Abstract
Background
Because most patients with small-sized non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) are asymptomatic, their lesions are detected by cancer screenings or routine checkups for other diseases. Incidences of multiple malignancies have been reported to be 27% in patients with stage I–III NSCLC. Some patients have treatment histories for other malignancies, and their small-sized NSCLC was incidentally detected during follow-up. There is no established report regarding the influence of multiple malignancies on small-sized NSCLC prognosis. Therefore, we investigated the correlation between multiple malignancies and surgical outcomes in patients with small-sized NSCLC.
Methods
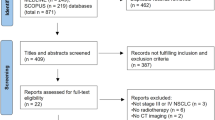
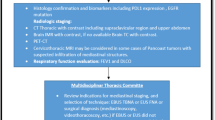
In total, 44 patients underwent definitive pulmonary resection for NSCLC of 1 cm or smaller between January 2003 and December 2012. Tumor size was measured by macroscopic findings of the resected specimens, and we then retrospectively investigated their clinical courses.
Results
One patient had hemoptysis symptoms, whereas 43 patients were asymptomatic; among them, NSCLC was detected by examinations for other diseases in 31 patients and by cancer screening in 12 patients. In total, 20 patients (45%) had multiple malignancies. The median follow-up period was 68 months. One patient had a recurrence from current NSCLC. No patients died of current NSCLC. The overall 5-year survival rate was 90% for all patients. Patients with multiple malignancies had significantly poorer prognoses compared with those without multiple malignancies (P = 0.016). However, patients with treatment intervals of more than 5 years had prognoses equivalent to those of patients without multiple malignancies (P = 0.829). Only the presence of multiple malignancies was a significantly poor prognostic factor in univariate and multivariate analyses.
Conclusion
NSCLC of 1 cm or smaller showed good prognoses. The presence of multiple malignancies was a significantly poor prognostic factor, and short treatment intervals also correlated with poor prognosis.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chen X, Gorlov IP, Ying J et al (2012) Initial medical attention on patients with early-stage non-small cell lung cancer. PLoS One 7:e32644
Rami-Porta R, Bolejack V, Crowley J et al (2015) The IASLC lung cancer staging project: proposals for the revisions of the T descriptors in the forthcoming eighth edition of the TNM classification for lung cancer. J Thorac Oncol 10:990–1003
Lv M, Zhang X, Shen Y et al (2017) Clinical analysis and prognosis of synchronous and metachronous multiple primary malignant tumors. Medicine (Baltim) 96:e6799
Kaufmann O, Dietel M (2000) Thyroid transcription factor-1 is the superior immunohistochemical marker for pulmonary adenocarcinomas and large cell carcinomas compared to surfactant proteins A and B. Histopathology (Oxf) 36:8–16
Shin B, Shin S, Chung MJ et al (2017) Different histological subtypes of peripheral lung cancer based on emphysema distribution in patients with both airflow limitation and CT-determined emphysema. Lung Cancer 104:106–110
Koo HJ, Do KH, Lee JB et al (2016) Lung cancer in combined pulmonary fibrosis and emphysema: a systematic review and meta-analysis. PLoS One 11:e0161437
Baba T, Uramoto H, Kuwata T et al (2011) A study of surgically resected peripheral non-small cell lung cancer with a tumor diameter of 1.0 cm or less. Scand J Surg 100:153–158
Zhu WY, Tan LL, Wang ZY et al (2016) Clinical characteristics and advantages of primary peripheral micro-sized lung adenocarcinoma over small-sized lung adenocarcinoma. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg 49:1095–1102
Kates M, Swanson S, Wisnivesky JP (2011) Survival following lobectomy and limited resection for the treatment of stage I non-small cell lung cancer ≤1 cm in size: a review of SEER data. Chest 139:491–496
Fujita S, Masago K, Takeshita J et al (2015) Multiple primary malignancies in patients with non-small cell lung cancer. Intern Med 54:325–331
Lee PC, Korst RJ, Port JL et al (2006) Long-term survival and recurrence in patients with resected non-small cell lung cancer 1 cm or less in size. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 132:1382–1389
Shakhar G, Ben-Eliyahu S (2003) Potential prophylactic measures against postoperative immunosuppression: could they reduce recurrence rates in oncological patients? Ann Surg Oncol 10:972–992
Hogan BV, Peter MB, Shenoy HG et al (2011) Surgery induced immunosuppression. Surgeon 9:38–43
Ohba T, Motoi N, Kimura Y et al (2010) Cytokeratin expression profiling is useful for distinguishing between primary squamous cell carcinoma of the lung and pulmonary metastases from tongue cancer. Pathol Int 60:575–580
Geurts TW, Nederlof PM, van den Brekel MW et al (2005) Pulmonary squamous cell carcinoma following head and neck squamous cell carcinoma: metastasis or second primary? Clin Cancer Res 11:6608–6614
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors of this manuscript have no relevant financial or other potential conflict of interest.
About this article
Cite this article
Tsukioka, T., Izumi, N., Mizuguchi, S. et al. Impact of multiple malignancies on surgical outcomes in patients with 1 cm or smaller non-small cell lung cancer. Int J Clin Oncol 23, 66–72 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10147-017-1185-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10147-017-1185-z