based Attributed Deep Neural Network for Underwater Image Restoration. ACM Transactions on Multimedia Computing, Communications and Applications 19(1), 1–23 (2023)
Chan, Y.-H., Zeng, Y.-Z., Wu, H.-C., Wu, M.-C., Sun, H.-M.: Effective Pneumothorax Detection for Chest X-ray Images Using Local Binary Pattern and Support Vector machine. Journal of Healthcare Engineering 2018 (2018)
Wang, X., Peng, Y., Lu, L., Lu, Z., Bagheri, M., Summers, R.M.: ChestX-ray8: Hospital-Scale Chest X-ray Database and Benchmarks on Weakly-Supervised Classification and Localization of Common Thorax Diseases. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 2097–2106 (2017)
Rajpurkar, P., Irvin, J., Ball, R.L., Zhu, K., Yang, B., Mehta, H., Duan, T., Ding, D., Bagul, A., Langlotz, C.P., et al: Deep learning for chest radiograph diagnosis: A retrospective comparison of the CheXNeXt algorithm to practicing radiologists. PLoS medicine 15(11), 1002686 (2018)
Chutia, U., Tewari, A.S., Singh, J.P.: Collapsed lung disease classification by coupling denoising algorithms and deep learning techniques. Network Modeling Analysis in Health Informatics and Bioinformatics 13(1), 1 (2023)
Tian, Y., Wang, J., Yang, W., Wang, J., Qian, D.: Deep multi-instance transfer learning for Pneumothorax classification in chest X-ray images. Medical Physics 49(1), 231–243 (2022)
Albahli, S., Rauf, H.T., Algosaibi, A., Balas, V.E.: AI-driven deep CNN approach for multi-label pathology classification using chest X-Rays. PeerJ Computer Science 7, 495 (2021)
Zhang, Q., Bai, C., Liu, Z., Yang, L.T., Yu, H., Zhao, J., Yuan, H.: A GPU-based residual network for medical image classification in smart medicine. Information Sciences 536, 91–100 (2020)
Bharati, S., Podder, P., Mondal, M.R.H.: Hybrid deep learning for detecting lung diseases from X-ray images. Informatics in Medicine Unlocked 20, 100391 (2020)
Aswiga, R., Shanthi, A.: Augmenting transfer learning with feature extraction techniques for limited breast imaging datasets. Journal of Digital Imaging 34(3), 618–629 (2021)
Dhasny, L.M., Prakash, M.: An improved convolution neural network and modified regularized K-Means-Based automatic lung nodule detection and classification. Journal of Digital Imaging 36, 1431–1446 (2023)
Yuan, H., Wu, Y., Dai, M.: Multi-modal feature fusion-based multi-branch classification network for pulmonary nodule malignancy suspiciousness diagnosis. Journal of Digital Imaging 36(2), 617–626 (2023)
Reza, A.M.: Realization of the contrast limited adaptive histogram equalization (CLAHE) for real-time image enhancement. Journal of VLSI Signal Processing Systems For Signal, Image and Video Technology 38, 35–44 (2004)
Tong, Z., Tanaka, G.: Hybrid pooling for enhancement of generalization ability in deep convolutional neural networks. Neurocomputing 333, 76–85 (2019)
Ru, L., Du, B., Zhan, Y., Wu, C.: Weakly-supervised semantic segmentation with visual words learning and hybrid pooling. International Journal of Computer Vision 130(4), 1127–1144 (2022)
Woo, S., Park, J., Lee, J.-Y., Kweon, I.S.: CBAM: Convolutional block attention module. In: Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), pp. 3–19 (2018)
Bastidas, A.A., Tang, H.: Channel attention networks. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops, pp. 0–0 (2019)
Yao, L., Poblenz, E., Dagunts, D., Covington, B., Bernard, D., Lyman, K.: Learning to diagnose from scratch by exploiting dependencies among labels. arXiv preprint arXiv:1710.10501 (2017)
Rajpurkar, P., Irvin, J., Zhu, K., Yang, B., Mehta, H., Duan, T., Ding, D., Bagul, A., Langlotz, C., Shpanskaya, K., et al.: CheXNet: Radiologist-Level Pneumonia Detection on Chest X-rays with Deep Learning. arXiv preprint arXiv:1711.05225 (2017)
Szegedy, C., Vanhoucke, V., Ioffe, S., Shlens, J., Wojna, Z.: Rethinking the Inception Architecture for Computer Vision. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 2818–2826 (2016)
Guan, Q., Huang, Y., Zhong, Z., Zheng, Z., Zheng, L., Yang, Y.: Diagnose like a Radiologist: Attention Guided Convolutional Neural Network for Thorax Disease Classification. arXiv preprint arXiv:1801.09927 (2018)
Zhou, B., Khosla, A., Lapedriza, A., Oliva, A., Torralba, A.: Learning deep features for discriminative localization. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 2921–2929 (2016)
Farag, M.M., Fouad, M., Abdel-Hamid, A.T.: Automatic Severity Classification of Diabetic Retinopathy Based on DenseNet and Convolutional Block Attention Module. IEEE Access 10, 38299–38308 (2022)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All the authors contributed equally.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Chutia, U., Tewari, A.S., Singh, J.P. et al. Classification of Lung Diseases Using an Attention-Based Modified DenseNet Model. J Digit Imaging. Inform. med. (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10278-024-01005-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10278-024-01005-0