Abstract
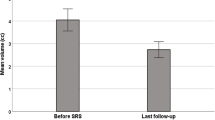
Few reports exist demonstrating the effects of stereotactic radiotherapy (SRT) on the central skull base meningiomas (CSMs). A retrospective analysis of 113 patients was performed. The median age was 62 (IQR 50–72) years old, and 78 patients (69%) were female. Upfront SRT was performed in 41 (36%), where 17 (15%) patients were asymptomatic. The other SRT was for postoperative adjuvant therapy in 32 (28%), and for the recurrent or relapsed tumors in 40 (35%) patients. Previous operation was done in 74 patients (66%). Among the available pathology in 46 patients, 37 (80%) were WHO grade I, 8 (17%) were grade II, and 1 (2%) was grade III. The median prescribed dose covered 95% of the planning target volume was 25 (IQR 21–25) Gy, and the median target volume was 9.5 (IQR 3.9–16.9) cm3. The median progression-free survival (PFS) was 48 (IQR 23–73) months and 84% and 78% were free of tumor progression at 5 and 10 years respectively. The median follow-up was 49 (IQR 28–83) months. PFS was better in grade I than grade II (p = 0.02). No other baseline factors including the history of previous operation were associated with PD or PFS. Adverse events of radiation therapy were radiation-induced optic neuropathy (0.9%), and cerebral edema (4.4%). Asymptomatic cavernous carotid stenosis was found in three (2.7%), five (4.4%) underwent ventriculoperitoneal shunt placement for normal pressure hydrocephalus, and five (4.4%) died. SRT is useful for the management of CSMs with a low rate of adverse events.


Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Data transparency was confirmed.
Code availability
Not applicable.
References
Conti A, Senger C, Acker G, Kluge A, Pontoriero A, Cacciola A, Pergolizzi S, Germanò A, Badakhshi H, Kufeld M, Meinert F, Nguyen P, Loebel F, Vajkoczy P, Budach V, Kaul D (2020) Correction to: Normofractionated stereotactic radiotherapy versus CyberKnife-based hypofractionation in skull base meningioma: a German and Italian pooled cohort analysis. Radiat Oncol 15:279. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13014-020-01707-z
Sheehan JP, Starke RM, Kano H, Kaufmann AM, Mathieu D, Zeiler FA, West M, Chao ST, Varma G, Chiang VLS, Yu JB, McBride HL, Nakaji P, Youssef E, Honea N, Rush S, Kondziolka D, Lee JYK, Bailey RL, Kunwar S, Petti P, Lunsford LD (2014) Gamma Knife radiosurgery for sellar and parasellar meningiomas: a multicenter study. 120:1268. https://doi.org/10.3171/2014.2.Jns13139
Benjamin P, Fahimian, Wang L (2014) Introduction to cyberknife technology. In: Chang SD, Veeravagu A (eds) CyberKnife stereotactic radiosurgery: brain, vol 1. Nova Science Publishers, Incorporated, pp 1–12
Conti A, Pontoriero A, Midili F, Iatì G, Siragusa C, Tomasello C, La Torre D, Cardali SM, Pergolizzi S, De Renzis C (2015) CyberKnife multisession stereotactic radiosurgery and hypofractionated stereotactic radiotherapy for perioptic meningiomas: intermediate-term results and radiobiological considerations. SpringerPlus 4:37. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40064-015-0804-2
National Cancer I (2010) Common terminology criteria for adverse events : (CTCAE)
Miyakawa A, Shibamoto Y, Otsuka S, Iwata H (2014) Applicability of the linear-quadratic model to single and fractionated radiotherapy schedules: an experimental study. J Radiat Res 55:451–454. https://doi.org/10.1093/jrr/rrt138
Marchetti M, Conti A, Beltramo G, Pinzi V, Pontoriero A, Tramacere I, Senger C, Pergolizzi S, Fariselli L (2019) Multisession radiosurgery for perioptic meningiomas: medium-to-long term results from a CyberKnife cooperative study. J Neurooncol 143:597–604. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-019-03196-x
Meniai-Merzouki F, Bernier-Chastagner V, Geffrelot J, Tresch E, Lacornerie T, Coche-Dequeant B, Lartigau E, Pasquier D (2018) Hypofractionated stereotactic radiotherapy for patients with intracranial meningiomas: impact of radiotherapy regimen on local control. Sci Rep 8:13666. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-018-32124-8
Patibandla MR, Lee C-c, Sheehan J (2017) Stereotactic radiosurgery of central skull base meningiomas—volumetric evaluation and long-term outcomes. World Neurosurg 108:176–184. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wneu.2017.08.166
Conti A, Pontoriero A, Iatì G, Cardali SM, Brogna A, Friso F, Rosetti V, Zoli M, Parisi S, Cacciola A, Lillo S, Pergolizzi S, Mazzatenta D (2020) Image-guided multisession radiosurgery of skull base meningiomas. Cancers 12.https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers12123569
Chang SD, Adler JR Jr, Martin DP (1998) LINAC radiosurgery for cavernous sinus meningiomas. Stereotact Funct Neurosurg 71:43–50. https://doi.org/10.1159/000029647
Morimoto M, Yoshioka Y, Shiomi H, Isohashi F, Konishi K, Kotsuma T, Fukuda S, Kagawa N, Kinoshita M, Hashimoto N, Yoshimine T, Koizumi M (2011) Significance of tumor volume related to peritumoral edema in intracranial meningioma treated with extreme hypofractionated stereotactic radiation therapy in three to five fractions. Jpn J Clin Oncol 41:609–616. https://doi.org/10.1093/jjco/hyr022
Engenhart R, Kimmig BN, Höver KH, Wowra B, Sturm V, van Kaick G, Wannenmacher M (1990) Stereotactic single high dose radiation therapy of benign intracranial meningiomas. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 19:1021–1026. https://doi.org/10.1016/0360-3016(90)90028-i
Nakamura S, Hiyama H, Arai K, Nakaya K, Sato H, Hayashi M, Kawamata T, Izawa M, Takakura K (1996) Gamma Knife radiosurgery for meningiomas: four cases of radiation-induced edema. Stereotact Funct Neurosurg 66(Suppl 1):142–145. https://doi.org/10.1159/000099804
Singh VP, Kansai S, Vaishya S, Julka PK, Mehta VS (2000) Early complications following gamma knife radiosurgery for intracranial meningiomas. J Neurosurg 93(Suppl 3):57–61. https://doi.org/10.3171/jns.2000.93.supplement
Vermeulen S, Young R, Li F, Meier R, Raisis J, Klein S, Kohler E (1999) A comparison of single fraction radiosurgery tumor control and toxicity in the treatment of basal and nonbasal meningiomas. Stereotact Funct Neurosurg 72(Suppl 1):60–66. https://doi.org/10.1159/000056440
Ma Z, Tang J, Qiu B, Hou Y, Peng Z, Liu Y (1998) [Gamma knife treatment of meningiomas]. Hunan yi ke da xue xue bao = Hunan yike daxue xuebao = Bulletin of Hunan Medical University 23:161–163
Common Terminology Criteria for Adverse Events (CTCAE) version 4.03. U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, National Institute of Health, National Cancer Institute. Available at: https://www.eortc.be/services/doc/ctc/CTCAE_4.03_201006-14_QuickReference_5x7.pdf
Pikis S, Bunevicius A, Sheehan J (2021) Outcomes from treatment of asymptomatic skull base meningioma with stereotactic radiosurgery. Acta Neurochir 163:83–88. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00701-020-04648-4
Schwartz TH, McDermott MW (2020) The Simpson grade: abandon the scale but preserve the message.1. https://doi.org/10.3171/2020.6.Jns201904
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors read and approved the final manuscript. SH made a study design, collected patient data, and drafted and revised the manuscript. KK contributed to revising the original draft. KS and SI were the supervisors.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval
This study was done under our institutional review board’s approval and did not require patient consent.
Consent to participate
Our institutional review board did not require informed consent for study participation because this study relied on information obtained as part of routine clinical practice.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hong, S., Sato, K., Kagawa, K. et al. The long-term outcome of CyberKnife-based stereotactic radiotherapy for central skull base meningiomas: a single-center experience. Neurosurg Rev 44, 3519–3526 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10143-021-01535-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10143-021-01535-z