Abstract
Background
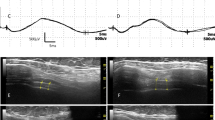
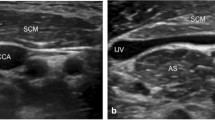
Respiratory failure represents an unavoidable step in patients with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) and other motor neuron diseases (MND). The development of diaphragm ultrasonography (DUS) provides an alternative useful and risk-free tool to supply clinical, functional, and neurophysiological assessment of respiratory muscle weakness. Our aim was to evaluate if sonographic changes (thickness and echogenicity in the costal portion of the diaphragm, at rest and during respiratory movements) may be used in ALS patients to assess disease severity over time, to rule out any risk or discomfort due to traditional neurophysiological investigations.
Methods
Twenty ALS patients (mean age, 64.6 ± 10.5 years) were enrolled and data were compared with age-matched healthy volunteers; DUS data were correlated with respiratory function and disease severity scale. Examinations were performed using Telemed Echo-wave II or Esaote MyLabGamma devices in conventional B-Mode.
Results
Mean resting thickness was reduced in all cases; changes in thickness during inspiration and expiration were also reduced (p < 0.0001) and lost in severe cases (n = 3). In bulbar-onset disease, respiratory scores were strictly correlated with the difference in diaphragm thickness between full inspiration—and expiration—as well as on the diaphragm thickness in expiration (p < 0.001).
Conclusions
DUS represents a simple, painless, and risk-free tool; moreover, it provides useful functional and structural insights to the understanding of diaphragm function and the degree of respiratory failure in ALS.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Salameh JS, Brown RH Jr, Berry JD (2015) Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis: review. Semin Neurol 35(4):469–476
de Carvalho M, Swash M (2016) Lower motor neuron dysfunction in ALS. Clin Neurophysiol 127(7):2670–2681
Huynh W, Simon NG, Grosskreutz J, Turner MR, Vucic S, Kiernan MC (2016) Assessment of the upper motor neuron in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Clin Neurophysiol 127(7):2643–2660
Logroscino G, Traynor BJ, Hardiman O, Chio’ A, Couratier P, Mitchell JD, Swingler RJ, Beghi E, EURALS (2008) Descriptive epidemiology of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis: new evidence and unsolved issues. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 79(1):6–11
Bensimon G, Lacomblez L, Meininger VA (1994) Controlled trial of riluzole in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. ALS/Riluzole Study Group. N Engl J Med 330(9):585–591
de Carvalho M, Dengler R, Eisen A, England JD, Kaji R, Kimura J, Mills K, Mitsumoto H, Nodera H, Shefner J, Swash M (2008) Electrodiagnostic criteria for diagnosis of ALS. Clin Neurophysiol 119(3):497–503
Sartucci F, Moscato G, Rossi C, Caleo M, Bocci T, Murri L, Giannini F, Rossi A (2010) Macro-EMG and MUNE changes in patients with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis: one-year follow up. Int J Neurosci 121(5):257–266
Bocci T, Pecori C, Giorli E, Briscese L, Tognazzi S, Caleo M, Sartucci F (2011) Differential motor neuron impairment and axonal regeneration in sporadic and familiar amyotrophic lateral sclerosis with SOD-1 mutations: lessons from neurophysiology. Int J Mol Sci 12:9203–9215
Vucic S, Ziemann U, Eisen A, Hallett M, Kiernan MC (2013) Transcranial magnetic stimulation and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis: pathophysiological insights. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 84(10):1161–1170
Geevasinga N, Loy CT, Menon P, de Carvalho M, Swash M, Schrooten M, Van Damme P, Gawel M, Sonoo M, Higashihara M, Noto Y, Kuwabara S, Kiernan MC, Macaskill P, Vucic S (2016) Awaji criteria improves the diagnostic sensitivity in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis: a systematic review using individual patient data. Clin Neurophysiol 127(7):2684–2691
Bocci T, Briscese L, Giorli E, Pecori C, Sartucci F (2012) Tongue’s motor evoked potentials in the diagnosis of primary lateral sclerosis (PLS): preliminary report. J Neurol Sci 316:67–71
Pinto S, Alves P, Pimentel B, Swash M, de Carvalho M (2016) Ultrasound for assessment of diaphragm in ALS. Clin Neurophysiol 127(1):892–897
Shoesmith CL, Findlater K, Rowe A, Strong MJ (2007) Prognosis of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis with respiratory onset. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 78(6):629–631
de Carvalho M, Costa J, Swash M (2005) Clinical trials in ALS: a review of the role of clinical and neurophysiological measurements. Amyotroph Lateral Scler Other Motor Neuron Disord 6(4):202–212
Tsuji Y, Noto YI, Shiga K, Teramukai S, Nakagawa M, Mizuno T (2017) A muscle ultrasound score in the diagnosis of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Clin Neurophysiol 128(6):1069–1074
Walker FO, Cartwright MS, Alter KE, Visser LH, Hobson-Webb LD, Padua L, Strakowski JA, Preston DC, Boon AJ, Axer H, van Alfen N, Tawfik EA, Wilder-Smith E, Yoon JS, Kim BJ, Breiner A, Bland JDP, Grimm A, Zaidman CM (2018) Indications for neuromuscular ultrasound: expert opinion and review of the literature. Clin Neurophysiol S1388–2457(18):31234–31233
Brooks BR, Miller RG, Swash M, Munsat TL, World Federation of Neurology Research Group on Motor Neuron Diseases (2000) El Escorial revisited: revised criteria for the diagnosis of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Amyotroph Lateral Scler Other Motor Neuron Disord 1(5):293–299
Arts IM, van Rooij FG, Overeem S, Pillen S, Janssen HM, Schelhaas HJ, Zwarts MJ (2008) Quantitative muscle ultrasonography in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Ultrasound Med Biol 34(3):354–361
Baldwin CE, Paratz JD, Bersten AD (2011) Diaphragm and peripheral muscle thickness on ultrasound: intra-rater reliability and variability of a methodology using non-standard recumbent positions. Respirology 16(7):1136–1143
Boon AJ, Harper CJ, Ghahfarokhi LS, Strommen JA, Watson JC, Sorenson EJ (2013) Two-dimensional ultrasound imaging of the diaphragm: quantitative values in normal subjects. Muscle Nerve 47(6):884–889
Cedarbaum JM, Stambler N, Malta E, Fuller C, Hilt D, Thurmond B, Nakanishi A (1999) The ALSFRS-R: a revised ALS functional rating scale that incorporates assessments of respiratory function. BDNF ALS Study Group (phase III). J Neurol Sci 169(1–2):13–21
Kaufmann P, Levy G, Thompson JL, Delbene ML, Battista V, Gordon PH, Rowland LP, Levin B, Mitsumoto H (2005) The ALSFRSr predicts survival time in an ALS clinic population. Neurology 64(1):38–43
Kollewe K, Mauss U, Krampfl K, Petri S, Dengler R, Mohammadi (2008) ALSFRS-R score and its ratio: a useful predictor for ALS-progression. J Neurol Sci 275(1–2):69–73
Janssens AI, Ruytings M, Al-Chalabi A, Chio A, Hardiman O, Mcdermott CJ, Meyer T, Mora G, Van Damme P, Van Den Berg LH, Vanhaecht K, Winkler AS, Sermeus W, ALS-CARE Consortium (2016) A mapping review of international guidance on the management and care of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS). Amyotroph Lateral Scler Frontotemporal Degener 17(5–6):325–336
Gil J, Funalot B, Verschueren A, Danel-Brunaud V, Camu W, Vandenberghe N, Desnuelle C, Guy N, Camdessanche JP, Cintas P, Carluer L, Pittion S, Nicolas G, Corcia P, Fleury MC, Maugras C, Besson G, Le Masson G, Couratier P (2008) Causes of death amongst French patients with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis: a prospective study. Eur J Neurol 15(11):1245–1251
Grimm A, Prell T, Décard BF, Schumacher U, Witte OW, Axer H, Grosskreutz J (2015) Muscle ultrasonography as an additional diagnostic tool for the diagnosis of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Clin Neurophysiol 126(4):820–827
Arts IM, Overeem S, Pillen S, Schelhaas HJ, Zwarts MJ (2011) Muscle ultrasonography to predict survival in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 82(5):552–554
Fantini R, Mandrioli J, Zona S, Antenora F, Iattoni A, Monelli M, Fini N, Tonelli R, Clini E, Marchioni A (2016) Ultrasound assessment of diaphragmatic function in patients with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Respirology 21(5):932–938
Miller RG, Anderson FA Jr, Bradley WG, Brooks BR, Mitsumoto H, Munsat TL, Ringel SP (2000) The ALS patient care database: goals, design, and early results. ALS C.A.R.E. Study Group. Neurology 54(1):53–57
Lyall RA, Donaldson N, Polkey MI, Leigh PN, Moxham J (2001) Respiratory muscle strength and ventilatory failure in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Brain 124(Pt 10):2000–2013
Fregonezi G, Araújo PR, Macêdo TL, Dourado Junior ME, Resqueti VR, Andrade Ade F (2013) Monitoring respiratory muscle strength assists in early diagnosis of respiratory dysfunction as opposed to the isolated use of pulmonary function evaluation in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Arq Neuropsiquiatr 71(3):146–152
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All the authors have contributed to the conception and design of the study, analysis, and interpretation of data and drafting of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical publication statement
We confirm that we have read the journal’s position on issues involved in ethical publication and affirm that this study is consistent with those guidelines.
Disclosure of conflicts of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOC 41 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sartucci, F., Pelagatti, A., Santin, M. et al. Diaphragm ultrasonography in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis: a diagnostic tool to assess ventilatory dysfunction and disease severity. Neurol Sci 40, 2065–2071 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10072-019-03938-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10072-019-03938-9