Abstract
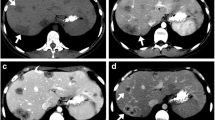
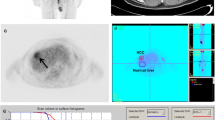
Hepatic epithelioid hemangioendothelioma (HEHE) is a low-to-intermediate-grade malignant mesenchymal tumor. The diagnostic and prognostic values of 2-[18F] fluoro-2-deoxy-D-glucose (18F-FDG) positron emission tomography/computed tomography (PET/CT) to patients with HEHE have not been fully validated. Patient survival outcomes (including overall survival [OS] and progression-free survival [PFS]), lesions characteristics and semi-quantitative parameters, in terms of maximum standardized uptake value (SUVmax), peak SUV (SUVpeak), total lesion glycolysis (TLG) and metabolic tumor volume (MTV) on 18F-FDG PET/CT of 20 cases with HEHE were measured and analyzed. A total of 310 liver lesions were detected (excluding the diffuse-type lesions in 3 cases). Most lesions had higher SUVmax in delayed imaging than in early imaging (P = 0.013). Patients with multiple organs involved had higher death rate (P = 0.022), higher progression rate (P = 0.020), shorter OS (P = 0.011), larger lesion SUVmax (P = 0.048) and TLG (P = 0.033) than those with only liver involved. The area under curves (AUCs) from the receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve analysis were 0.960, 0.949, 0.980 and 0.960 for SUVmax, SUVpeak, TLG and MTV, respectively, in predicting OS (P = 0.005, 0.008, 0.001 and 0.024, respectively). For predicting PFS, the AUCs were 0.791, 0.824, 0.857 and 0.813 (P = 0.036, 0.019, 0.010 and 0.024), respectively. Dual-time-point imaging may improve lesions detectability. Patients with multiple organ involved had worse prognosis. The higher SUVmax, SUVpeak, TLG and MTV of lesions, the worse prognosis of patients were found.





Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- 18F-FDG:
-
2-[18F] Fluoro-2-deoxy-D-glucose
- PET/CT:
-
Positron emission tomography/computed tomography
- HEHE:
-
Hepatic epithelioid hemangioendothelioma
- OS:
-
Overall survival
- PFS:
-
Progression-free survival
- SUVmax :
-
Maximum standardized uptake value
- SUVpeak :
-
Peak SUV
- TLG:
-
Total lesion glycolysis
- MTV:
-
Metabolic tumor volume
- VOI:
-
Volume of interest
- WB:
-
Whole body
- RI:
-
Retention index
- ROC:
-
Receiver operating characteristic
- AUCs:
-
Areas under curves
- SD:
-
Standard deviation
- g:
-
Gram
References
Ishak KG, Sesterhenn IA, Goodman ZD, et al. Epithelioid hemangioendothelioma of the liver: a clinicopathologic and follow-up study of 32 cases [J]. Hum Pathol. 1984;15(9):839–52.
Epelboym Y, Engelkemier DR, Thomas-Chausse F, et al. Imaging findings in epithelioid hemangioendothelioma [J]. Clin Imaging. 2019;58:59–655.
Dong A, Dong H, Wang Y, et al. MRI and FDG PET/CT findings of hepatic epithelioid hemangioendothelioma [J]. Clin Nucl Med. 2013;38(2):e66–73.
Mamone G, Miraglia R. The, "Target sign" and the "Lollipop sign" in hepatic epithelioid hemangioendothelioma [J]. Abdom Radiol. 2019;44(4):1617–20.
Thomas RM, Aloia TA, Truty MJ, et al. Treatment sequencing strategy for hepatic epithelioid haemangioendothelioma [J]. HPB Oxford. 2014;16(7):677–85.
Remiszewski P, Szczerba E, Kalinowski P, et al. Epithelioid hemangioendothelioma of the liver as a rare indication for liver transplantation [J]. World J Gastroenterol. 2014;20(32):11333–9.
Sangro B, Inarrairaegui M, Fernandez-Ros N. Malignant epithelioid hemangioendothelioma of the liver successfully treated with Sorafenib [J]. Rare Tumors. 2012;4(2):e34.
Soape MP, Verma R, Payne JD, et al. Treatment of Hepatic Epithelioid Hemangioendothelioma: Finding Uses for Thalidomide in a New Era of Medicine [J]. Case Rep Gastrointest Med. 2015;2015:326795.
Eisenhauer EA, Therasse P, Bogaerts J, et al. New response evaluation criteria in solid tumours: revised RECIST guideline (version 1.1) [J]. Eur J Cancer. 2009;45(2):228–47.
Davison J, Mercier G, Russo G, et al. PET-based primary tumor volumetric parameters and survival of patients with non-small cell lung carcinoma [J]. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2013;200(3):635–40.
Woodall CE, Scoggins CR, Lewis AM, et al. Hepatic malignant epithelioid hemangioendothelioma: a case report and review of the literature [J]. Am Surg. 2008;74(1):64–8.
Doyle LA. Sarcoma classification: an update based on the 2013 World Health Organization Classification of tumors of soft tissue and bone [J]. Cancer. 2014;120(12):1763–74.
Shiba S, Imaoka H, Shioji K, et al. Clinical characteristics of Japanese patients with epithelioid hemangioendothelioma: a multicenter retrospective study [J]. BMC Cancer. 2018;18(1):993.
Spasic S, Brcic I, Freire R, et al. Epithelioid hemangioendothelioma of the bowel in crohn's disease: the first reported case [J]. Int J Surg Pathol. 2019;27(4):423–6.
Guo Q, Xue J, Xu L, et al. The clinical features of epithelioid hemangioendothelioma in a Han Chinese population: a retrospective analysis [J]. Medicine. 2017;96(26):e7345.
Da Ines D, Petitcolin V, Joubert-Zakeyh J, et al. Epithelioid hemangioendothelioma of the liver with metastatic coeliac lymph nodes in an 11-year-old boy [J]. Pediatr Radiol. 2010;40(7):1293–6.
Gurung S, Fu H, Zhang WW, et al. Hepatic epithelioid hemangioendothelioma metastasized to the peritoneum, omentum and mesentery: a case report [J]. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2015;8(5):5883–9.
Bozkurt O, Demir O, Yener S, et al. Malignant epithelioid hemangioendothelioma of the adrenal gland treated by laparoscopic excision [J]. Urology. 2015;85(3):e15–16.
Cabuk FK, Aktepe F, Ilgun AS, et al. A rare tumor that mimicked metastasis in a patient with breast cancer: epithelioid hemangioendothelioma [J]. J Breast Health. 2016;12(2):83–5.
Ono M, Kasuga Y, Uehara T, et al. Epithelioid hemangioendothelioma of the thyroid: a case report [J]. Surg Case Rep. 2017;3(1):18.
Sancheti S, Singh JN, Malik A, et al. Epithelioid hemangioendothelioma of hypopharynx: A rare presentation [J]. Indian J Dent. 2016;7(2):109–11.
Ogita S, Endo T, Nomura K, et al. Nasal cavity epithelioid hemangioendothelioma invading the anterior skull base [J]. Surg Neurol Int. 2016;7:53.
Kumar A, Lopez YK, Arrossi AV, et al. Mediastinal Epithelioid Hemangioendothelioma [J]. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2016;193(4):e7–8.
Dutta M, Roy K. Epithelioid hemangioendothelioma of tongue presenting as a papilloangioma in a pregnant woman [J]. Ear Nose Throat J. 2016;95(8):E43–45.
Liu Y, Liu A, Wu J, et al. Epithelioid hemangioendothelioma arising from the kidney: a rare case report [J]. Medicine (Baltimore). 2019;98(34):e16537.
Arif SH, Mohammed AA. Epithelioid hemangioendothelioma of the pancreas presented as massive hematemesis [J]. Int J Surg Case Rep. 2019;64:147–9.
Petrella F, Bonalumi G, Andreini D, et al. Primary epithelioid hemangioendothelioma of the heart [J]. Am Surg. 2018;84(6):e199–e200.
Mehrabi A, Kashfi A, Fonouni H, et al. Primary malignant hepatic epithelioid hemangioendothelioma: a comprehensive review of the literature with emphasis on the surgical therapy [J]. Cancer. 2006;107(9):2108–21.
Lin E, Agoff N. Recurrent hepatic epithelioid hemangioendothelioma: detection by FDG PET/CT [J]. Clin Nucl Med. 2007;32(12):949–51.
Suga K, Kawakami Y, Hiyama A, et al. F-18 FDG PET/CT monitoring of radiation therapeutic effect in hepatic epithelioid hemangioendothelioma [J]. Clin Nucl Med. 2009;34(3):199–202.
Jiang L, Tan H, Panje CM, et al. Role of 18F-FDG PET/CT Imaging in Intrahepatic Cholangiocarcinoma [J]. Clin Nucl Med. 2016;41(1):1–7.
Tan GJ, Berlangieri SU, Lee ST, et al. FDG PET/CT in the liver: lesions mimicking malignancies [J]. Abdom Imaging. 2014;39(1):187–95.
Furui S, Itai Y, Ohtomo K, et al. Hepatic epithelioid hemangioendothelioma: report of five cases [J]. Radiology. 1989;171(1):63–8.
Galletto Pregliasco A, Wendum D, Goumard C, et al. Hepatic epithelioid hemangioendothelioma [J]. Clin Res Hepatol Gastroenterol. 2016;40(2):136–8.
Makhlouf HR, Ishak KG, Goodman ZD. Epithelioid hemangioendothelioma of the liver: a clinicopathologic study of 137 cases [J]. Cancer. 1999;85(3):562–82.
Kitapci MT, Akkas BE, Gullu I, et al. FDG-PET/CT in the evaluation of epithelioid hemangioendothelioma of the liver: the role of dual-time-point imaging. A case presentation and review of the literature [J]. Ann Nucl Med. 2010;24(7):549–53.
Takeuchi S, Rohren EM, Abdel-Wahab R, et al. Refining prognosis in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma through incorporation of metabolic imaging biomarkers [J]. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2017;44(6):969–78.
Lee JW, Hwang SH, Kim HJ, et al. Volumetric parameters on FDG PET can predict early intrahepatic recurrence-free survival in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma after curative surgical resection [J]. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2017;44(12):1984–94.
Woo JH, Kim TJ, Lee KS, et al. Epithelioid hemangioendothelioma in the thorax: Clinicopathologic, CT, PET, and prognostic features [J]. Medicine (Baltimore). 2016;95(30):e4348.
Acknowledgements
We thank Yuan Ji, M.D., Ph.D. for pathologic diagnosis in immunohistochemistry.
Funding
This study was partially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (grant number: 81701730), the training program for excellent young medical talents of Zhongshan Hospital of Fudan University (grant number: 2019ZSYQ28) and the Shanghai "Rising Stars of Medical Talent" Youth Development Program (receiver: LG).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
WW, LG and SH contributed to study design, statistical analysis and overall manuscript generation; Material preparation and data collection were performed by HP, PL, GT, YH, YY and LR. All coauthors read and approved the entire manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Ethics approval and consent to participate
This study was approved by the institutional ethics committee. Informed consent was obtained from all patients included in the study.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, W., Liu, G., Hu, P. et al. Imaging characteristics and prognostic values of hepatic epithelioid hemangioendothelioma on 18F-FDG PET/CT. Clin Exp Med 20, 557–567 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10238-020-00653-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10238-020-00653-0