Abstract
Objective
To compare the presence of allodynia, pain catastrophizing, and the impact of headaches on patients with cluster headache (CH) and healthy individuals. Our second aim was to analyze the relationship between catastrophism, psychological comorbidities, and the impact in CH.
Methods
We designed this cross-sectional study to compare various factors among 47 patients diagnosed with CH and 40 healthy controls, and then focus on catastrophism, anxiety, depression, and impact in the CH group.
Results
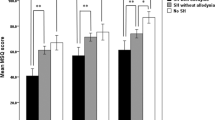
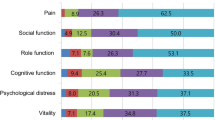
There were statistically significant differences between CH and the asymptomatic group in Allodynia Symptom Checklist (ASC) (p < 0.001), Pain Catastrophizing Scale (p < 0.001), and HIT-6 (p < 0.001) scores. We found a correlation among ASC, PCS, anxiety-depression, EuroQoL, and HIT-6 for the CH group. In this group, we observed a strong positive correlation between PCS and anxiety (rho = 0.69; p < 0.001), PCS and depression (rho = 0.62; p < 0.001) and depression and EuroQoL (rho = − 0.68; p < 0.001). The regression model showed that the combination of anxiety and HIT-6 was a significant predictor of PCS (adjusted R2 = 0.52).
Discussion
Our findings reveal significant differences regarding allodynia, pain catastrophism, and impact in CH group compared with controls. We found a significant relationship between psychological comorbidity, pain catastrophism, and quality of life in CH patients. Anxiety and HIT-6 were a predictor (adjusted R2 = 52%) of pain catastrophism. Screening for these comorbidities should be implemented through a multidisciplinary approach.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Vincent M, Wang S (2018) Headache Classification Committee of the International Headache Society (IHS) The international classification of headache disorders, 3rd edition. Cephalalgia. 38(1):1–211
Ashkenazi A (2010) Allodynia in cluster headache. Curr Pain Headache Rep. 14(2):140–144
Lipton RB, Fanning KM, Buse DC, Martin VT, Hohaia LB, Adams AM, Reed ML, Goadsby PJ (2019) Migraine progression in subgroups of migraine based on comorbidities: results of the CaMEO Study. Neurology. 93:e2224–e2236
Gil-Martínez A, Navarro-Fernández G, Mangas-Guijarro MÁ, Díaz-de-Terán J (2019) Hyperalgesia and central sensitization signs in patients with cluster headache: a cross-sectional study. Pain Med. 0(0):1–9
Gómez-Mayordomo V, Palacios-Ceña M, Guerrero-Peral Á, Fuensalida-Novo S, Fernández-de-las-Peñas C, Cuadrado ML (2020) Widespread hypersensitivity to pressure pain in men with cluster headache during prolonged remission is not related to the levels of depression and anxiety. Pain Pract 20(2):147–153
May A, Schwedt TJ, Magis D, Pozo-Rosich P, Evers S, Wang SJ (2018) Cluster headache. Nat Rev Dis Prim 4:1–17. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrdp.2018.6
Quartana PJ, Edwards RR (2009) Pain catastrophizing: a critical review. Expert Rev Neurother 9(5):745–758 Available from: http://www.tandfonline.com/doi/pdf/10.1586/ern.09.34?needAccess=true
Holroyd KA, Drew JB, Cottrell CK, Romanek KM, Heh V (2007) Impaired functioning and quality of life in severe migraine: the role of catastrophizing and associated symptoms. Cephalalgia. 27(10):1156–1165
Stern AF (2014) The Hospital Anxiety and Depression Scale. Occup Med (Chic Ill). 64(5):393–394
Rendas-Baum R, Yang M, Varon SF, Bloudek LM, DeGryse RE, Kosinski M (2014) Validation of the headache impact test (HIT-6) in patients with chronic migraine. Health Qual Life Outcomes. 12(1):1–10
Lipton RB, Bigal ME, Ashina S, Burstein R, Silberstein S, Reed ML, Serrano D, Stewart WF, American Migraine Prevalence Prevention Advisory Group (2008) Cutaneous allodynia in the migraine population. Ann Neurol. 63(2):148–158
Pedler A (2010) The pain catastrophising scale. J Physiother. 56(3):137
Szende A, Janssen B, Cabasés J (eds) (2014) Self-reported population health: an international perspective based on EQ-5D. Springer
Rodero B, García-Campayo J, Casanueva B, del Hoyo YL, Serrano-Blanco A, Luciano JV (2010) Validation of the Spanish version of the Chronic Pain Acceptance Questionnaire (CPAQ) for the assessment of acceptance in fibromyalgia. Health Qual Life Outcomes. 8:1–10
Mouri H (2013) Log-normal distribution from a process that is not multiplicative but is additive. Phys Rev E Stat Nonlinear Soft Matter Phys. 88(4):1–7
Wilbrink LA, Louter MA, Teernstra OPM, Van Zwet EW, Huygen FJPM, Haan J et al (2017) Allodynia in cluster headache. Pain. 158(6):1113–1117
Fernández-de-las-Peñas C, Ortega-Santiago R, Cuadrado ML, López-de-Silanes C, Pareja JA (2011) Bilateral widespread mechanical pain hypersensitivity as sign of central sensitization in patients with cluster headache. Headache. 51(3):384–391
Ladda J, Straube A, Förderreuther S, Krause P, Eggert T (2006) Quantitative sensory testing in cluster headache: Increased sensory thresholds. Cephalalgia. 26(9):1043–1050
Kim BS, Park JW, Sohn JH, Lee MJ, Kim BK, Chu MK et al (2019) Associated factors and clinical implication of cutaneous allodynia in patients with cluster headache: a prospective multicentre study. Sci Rep. 9(1):1–8
Louter MA, Wilbrink LA, Haan J, Van Zwet EW, Van Oosterhout WPJ, Zitman FG et al (2016) Cluster headache and depression. Neurology. 87(18):1899–1906
Donnet A, Lanteri-Minet M, Guegan-Massardier E, Mick G, Fabre N, Géraud G et al (2007) Chronic cluster headache: a French clinical descriptive study. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 78(12):1354–1358
Jürgens TP, Gaul C, Lindwurm A, Dresler T, Paelecke-Habermann Y, Schmidt-Wilcke T, Lürding R, Henkel K, Leinisch E (2011) Impairment in episodic and chronic cluster headache. Cephalalgia. 31(6):671–682
Xie Q, Huang Q, Wang J, Li N, Tan G, Zhou J (2013) Clinical features of cluster headache: an outpatient clinic study from China. Pain Med (United States). 14(6):802–807
D’Amico D, Raggi A, Grazzi L, Lambru G (2020) Disability, quality of life, and socioeconomic burden of cluster headache: a critical review of current evidence and future perspectives. Headache. 60(4):809–818
Jensen RM, Lyngberg A, Jensen RH (2007) Burden of cluster headache. Cephalalgia. 27(6):535–541
Pohl H, Gantenbein AR, Sandor PS, Schoenen J, Andrée C (2020) Interictal burden of cluster headache: results of the EUROLIGHT Cluster Headache Project, an internet-based, cross-sectional study of people with cluster headache. Headache. 60(2):360–369
Sohn JH, Park JW, Lee MJ, Chung PW, Chu MK, Chung JM, Ahn JY, Kim BS, Kim SK, Choi YJ, Kim D, Song TJ, Oh K, Moon HS, Park KY, Kim BK, Bae DW, Chung CS, Cho SJ (2020) Clinical factors influencing the impact of cluster headache from a prospective multicenter study. Scientific Reports 10(1):2428
Gil-Martínez A, Navarro-Fernández G, Mangas-Guijarro MÁ, Lara-Lara M, López-López A, Fernández-Carnero J, la Touche R (2017) Comparison between chronic migraine and temporomandibular disorders in pain-related disability and fear-avoidance behaviors. Pain Med (United States). 18(11):2214–2223
Kneeland ET, Griffin ML, Taghian N, Weiss RD, McHugh RK (2019) Associations between pain catastrophizing and clinical characteristics in adults with substance use disorders and co-occurring chronic pain. Am J Drug Alcohol Abuse 45(5):488–494. https://doi.org/10.1080/00952990.2019.1581793
Sullivan MJL, Thorn B, Haythornthwaite JA, Keefe F, Martin M, Bradley LA, Lefebvre JC (2001) Theoretical perspectives on the relation between catastrophizing and pain. Clin J Pain. 17(1):52–64
Goli Z, Asghari A, Moradi A (2016) Effects of mood induction on the pain responses in patients with migraine and the role of pain catastrophizing. Clin Psychol Psychother. 23(1):66–76
Schenck LAM, Andrasik F (2019) Behavioral and psychological aspects of cluster headache: an overview. Neurol Sci. 40:3–7
Piacentini SHMJ, Draghi L, Cecchini AP, Leone M (2017) Personality disorders in cluster headache: a study using the Millon Clinical Multiaxial Inventory-III. Neurol Sci. 38:181–184
Edwards RR, Kronfli T, Haythornthwaite JA, Smith MT, McGuire L, Page GG (2008) Association of catastrophizing with interleukin-6 responses to acute pain. Pain 140(1):135–144. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pain.2008.07.024
Ferraro S, Nigri A, Bruzzone MG, Demichelis G, Pinardi C, Brivio L et al (2019) Cluster headache: insights from resting-state functional magnetic resonance imaging. Neurol Sci.:8–10
Giani L, Cecchini AP, Leone M (2020) Anti-CGRP in cluster headache therapy: a response. Neurol Sci. 41(9):2641
Klan T, Bräscher AK, Vales A, Liesering-Latta E, Witthöft M, Gaul C (2020) Determination of psychosocial factors in cluster headache – construction and psychometric properties of the Cluster Headache Scales (CHS). Cephalalgia. 40(11):1240–1249
Mardian AS, Hanson ER, Villarroel L, Karnik AD, Sollenberger JG, Okvat HA et al (2020) Flipping the pain care model : a sociopsychobiological approach to high-value chronic pain care. 0(0):1–13
Abu Bakar N, Torkamani M, Tanprawate S, Lambru G, Matharu M, Jahanshahi M (2016) The development and validation of the Cluster Headache Quality of life scale (CHQ). J Headache Pain 17(1):1–9. https://doi.org/10.1186/s10194-016-0674-1
Allena M, De Icco R, Sances G, Ahmad L, Putortì A, Pucci E et al (2019) Gender differences in the clinical presentation of cluster headache: a role for sexual hormones? Front Neurol. 10(November):1–7
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
All participants voluntarily signed the informed consent after the explanation of the study, ensuring the confidentiality of their personal data. This study was approved by the Ethics and Clinical Research Committee of La Paz University Hospital (PI-3387).
Conflict of interest
None.
Ethical approval
None.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Díaz-de-Terán, J., Sastre-Real, M., Lobato-Pérez, L. et al. Cluster headache, beyond the pain: a comparative cross-sectional study. Neurol Sci 42, 3673–3680 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10072-020-04996-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10072-020-04996-0