Abstract
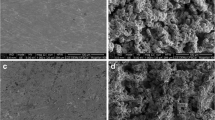
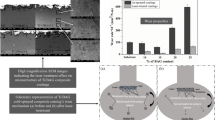
Surface treatment by laser irradiation can change the topography of titanium; however, little is known about the changes it causes when applied to other coatings. This study aimed to evaluate the influence of Er:YAG laser irradiation on the surface properties of titanium-aluminum-vanadium (Ti-6Al-4V) discs. Four Ti-6Al-4V surfaces were evaluated (n = 10): CON—control, machined without surface treatment; LT—machined + laser treatment; HA—hydroxyapatite coating; and LT-HA—hydroxyapatite coating + laser treatment. For the laser treatment, an Er:YAG laser with a wavelength of 2940 nm, a frequency of 10 Hz, and an energy density of 12.8 J/cm2 was used. The morphology of the coating was investigated by scanning electron microscopy and the surface composition by energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy. The influence of laser irradiation treatment on roughness and wettability was also evaluated. The Er:YAG laser promoted a significant reduction in the roughness Sa (p < 0.05) and in the contact angle (p = 0.002) of the LT surface compared to the CON surface. On the LT-HA surface, a significant decrease in roughness was observed only for the Rz parameter (p = 0.015) and an increase in the contact angle (p < 0.001) compared to the HA surface. The use of the Er:YAG laser with the evaluated parameters decreased the surface roughness and improved the wetting capacity of machined without surface treatment. In the group with hydroxyapatite coating, the laser influenced the surface roughness only for the parameter Rz and reduced their wetting capacity.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Safi IN, Hussein BMA, Al Shammari AM, Tawfiq TA (2019) Implementation and characterization of coating pure titanium dental implant with sintered β-TCP by using Nd:YAG laser. Saudi Dent J 31:242–250. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sdentj.2018.12.004
Tiainen L, Abreu P, Buciumeanu M et al (2019) Novel laser surface texturing for improved primary stability of titanium implants. J Mech Behav Biomed Mater 98:26–39. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmbbm.2019.04.052
Simões IG, dos Reis AC, da Costa Valente ML (2021) Analysis of the influence of surface treatment by high-power laser irradiation on the surface properties of titanium dental implants: a systematic review. J Prosthet Dent. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.prosdent.2021.07.026
Cura AC, Zuchuat JI, Tribbia LT et al (2022) Sandblasted, acid etched and UV irradiated titanium surface for dental implants: in vitro and in vivo analysis. Materialia (Oxf) 21:101302. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mtla.2021.101302
Souza JCM, Sordi MB, Kanazawa M et al (2019) Nano-scale modification of titanium implant surfaces to enhance osseointegration. Acta Biomater 94:112–131. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actbio.2019.05.045
Yu Z, Yang G, Zhang W, Hu J (2018) Investigating the effect of picosecond laser texturing on microstructure and biofunctionalization of titanium alloy. J Mater Process Technol 255:129–136. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmatprotec.2017.12.009
Łęcka KM, Gąsiorek J, Mazur-Nowacka A et al (2019) Adhesion and corrosion resistance of laser-oxidized titanium in potential biomedical application. Surf Coat Technol 366:179–189. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.surfcoat.2019.03.032
Rafiee K, Naffakh-Moosavy H, Tamjid E (2020) The effect of laser frequency on roughness, microstructure, cell viability and attachment of Ti6Al4V alloy. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 109:110637. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msec.2020.110637
Menci G, Demir AG, Waugh DG et al (2019) Laser surface texturing of β-Ti alloy for orthopaedics: effect of different wavelengths and pulse durations. Appl Surf Sci 489:175–186. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2019.05.111
Lee BEJ, Exir H, Weck A, Grandfield K (2018) Characterization and evaluation of femtosecond laser-induced sub-micron periodic structures generated on titanium to improve osseointegration of implants. Appl Surf Sci 441:1034–1042. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2018.02.119
Gnilitskyi I, Pogorielov M, Viter R et al (2019) Cell and tissue response to nanotextured Ti6Al4V and Zr implants using high-speed femtosecond laser-induced periodic surface structures. Nanomedicine 21:102036. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nano.2019.102036
Frostevarg J, Olsson R, Powell J et al (2019) Formation mechanisms of surfaces for osseointegration on titanium using pulsed laser spattering. Appl Surf Sci 485:158–169. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2019.04.187
Sadeghi M, Kharaziha M, Salimijazi HR, Tabesh E (2019) Role of micro-dimple array geometry on the biological and tribological performance of Ti6Al4V for biomedical applications. Surf Coat Technol 362:282–292. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.surfcoat.2019.01.113
Luo X, Yao S, Zhang H et al (2020) Biocompatible nano-ripples structured surfaces induced by femtosecond laser to rebel bacterial colonization and biofilm formation. Opt Laser Technol 124:105973. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.optlastec.2019.105973
Medvids A, Onufrijevs P, Kaupužs J et al (2021) Anatase or rutile TiO2 nanolayer formation on Ti substrates by laser radiation: mechanical, photocatalytic and antibacterial properties. Opt Laser Technol 138:106898. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.optlastec.2020.106898
Tsai M-H, Haung C-F, Shyu S-S et al (2015) Surface modification induced phase transformation and structure variation on the rapidly solidified recast layer of titanium. Mater Charact 106:463–469. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matchar.2015.06.004
Khoo LK, Sakdajeyont W, Khanijou M et al (2019) Titanium fixture implants treated by laser in dentistry: review article. J Oral Maxillofac Surg Med Pathol 31:381–385. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ajoms.2019.08.001
Stango SAX, Karthick D, Swaroop S et al (2018) Development of hydroxyapatite coatings on laser textured 316 LSS and Ti-6Al-4V and its electrochemical behavior in SBF solution for orthopedic applications. Ceram Int 44:3149–3160. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2017.11.083
Behera RR, Hasan A, Sankar MR, Pandey LM (2018) Laser cladding with HA and functionally graded TiO2-HA precursors on Ti–6Al–4V alloy for enhancing bioactivity and cyto-compatibility. Surf Coat Technol 352:420–436. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.surfcoat.2018.08.044
Lin Z, Strauss FJ, Lang NP et al (2021) Efficacy of laser monotherapy or non-surgical mechanical instrumentation in the management of untreated periodontitis patients. A systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin Oral Investig 25:375–391. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00784-020-03584-y
Miranda G, Sousa F, Costa MM et al (2019) Surface design using laser technology for Ti6Al4V-hydroxyapatite implants. Opt Laser Technol 109:488–495. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.optlastec.2018.08.034
Fathi AM, Ahmed MK, Afifi M et al (2021) Taking hydroxyapatite-coated titanium implants two steps forward: surface modification using graphene mesolayers and a hydroxyapatite-reinforced polymeric scaffold. ACS Biomater Sci Eng 7:360–372. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsbiomaterials.0c01105
Pires LC, Guastaldi FPS, Nogueira AVB et al (2019) Physicochemical, morphological, and biological analyses of Ti-15Mo alloy surface modified by laser beam irradiation. Lasers Med Sci 34:537–546. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10103-018-2626-2
Faria D, Abreu CS, Buciumeanu M et al (2018) Ti6Al4V laser surface preparation and functionalization using hydroxyapatite for biomedical applications. J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater 106:1534–1545. https://doi.org/10.1002/jbm.b.33964
dos Santos ML, dos Santos RC, de Almeida FE, Guastaldi AC (2018) Calcium phosphates of biological importance based coatings deposited on Ti-15Mo alloy modified by laser beam irradiation for dental and orthopedic applications. Ceram Int 44:22432–22438. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2018.09.010
Raimbault O, Benayoun S, Anselme K et al (2016) The effects of femtosecond laser-textured Ti-6Al-4V on wettability and cell response. Materials Science and Engineering: C 69:311–320. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msec.2016.06.072
Cunha A, Serro AP, Oliveira V et al (2013) Wetting behaviour of femtosecond laser textured Ti–6Al–4V surfaces. Appl Surf Sci 265:688–696. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2012.11.085
Ayobian-Markazi N, Karimi M, Safar-Hajhosseini A (2015) Effects of Er: YAG laser irradiation on wettability, surface roughness, and biocompatibility of SLA titanium surfaces: an in vitro study. Lasers Med Sci 30:561–566. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10103-013-1361-y
Jiang J, Han G, Zheng X et al (2019) Characterization and biocompatibility study of hydroxyapatite coating on the surface of titanium alloy. Surf Coat Technol 375:645–651. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.surfcoat.2019.07.067
Ke D, Vu AA, Bandyopadhyay A, Bose S (2019) Compositionally graded doped hydroxyapatite coating on titanium using laser and plasma spray deposition for bone implants. Acta Biomater 84:414–423. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actbio.2018.11.041
Jing Z, Cao Q, Jun H (2021) Corrosion, wear and biocompatibility of hydroxyapatite bio-functionally graded coating on titanium alloy surface prepared by laser cladding. Ceram Int 47:24641–24651. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2021.05.186
Li HC, Wang DG, Hu C et al (2021) Effect of Na2O and ZnO on the microstructure and properties of laser cladding derived CaO-SiO2 ceramic coatings on titanium alloys. J Colloid Interface Sci 592:498–508. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2021.02.064
Park C-Y, Kim S-G, Kim M-D et al (2005) Surface properties of endosseous dental implants after NdYAG and CO2 laser treatment at various energies. J. Maxillofac. Surg. 63:1522–1527. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.joms.2005.06.015
Huang P, Chen X, Chen Z et al (2021) Efficacy of Er:YAG laser irradiation for decontamination and its effect on biocompatibility of different titanium surfaces. BMC Oral Health 21:649. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12903-021-02006-z
Shin S-I, Lee E-K, Kim J-H et al (2013) The effect of Er:YAG laser irradiation on hydroxyapatite-coated implants and fluoride-modified TiO2-blasted implant surfaces: a microstructural analysis. Lasers Med Sci 28:823–831. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10103-012-1162-8
de Souza ID, Cruz MAE, de Faria AN et al (2014) Formation of carbonated hydroxyapatite films on metallic surfaces using dihexadecyl phosphate–LB film as template. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces 118:31–40. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfb.2014.03.029
Tas AC (2000) Synthesis of biomimetic Ca-hydroxyapatite powders at 37°C in synthetic body fluids. Biomaterials 21:1429–1438. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0142-9612(00)00019-3
Katahira K, Ezura A, Ohkawa K et al (2016) Generation of bio-compatible titanium alloy surfaces by laser-induced wet treatment. CIRP Annals 65:237–240. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cirp.2016.04.053
Baloyi NM, Popoola API, Pityana SL (2015) Microstructure, hardness and corrosion properties of laser processed Ti6Al4V-based composites. Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 25:2912–2923. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1003-6326(15)63917-6
Lin X, Li X, Li G et al (2020) Micro-dot-matrix induced by femtosecond laser on titanium surface for Ca-P phase deposition. Appl Surf Sci 499:143925. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2019.143925
Ciganovic J, Stasic J, Gakovic B et al (2012) Surface modification of the titanium implant using TEA CO2 laser pulses in controllable gas atmospheres – comparative study. Appl Surf Sci 258:2741–2748. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2011.10.125
Milovanović DS, Radak BB, Gaković BM et al (2010) Surface morphology modifications of titanium based implant induced by 40picosecond laser pulses at 266nm. J Alloys Compd 501:89–92. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2010.04.047
Ruiz GCM, Cruz MAE, Faria AN et al (2017) Biomimetic collagen/phospholipid coatings improve formation of hydroxyapatite nanoparticles on titanium. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 77:102–110. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msec.2017.03.204
Wang Q, Ding C, Zhou Y et al (2018) Universal and biocompatible hydroxyapatite coating induced by phytic acid-metal complex multilayer. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces 169:478–485. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfb.2018.05.057
Yang J, Zhang K, Que K et al (2018) Surface modification of titanium with hydroxyapatite layer induced by phase-transited lysozyme coating. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 92:206–215. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msec.2018.05.055
Stubinger S, Etter C, Miskiewicz M et al (2010) Surface alterations of polished and sandblasted and acid-etched titanium implants after Er:YAG, carbon dioxide, and diode laser irradiation. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants 25:104–111
Lee J-H, Kwon Y-H, Herr Y et al (2011) Effect of erbium-doped: yttrium, aluminium and garnet laser irradiation on the surface microstructure and roughness of sand-blasted, large grit, acid-etched implants. J Periodontal Implant Sci 41:135. https://doi.org/10.5051/jpis.2011.41.3.135
Jaritngam P, Tangwarodomnukun V, Qi H, Dumkum C (2020) Surface and subsurface characteristics of laser polished Ti6Al4V titanium alloy. Opt Laser Technol 126:106102. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.optlastec.2020.106102
Andrukhov O, Huber R, Shi B et al (2016) Proliferation, behavior, and differentiation of osteoblasts on surfaces of different microroughness. Dent. Mater. J. 32:1374–1384. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dental.2016.08.217
Wennerberg A, Albrektsson T (2009) Effects of titanium surface topography on bone integration: a systematic review. Clin Oral Implants Res 20:172–184. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1600-0501.2009.01775.x
Yang Y, Serpersu K, He W et al (2011) Osteoblast interaction with laser cladded HA and SiO2-HA coatings on Ti–6Al–4V. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 31:1643–1652. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msec.2011.07.009
Chien CS, Liao TY, Hong TF et al (2011) Investigation into microstructural properties of fluorapatite Nd-YAG laser clad coatings with PVA and WG binders. Surf Coat Technol 205:3141–3146. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.surfcoat.2010.11.028
dos Santos LCP, Malheiros FC, Guarato AZ (2020) Surface parameters of as-built additive manufactured metal for intraosseous dental implants. J Prosthet Dent 124:217–222. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.prosdent.2019.09.010
Almas K, Smith S, Kutkut A (2019) What is the best micro and macro dental implant topography? Dent Clin North Am 63:447–460. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cden.2019.02.010
Huo F, Guo W, Wu H et al (2018) Fabrication of biomimetic resorption lacunae-like structure on titanium surface and its osteoblast responses. Appl Surf Sci 436:11–21. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2017.11.282
Medvedev AE, Ng HP, Lapovok R et al (2016) Effect of bulk microstructure of commercially pure titanium on surface characteristics and fatigue properties after surface modification by sand blasting and acid-etching. J Mech Behav Biomed Mater 57:55–68. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmbbm.2015.11.035
Butt A, Hamlekhan A, Patel S et al (2015) A novel investigation of the formation of titanium oxide nanotubes on thermally formed oxide of Ti-6Al-4V. J Oral Implantol 41:523–531. https://doi.org/10.1563/AAID-JOI-D-13-00340
Alves SA, Patel SB, Sukotjo C et al (2017) Synthesis of calcium-phosphorous doped TiO2 nanotubes by anodization and reverse polarization: a promising strategy for an efficient biofunctional implant surface. Appl Surf Sci 399:682–701. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2016.12.105
Ferraris S, Vitale A, Bertone E et al (2016) Multifunctional commercially pure titanium for the improvement of bone integration: multiscale topography, wettability, corrosion resistance and biological functionalization. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 60:384–393. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msec.2015.11.049
Fernandez-Garcia E, Chen X, Gutierrez-Gonzalez CF et al (2015) Peptide-functionalized zirconia and new zirconia/titanium biocermets for dental applications. J Dent 43:1162–1174. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jdent.2015.06.002
Khosroshahi ME, Mahmoodi M, Saeedinasab H (2009) In vitro and in vivo studies of osteoblast cell response to a titanium-6 aluminium-4 vanadium surface modified by neodymium:yttrium–aluminium–garnet laser and silicon carbide paper. Lasers Med Sci 24:925–939. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10103-008-0628-1
Hao L, Lawrence J (2007) Wettability modification and the subsequent manipulation of protein adsorption on a Ti6Al4V alloy by means of CO2 laser surface treatment. J Mater Sci Mater Med 18:807–817. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10856-006-0002-4
Giannelli M, Bani D, Tani A et al (2017) Effects of an erbium:yttrium-aluminum-garnet laser and ultrasonic scaler on titanium dioxide-coated titanium surfaces contaminated with subgingival plaque: an in vitro study to assess post-treatment biocompatibility with osteogenic cells. J Periodontol 88:1211–1220. https://doi.org/10.1902/jop.2017.170195
Funding
This work was supported by FAPESP—Foundation for Research Support of the State of São Paulo (grant number 2019/09213-3).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Isadora Gazott Simões: conceptualization, investigation, methodology, validation, investigation, resources, data curation, writing—original draft, writing—review and editing, funding acquisition. Simone Kreve: methodology. Marcos Antônio Eufrásio Cruz: methodology. André Luís Botelho: methodology, writing—original draft. Ana Paula Ramos: methodology, resources. Andrea Candido dos Reis: term, conceptualization, methodology, resources, writing—review and editing, supervision. Mariana Lima da Costa Valente: term, conceptualization, investigation, methodology, formal analysis, resources, data curation, supervision, writing—original draft, writing—review and editing, project administration, funding acquisition.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
Not applicable.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Simões, I.G., Kreve, S., Cruz, M.A.E. et al. Influence of Er:YAG laser irradiation on surface properties of Ti-6Al-4V machined and hydroxyapatite coated. Lasers Med Sci 38, 48 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10103-023-03719-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10103-023-03719-z