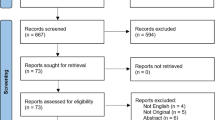
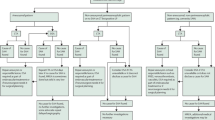
Abstract
We aimed to investigate the efficacy of our multimodal strategies and propose a treatment algorithm for ruptured vertebral artery dissecting aneurysms (VADAs). This study included 41 patients treated at a single institution between 2015 and 2022. The treatment modalities were justified based on the collateral circulation and aneurysm location related to the posterior inferior cerebellar artery (PICA). Treatment outcomes and complications of each treatment group were analyzed. The association between the collateral blood flow and the postoperative vertebrobasilar ischemia (VBI) was also investigated. There were 17 post-PICA, 10 PICA-involved, 7 pre-PICA, and 7 non-PICA types. Reconstruction techniques included flow diversion devices (n = 11) and stent-assisted coiling (n = 3). Deconstruction techniques included coil trapping (n=17) and microsurgical parent artery occlusion with (n = 8) or without PICA revascularization (n = 2). Five (18.5%) of the deconstruction group had postoperative VBI. Overall favorable outcomes in both groups were observed in 70.7% of patients with a mean follow-up time of 21.5 months. Poor World Federation of Neurosurgical Societies grade (IV-V) was identified as a predictor of unfavorable outcomes (p = 0.003). In addition, the VA4/BA4 ratio > 0.22, the presence of collateral blood flow from the posterior communicating artery (PcomA), and a contralateral VA diameter > 2.5 mm were associated with a lower risk of postoperative VBI. In summary, the proposed strategic treatment in this study is pragmatic, yielding satisfactory results where a deconstructive technique should be used with caution, particularly when there is a flow mismatch or the absence of collateral PcomA in the vertebrobasilar circulation.








Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Not applicable
Code availability
Not applicable
References
Aihara M, Naito I, Shimizu T, Matsumoto M, Asakura K, Miyamoto N, Yoshimoto Y (2018) Predictive factors of medullary infarction after endovascular internal trapping using coils for vertebral artery dissecting aneurysms. J Neurosurg 129:107–113. https://doi.org/10.3171/2017.2.Jns162916
Aymard A, Gobin YP, Hodes JE, Bien S, Rüfenacht D, Reizine D, George B, Merland JJ (1991) Endovascular occlusion of vertebral arteries in the treatment of unclippable vertebrobasilar aneurysms. J Neurosurg 74:393–398. https://doi.org/10.3171/jns.1991.74.3.0393
Bhogal P, Brouwer PA, Söderqvist ÅK, Ohlsson M, Andersson T, Holmin S, Söderman M (2015) Patients with subarachnoid haemorrhage from vertebrobasilar dissection: treatment with stent-in-stent technique. Neuroradiology 57:605–614. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00234-015-1505-9
Bier G, Bongers MN, Hempel J-M, Örgel A, Hauser T-K, Ernemann U, Hennersdorf F (2017) Follow-up CT and CT angiography after intracranial aneurysm clipping and coiling—improved image quality by iterative metal artifact reduction. Neuroradiology 59:649–654. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00234-017-1855-6
Cerejo R, Bain M, Moore N, Hardman J, Bauer A, Hussain MS, Masaryk T, Rasmussen P, Toth G (2017) Flow diverter treatment of intracranial vertebral artery dissecting pseudoaneurysms. J Neurointerv Surg 9:1064–1068. https://doi.org/10.1136/neurintsurg-2017-013020
Chalouhi N, Zanaty M, Whiting A, Tjoumakaris S, Hasan D, Ajiboye N, Hann S, Rosenwasser RH, Jabbour P (2015) Treatment of ruptured intracranial aneurysms with the pipeline embolization device. Neurosurgery 76:165-172. discussion 172. https://doi.org/10.1227/neu.0000000000000586
Chen JA, Garrett MC, Mlikotic A, Ausman JI (2019) Treatment of intracranial vertebral artery dissecting aneurysms involving the posterior inferior cerebellar artery origin. Surg Neurol Int 10:116. https://doi.org/10.25259/sni-281-2019
Debette S, Compter A, Labeyrie M-A, Uyttenboogaart M, Metso TM, Majersik JJ, Goeggel-Simonetti B, Engelter ST, Pezzini A, Bijlenga P, Southerland AM, Naggara O, Béjot Y, Cole JW, Ducros A, Giacalone G, Schilling S, Reiner P, Sarikaya H, Welleweerd JC, Kappelle LJ, de Borst GJ, Bonati LH, Jung S, Thijs V, Martin JJ, Brandt T, Grond-Ginsbach C, Kloss M, Mizutani T, Minematsu K, Meschia JF, Pereira VM, Bersano A, Touzé E, Lyrer PA, Leys D, Chabriat H, Markus HS, Worrall BB, Chabrier S, Baumgartner R, Stapf C, Tatlisumak T, Arnold M, Bousser M-G (2015) Epidemiology, pathophysiology, diagnosis, and management of intracranial artery dissection. Lancet Neurol 14:640–654. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1474-4422(15)00009-5
Endo H, Matsumoto Y, Kondo R, Sato K, Fujimura M, Inoue T, Shimizu H, Takahashi A, Tominaga T (2013) Medullary infarction as a poor prognostic factor after internal coil trapping of a ruptured vertebral artery dissection: clinical article. J Neurosurg JNS 118:131–139. https://doi.org/10.3171/2012.9.JNS12566
Guerrero WR, Ortega-Gutierrez S, Hayakawa M, Derdeyn CP, Rossen JD, Hasan D, Samaniego EA (2018) Endovascular treatment of ruptured vertebrobasilar dissecting aneurysms using flow diversion embolization devices: single-institution experience. World Neurosurg 109:e164–e169. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wneu.2017.09.125
Hademenos GJ, Massoud TF (1997) Biophysical mechanisms of stroke. Stroke 28:2067–2077. https://doi.org/10.1161/01.str.28.10.2067
Hamada J, Kai Y, Morioka M, Yano S, Todaka T, Ushio Y (2003) Multimodal treatment of ruptured dissecting aneurysms of the vertebral artery during the acute stage. J Neurosurg 99:960–966. https://doi.org/10.3171/jns.2003.99.6.0960
Hamasaki O, Ikawa F, Hidaka T, Kurokawa Y, Yonezawa U (2014) Treatment of ruptured vertebral artery dissecting aneurysms A short report. Interv Neuroradiol 20:304–311. https://doi.org/10.15274/inr-2014-10024
Hatano Y, Ota N, Noda K, Okada Y, Suzuki Y, Fukuyama S, Tanada S, Hashimoto A, Kondo T, Miyazaki T, Kinoshita Y, Kamiyama H, Tokuda S, Tanikawa R (2019) Surgical microanatomy of the occipital artery for suboccipital muscle dissection and intracranial artery reconstruction. Surg Neurol Int 10:127. https://doi.org/10.25259/sni-16-2019
Hong JM, Chung CS, Bang OY, Yong SW, Joo IS, Huh K (2009) Vertebral artery dominance contributes to basilar artery curvature and peri-vertebrobasilar junctional infarcts. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 80:1087–1092. https://doi.org/10.1136/jnnp.2008.169805
Iihara K, Sakai N, Murao K, Sakai H, Higashi T, Kogure S, Takahashi JC, Nagata I (2002) Dissecting aneurysms of the vertebral artery: a management strategy. J Neurosurg 97:259–267. https://doi.org/10.3171/jns.2002.97.2.0259
Ikeda H, Imamura H, Mineharu Y, Tani S, Adachi H, Sakai C, Ishikawa T, Asai K, Sakai N (2016) Effect of coil packing proximal to the dilated segment on postoperative medullary infarction and prognosis following internal trapping for ruptured vertebral artery dissection. Interv Neuroradiol 22:67–75. https://doi.org/10.1177/1591019915609127
Imahori T, Shose H, Okamura Y, Kohmura E (2019) Deploying 5 overlapping enterprise stents and coiling for treating hemorrhagic vertebral artery dissecting aneurysm. World Neurosurgery 132:177–181. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wneu.2019.08.226
Jeng JS, Yip PK (2004) Evaluation of vertebral artery hypoplasia and asymmetry by color-coded duplex ultrasonography. Ultrasound Med Biol 30:605–609. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ultrasmedbio.2004.03.004
Kanematsu Y, Satomi J, Korai M, Okazaki T, Yamaguchi I, Tada Y, Uno M, Nagahiro S, Takagi Y (2018) Flow alteration therapy for ruptured vertebral artery dissecting aneurysms involving the posterior inferior cerebellar artery. Neurol Med Chir (Tokyo) 58:341–349. https://doi.org/10.2176/nmc.oa.2018-0076
Kim BM, Shin YS, Kim SH, Suh SH, Ihn YK, Kim DI, Kim DJ, Park SI (2011) Incidence and risk factors of recurrence after endovascular treatment of intracranial vertebrobasilar dissecting aneurysms. Stroke 42:2425–2430. https://doi.org/10.1161/strokeaha.111.617381
Kobayashi S, Karasudani H, Koguchi Y, Tsuru K, Wada M, Miyata A, Nakamura H, Satoh A, Watanabe Y, Yagishita T (2004) Endovascular treatment for ruptured VA dissecting aneurysm involving the origin of PICA. Interv Neuroradiol 10(Suppl 1):173–179. https://doi.org/10.1177/15910199040100s130
Korai M, Kanematsu Y, Yamaguchi I, Yamaguchi T, Yamamoto Y, Yamamoto N, Miyamoto T, Shimada K, Satomi J, Hanaoka M, Matsuzaki K, Satoh K, Takagi Y (2021) Subarachnoid hemorrhage due to rupture of vertebral artery dissecting aneurysms: treatments, outcomes, and prognostic factors. World Neurosurg 152:e86–e93. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wneu.2021.05.018
Lee HJ, Cho WC, Choi JH, Kim B-s, Shin YS (2022) Comparison of parent artery occlusion and stent-assisted treatments in ruptured vertebral artery dissecting aneurysms. World Neurosurg. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wneu.2022.08.047
Lee HJ, Choi JH, Lee KS, Kim BS, Shin YS (2022) Clinical and radiological risk factors for rupture of vertebral artery dissecting aneurysm: significance of the stagnation sign. J Neurosurg 137:329–334. https://doi.org/10.3171/2021.9.JNS211848
Lee W, Han HJ, Kim J, Park KY, Kim YB, Jang CK, Chung J (2022) Flow diverter for the treatment of large (> 10 mm) vertebral artery dissecting aneurysms. Acta Neurochirurgica 164:1247–1254. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00701-021-04965-2
Levitt MR, Park MS, Albuquerque FC, Moon K, Kalani MYS, McDougall CG (2016) Posterior inferior cerebellar artery patency after flow-diverting stent treatment. Am J Neuroradiol 37:487. https://doi.org/10.3174/ajnr.A4550
Lin N, Brouillard AM, Keigher KM, Lopes DK, Binning MJ, Liebman KM, Veznedaroglu E, Magarik JA, Mocco J, Duckworth EA, Arthur AS, Ringer AJ, Snyder KV, Levy EI, Siddiqui AH (2015) Utilization of pipeline embolization device for treatment of ruptured intracranial aneurysms: US multicenter experience. J NeuroInterv Surg 7:808. https://doi.org/10.1136/neurintsurg-2014-011320
Lozupone E, Piano M, Valvassori L, Quilici L, Pero G, Visconti E, Boccardi E (2018) Flow diverter devices in ruptured intracranial aneurysms: a single-center experience. J Neurosurg 128:1037–1043. https://doi.org/10.3171/2016.11.Jns161937
Madaelil TP, Wallace AN, Chatterjee AN, Zipfel GJ, Dacey RG Jr, Cross DT 3rd, Moran CJ, Derdeyn CP (2016) Endovascular parent vessel sacrifice in ruptured dissecting vertebral and posterior inferior cerebellar artery aneurysms: clinical outcomes and review of the literature. J Neurointerv Surg 8:796–801. https://doi.org/10.1136/neurintsurg-2015-011732
Maus V, Mpotsaris A, Dorn F, Möhlenbruch M, Borggrefe J, Stavrinou P, Abdullayev N, Barnikol UB, Liebig T, Kabbasch C (2018) The use of flow diverter in ruptured, dissecting intracranial aneurysms of the posterior circulation. World Neurosurg 111:e424–e433. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wneu.2017.12.095
Maybaum J, Henkes H, Aguilar-Pérez M, Hellstern V, Gihr GA, Härtig W, Reisberg A, Mucha D, Schüngel MS, Brill R, Quäschling U, Hoffmann KT, Schob S (2021) Flow diversion for reconstruction of intradural vertebral artery dissecting aneurysms causing subarachnoid hemorrhage-a retrospective study from four neurovascular centers. Front Neurol 12:700164. https://doi.org/10.3389/fneur.2021.700164
Mendez AA, McCarthy DJ, Tonetti DA, Desai SM, Mountz JM, Gardner PA, Jovin TG, Jadhav AP (2022) Angiographic predictors of outcomes after balloon test occlusion. Stroke: Vasc Interv Neurol 2:e000371. https://doi.org/10.1161/SVIN.122.000371
Mizutani T, Aruga T, Kirino T, Miki Y, Saito I, Tsuchida T (1995) Recurrent subarachnoid hemorrhage from untreated ruptured vertebrobasilar dissecting aneurysms. Neurosurgery 36:905-911. discussion 912-903. https://doi.org/10.1227/00006123-199505000-00003
Narata AP, Yilmaz H, Schaller K, Lovblad KO, Pereira VM (2012) Flow-diverting stent for ruptured intracranial dissecting aneurysm of vertebral artery. Neurosurgery 70:982-988. discussion 988-989. https://doi.org/10.1227/NEU.0b013e318236715e
Natarajan SK, Lin N, Sonig A, Rai AT, Carpenter JS, Levy EI, Siddiqui AH (2016) The safety of Pipeline flow diversion in fusiform vertebrobasilar aneurysms: a consecutive case series with longer-term follow-up from a single US center. J Neurosurg 125:111–119. https://doi.org/10.3171/2015.6.Jns1565
Park KW, Park JS, Hwang SC, Im SB, Shin WH, Kim BT (2008) Vertebral artery dissection: natural history, clinical features and therapeutic considerations. J Korean Neurosurg Soc 44:109–115. https://doi.org/10.3340/jkns.2008.44.3.109
Pomeraniec IJ, Mastorakos P, Raper D, Park MS (2020) Rerupture following flow diversion of a dissecting aneurysm of the vertebral artery: case report and review of the literature. World Neurosurg 143:171–179. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wneu.2020.07.149
Rabinov JD, Hellinger FR, Morris PP, Ogilvy CS, Putman CM (2003) Endovascular management of vertebrobasilar dissecting aneurysms. Am J Neuroradiol 24:1421
Ro A, Kageyama N, Abe N, Takatsu A, Fukunaga T (2009) Intracranial vertebral artery dissection resulting in fatal subarachnoid hemorrhage: clinical and histopathological investigations from a medicolegal perspective. J Neurosurg 110:948–954. https://doi.org/10.3171/2008.11.Jns08951
Satow T, Ishii D, Iihara K, Sakai N (2014) Endovascular treatment for ruptured vertebral artery dissecting aneurysms: results from Japanese Registry of Neuroendovascular Therapy (JR-NET) 1 and 2. Neurol Med Chir (Tokyo) 54:98–106. https://doi.org/10.2176/nmc.oa.2013-0184
Sorteberg A (2014) Balloon occlusion tests and therapeutic vessel occlusions revisited: when, when not, and how. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 35:862–865. https://doi.org/10.3174/ajnr.A3852
Steinberg GK, Drake CG, Peerless SJ (1993) Deliberate basilar or vertebral artery occlusion in the treatment of intracranial aneurysms. Immediate results and long-term outcome in 201 patients. J Neurosurg 79:161–173. https://doi.org/10.3171/jns.1993.79.2.0161
Sugiu K, Takahashi K, Muneta K, Ohmoto T (2004) Rebleeding of a vertebral artery dissecting aneurysm during stent-assisted coil embolization: a pitfall of the "stent and coil" technique. Surg Neurol 61:365-370. discussion 370. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0090-3019(03)00515-9
Sugiu K, Tokunaga K, Watanabe K, Sasahara W, Ono S, Tamiya T, Date I (2005) Emergent endovascular treatment of ruptured vertebral artery dissecting aneurysms. Neuroradiology 47:158–164. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00234-005-1341-4
Suh SH, Kim BM, Park SI, Kim DI, Shin YS, Kim EJ, Chung EC, Koh JS, Shin HC, Choi CS, Won YS (2009) Stent-assisted coil embolization followed by a stent-within-a-stent technique for ruptured dissecting aneurysms of the intracranial vertebrobasilar artery. Clinical article. J Neurosurg 111:48–52. https://doi.org/10.3171/2009.2.Jns081418
Thierfelder KM, Baumann AB, Sommer WH, Armbruster M, Opherk C, Janssen H, Reiser MF, Straube A, Lv B (2014) Vertebral artery hypoplasia. Stroke 45:1363–1368. https://doi.org/10.1161/STROKEAHA.113.004188
Wongsuriyanan S, Sriamornrattanakul K (2020) Blind-alley formation and occipital artery-posterior inferior cerebellar artery bypass for the treatment of unclippable vertebral artery aneurysms with posterior inferior cerebellar artery involvement. World Neurosurg 138:e539–e550. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wneu.2020.02.174
Yamaura I, Tani E, Yokota M, Nakano A, Fukami M, Kaba K, Matsumoto T (1999) Endovascular treatment of ruptured dissecting aneurysms aimed at occlusion of the dissected site by using Guglielmi detachable coils. J Neurosurg 90:853–856. https://doi.org/10.3171/jns.1999.90.5.0853
Zhao K-J, Fang Y-B, Huang Q-H, Xu Y, Hong B, Li Q, Liu J-M, Zhao W-Y, Deng B-Q (2013) Reconstructive treatment of ruptured intracranial spontaneous vertebral artery dissection aneurysms: long-term results and predictors of unfavorable outcomes. PLOS ONE 8:e67169. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0067169
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceptualization: Gahn Duangprasert. Methodology: Gahn Duangprasert, Raywat Noiphithak. Investigation: Gahn Duangprasert, Sasikan Sukhor. Data curation: Gahn Duangprasert. Statistical analysis: Gahn Duangprasert. Writing—original draft: Gahn Duangprasert. Writing—review and editing: Gahn Duangprasert, Raywat Noiphithak. Visualization: all authors. Project administration: Gahn Duangprasert, Raywat Noiphithak. Supervision: Dilok Tantongtip
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Retrospective chart review study involving human participants was in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki Declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards. The Human Investigation Committee (IRB) of Thammasat University approved this study (MTU-EC-SU-0–055/65).
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Duangprasert, G., Noiphithak, R., Sukhor, S. et al. Efficacy and predicting factors of multimodal treatment for ruptured intracranial vertebral artery dissecting aneurysms. Neurosurg Rev 46, 321 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10143-023-02226-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10143-023-02226-7