Abstract
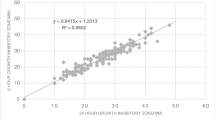
The disc diffusion test is used for antimicrobial susceptibility testing worldwide. In this study, the performance of both Bio-Rad® antibiotic discs (as compared with Oxoid® discs) and the ADAGIO™ automated system for the reading of disc diffusion test results was evaluated with American Type Culture Collection (ATCC) quality control (QC) and wild strains of bacteria. Inhibition zones of both disc brands were read manually and through use of the ADAGIO™ system. Categorized interpretation of the results for each strain and antibiotic combination was summarized according to the Clinical Laboratory Standards Institute MS-100 (2017 update) manual and ADAGIO™ readings. Eight ATCC QC strains and 120 different wild strains were evaluated, to give a total of 1226 antibiotic/bacteria combinations and 2486 manual readings. One major error and four minor errors (0.08% and 0.34%, respectively) were detected via manual readings of the Bio-Rad® discs as compared with the Oxoid® discs. For the same number of antibiotic/bacteria combinations, five minor errors and one major error (0.42% and 0.08%, respectively) were detected with the Bio-Rad® discs read by the ADAGIO™ system. In addition, the number of times the automatic reading needed manual edition with Bio-Rad® discs was statistically lower than it did with Oxoid® discs (3.7% vs. 5.7%, p < 0.05). These findings support the hypothesis that Bio-Rad discs are not inferior to Oxoid® discs, and the performance of the ADAGIO™ system is comparable to that of manual readings with both disc brands.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Jorgensen JH, Ferraro MJ (2009) Antimicrobial susceptibility testing: a review of general principles and contemporary practices. Clin Infect Dis 49(11):1749–1755
Périllaud C, Pilmis B, Diep J, de Ponfilly GP, Vidal B, Couzigou C, Mizrahi A, Lourtet-Hascoët J, Le Monnier A, Nguyen Van JC (2019) Prospective evaluation of rapid antimicrobial susceptibility testing by disk diffusion on Mueller-Hinton rapid-SIR directly on blood cultures. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis 93(1):14–21
Chandrasekaran S, Abbott AN, Campeau S, Zimmer BL, Weinstein MP, Thrupp L, Hejna J, Walker L, Ammann T, Kirn TJ, Patel R, Humphries RM (2018) Direct-from-blood-culture disk diffusion to determine antimicrobial susceptibility of gram-negative bacteria: preliminary report from the Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute methods development and standardization working group. J Clin Microbiol 56(3):e01678–e01617
Hombach M, Jetter M, Blöchliger N, Kolesnik-Glodmann N, Böttger EC (2017) Fully automated disc diffusion for rapid antibiotic susceptibility test results: a proof-of-principle study. J Antimicrob Chemother 72(6):1659–1668
Hombach M, Zbinden R, Böttger EC (2013) Standardisation of disk diffusion results for antibiotic susceptibility testing using the sirscan automated zone reader. BMC Microbiol 13(1):225
Kolbert M, Chegrani F, Shah PM (2004) Evaluation of the OSIRIS video reader as an automated measurement system for the agar disk diffusion technique. Clin Microbiol Infect 10(5):416–420
Lestari ES, Severin JA, Filius PMG, Kuntaman K, Offra Duerink D, Hadi U, Wahjono H, Verbrugh HA (2008) Comparison of the accuracy of disk diffusion zone diameters obtained by manual zone measurements to that by automated zone measurements to determine antimicrobial susceptibility. J Microbiol Methods 75(2):177–181
Sánchez M, Sánchez del Saz B, Loza E, Baquero F, Cantón R (2001) Evaluation of the OSIRIS video reader system for disk diffusion susceptibility test reading. Clin Microbiol Infect 7(7):352–357
Medeiros AA, Crellin J (2000) Evaluation of the Sirscan automated zone reader in a clinical microbiology laboratory. J Clin Microbiol 38(4):1688–1693
Andrews JM, Boswell FJ, Wise R (2000) Evaluation of the Oxoid Aura image system for measuring zones of inhibition with the disc diffusion technique. J Antimicrob Chemother 46(4):535–540
Korgenski EK, Daly JA (1998) Evaluation of the BIOMIC video reader system for determining interpretive categories of isolates on the basis of disk diffusion susceptibility results. J Clin Microbiol 36(1):302–304
Joshi A, Iyer V, Balasubramaniam U, Kagal A, Bharadwaj R (2008) Comparison of efficacy of three commercially available antibiotic discs. Indian J Med Microbiol 26(2):160–162
Åhman J, Matuschek E, Kahlmeter G (2019) The quality of antimicrobial discs from nine manufacturers—EUCAST evaluations in 2014 and 2017. Clin Microbiol Infect 25(3):346–352
Idelevich EA, Becker K, Schmitz J, Knaack D, Peters G, Köck R (2016) Evaluation of an automated system for reading and interpreting disk diffusion antimicrobial susceptibility testing of fastidious bacteria. PLoS One 11(7):e0159183
Weinstein MP, Patel JB, Campeau S, et al. (2018) Performance Standards for Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing M100 (28th edn) A Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute publication. http://homenew.clalit.org.il/sites/Communities/logi/rechesh/Reagent/CLSI/M100Ed28E.pdf Wayne USA. www.clsi.org. Accessed 1 Apr 2018.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Strauss, M., Zoabi, K., Sagas, D. et al. Evaluation of Bio-Rad® discs for antimicrobial susceptibility testing by disc diffusion and the ADAGIO™ system for the automatic reading and interpretation of results. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis 39, 375–384 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10096-019-03735-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10096-019-03735-4