Abstract
Objectives
To compare the efficacy and safety of tocilizumab with those of abatacept in patients with active rheumatoid arthritis not responding to anti-tumor necrosis factor therapy.
Methods
A prospective, open-label study was carried out on adult females with moderate-to-severe rheumatoid arthritis. Patients were randomly assigned to receive either intravenous tocilizumab or abatacept treatment. History taking, clinical examination, and laboratory evaluation were done at baseline and during a 24-week period of follow-up. Disease activity was calculated using the DAS28-ESR score. The incidence of accompanying adverse events was evaluated and all statistical analyses were performed by InStat.
Results
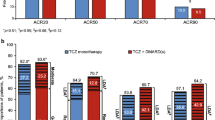
One hundred thirty-two patients were enrolled and classified randomly into the tocilizumab (n = 68) and abatacept (n = 64) groups. By week 24, the mean DAS28-ESR was significantly reduced in both groups (P < 0.0001) in association with significant reductions in CRP, ESR, and HAQ scores. No significant difference in the incidence rate of adverse effects appeared between both study groups. However, there were marked declines in the hemoglobin levels (P = 0.003) and neutrophil count (P = 0.002) together with significant elevations in systolic blood pressure (P = 0.002), liver enzymes (P = 0.001), total cholesterol (P = 0.001), and high-density lipoproteins (P = 0.002) in the tocilizumab group compared with the abatacept group.
Conclusion
Both intravenous abatacept and tocilizumab significantly decreased the disease activity and improved the physical function in rheumatoid arthritis patients who failed to respond to anti-tumor necrosis factor therapy. Although the efficacy of both drugs was similar, abatacept showed a more promising short-term safety profile since it was associated with less adverse effects and better laboratory outcomes.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Giles J, Bathon JM (2010) Management of rheumatoid arthritis: synovitis. Rheumatology 1:955–963
Emery P, Breedveld FC, Hall S, Durez P, Chang DJ, Robertson D, Singh A, Pedersen RD, Koenig AS, Freundlich B (2008) Comparison of methotrexate monotherapy with a combination of methotrexate and etanercept in active, early, moderate to severe rheumatoid arthritis (COMET): a randomized, double-blind, parallel treatment trial. Lancet 372:375–382
Finckh A, Simard JF, Gabay C, Guerne PA (2006) Evidence for differential acquired drug resistance to anti-tumor necrosis factor agents in rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis 65:746–752
Du Pan SM, Dehler S, Ciurea A et al (2009) Comparison of drug retention rates and causes of drug discontinuation between anti-tumor necrosis factor agents in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum 61:560–568
Buch MH (2010) Sequential use of biologic therapy in rheumatoid arthritis. Curr Opin Rheumatol 22:321–329
Harrold LR, Reed GW, Solomon DH, Curtis JR et al (2016) Comparative effectiveness of abatacept versus tocilizumab in rheumatoid arthritis patients with prior TNFi exposure in the US Corrona registry and Joel M. Kremer 5,6. Arthritis Res Ther 18:280
Moots RJ, Sebba A, Rigby W, Ostor A, Porter-Brown B, Donaldson F, Dimonaco S, Rubbert-Roth A, van Vollenhoven R, Genovese MC (2017) Effect of tocilizumab on neutrophils in adult patients with rheumatoid arthritis: pooled analysis of data from phase 3 and 4 clinical trials. Rheumatology 56:541–549
Nishimoto N, Terao K, Mima T, Nakahara H, Takagi N, Kakehi T (2008) Mechanisms and pathologic significances in increase in serum interleukin-6 (IL-6) and soluble IL-6 receptor after administration of an anti-IL-6 receptor antibody, tocilizumab, in patients with rheumatoid arthritis and Castleman disease. Blood 112:3959–3964
Smolen JS, Beaulieu A, Rubbert-Roth A, Ramos-Remus C, Rovensky J, Alecock E, Woodworth T, Alten R (2008) Effect of interleukin-6 receptor inhibition with tocilizumab in patients with rheumatoid arthritis (OPTION study): a double blind, placebo-controlled, randomized trial. Lancet 371:987–997
Nishimoto N, Hashimoto J, Miyasaka N et al (2007) Study of active controlled monotherapy used for rheumatoid arthritis, an IL-6 inhibitor—evidence of clinical and radiographic benefit from an X-ray reader-blinded randomized controlled trial of tocilizumab. Ann Rheum Dis 6:1162–1167
Nishimoto N, Miyasaka N, Yamamoto K, Kawai S, Takeuchi T, Azuma J (2009) Long-term safety and efficacy of tocilizumab, an anti-IL-6 receptor monoclonal antibody, in monotherapy, in patients with rheumatoid arthritis (the STREAM study): evidence of safety and efficacy in a 5-year extension study. Ann Rheum Dis 68:1580–1584
Bluestone J, St. Clair E, Turka L (2006) CTLA4Ig: bridging the basic immunology with clinical application. Immunity 24:233–238
Cron RQ (2005) A signal achievement in the treatment of arthritis [editorial]. Arthritis Rheum 52:2229–2232
Langford CA, Cuthbertson D, Ytterberg SR, Khalidi N, Monach PA, Carette S, Seo P, Moreland LW, Weisman M, Koening CL, Sreih AG, Spiera R, McAlear C, Warrington KJ, Pagnoux C, McKinnon K, Forbess LJ, Hoffman GS, Borchin R, Krischer JP, Merkel PA, Vasculitis Clinical Research Consortium (2017) A randomized, double-blind trial of abatacept (CTLA-4Ig) for the treatment of Takayasu arteritis. Arthritis Rheumatol 69(4):846–853
Aletaha D, Neogi T, Silman AJ, Funovits J, Felson DT, Bingham CO III, Birnbaum NS, Burmester GR, Bykerk VP, Cohen MD, Combe B, Costenbader KH, Dougados M, Emery P, Ferraccioli G, Hazes JMW, Hobbs K, Huizinga TWJ, Kavanaugh A, Kay J, Kvien TK, Laing T, Mease P, Ménard HA, Moreland LW, Naden RL, Pincus T, Smolen JS, Stanislawska-Biernat E, Symmons D, Tak PP, Upchurch KS, Vencovský J, Wolfe F, Hawker G (2010) Rheumatoid arthritis classification criteria: an American College of Rheumatology/European League Against Rheumatism collaborative initiative. Arthritis Rheum 62:2569–2581
Sakpal TV (2010) Sample size estimation in clinical trial. Perspect Clin Res 1(2):67–69
Prevoo ML, van’t Hof MA, Kuper HH et al (1995) Modified disease activity scores that include twenty-eight-joint counts. Development and validation in a prospective longitudinal study of patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum 38(1):44–48
Kubo S, Nakayamada S, Nakano K et al (2015) Comparison of the efficacies of abatacept and tocilizumab in patients with rheumatoid arthritis by propensity score matching. Ann Rheum Dis. https://doi.org/10.1136/annrheumdis-207784
Pascart T, Philippe P, Drumez E, Deprez X, Cortet B, Duhamel A, Houvenagel E, Flipo RM (2016) Comparative efficacy of tocilizumab, abatacept and rituximab after non-TNF inhibitor failure: results from a multicenter study. Int J Rheum Dis 19(11):1093–1102
Jones G, Ding C (2010) Tocilizumab: a review of its safety and efficacy in rheumatoid arthritis. Clin Med Insights Arthritis Musculoskelet Disord 3:81–89
King-Konert C, von Hinüber U, Richter C et al (2016) ROUTINE—a prospective, multicenter, non-interventional, observational study to evaluate the safety and effectiveness of intravenous tocilizumab for the treatment of active rheumatoid arthritis in daily practice in Germany. Rheumatology 55:624–635
Schiff M, Poncet C, Le Bars M (2010) Efficacy and safety of abatacept therapy for rheumatoid arthritis in routine clinical practice. Int J Clin Rheumatol 5(5):581–591
Leffers HC, Ostergaard M, Glintborg B, Krogh NS et al (2011) Efficacy of abatacept and tocilizumab in patients with rheumatoid arthritis treated in clinical practice: results from the nationwide Danish DANBIO registry. Ann Rheum Dis 70(7):1216–1222
Hirabara S, Takahashi N, Fukaya N, Hiroyuki H et al (2014) Clinical efficacy of abatacept, tocilizumab, and etanercept in Japanese rheumatoid arthritis patients with inadequate response to anti-TNF monoclonal antibodies. Clin Rheumatol 33:1247–1254
Emery P, Keystone E, Tony HP, Cantagrel A, van Vollenhoven R, Sanchez A, Alecock E, Lee J, Kremer J (2008) IL-6 receptor inhibition with tocilizumab improves treatment outcomes in patients with rheumatoid arthritis refractory to anti-tumour necrosis factor biologicals: results from a 24-week multicenter randomized placebo-controlled trial. Ann Rheum Dis 67(11):1516–1523
Genovese MC, Schiff M, Luggen M, Becker JC et al (2008) Efficacy and safety of the selective co-stimulation modulator abatacept following 2 years of treatment in patients with rheumatoid arthritis and an inadequate response to anti-tumour necrosis factor therapy. Ann Rheum Dis 67(4):547–554
Schiff M, Pritchard C, Huffstutter JE, Rodriguez-Valverde V, Durez P, Zhou X, Li T, Bahrt K, Kelly S, le Bars M, Genovese MC (2009) The 6-month safety and efficacy of abatacept in patients with rheumatoid arthritis who underwent a washout after anti-tumour necrosis factor therapy or were directly switched to abatacept: the ARRIVE trial. Ann Rheum Dis 68:1708–1714
Westhovens R, Kremer JM, Emery P, Russell AS, Alten R, Barré E, Dougados M (2014) Long-term safety and efficacy of abatacept in patients with rheumatoid arthritis and an inadequate response to methotrexate: a 7-year extended study. Clin Exp Rheumatol 32:553–562
Gottenberg JE, Morel J, Constantin A et al (2016) Long-term registry data in 4498 patients with rheumatoid arthritis indicate a similar safety but a different drug retention between abatacept, rituximab and tocilizumab. Arthr Rheumatol. 68(Suppl 10):2550–2553
Gottenberg JE, Morel J, Constantin A et al (2016) Similar rates of death, serious infections, cancers, major cardiovascular events in patients treated with abatacept, rituximab and tocilizumab: long-term registry data in 4498 patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Arthr Rheumatol 68(Suppl 10):3536–3537
Jones G, Sebba A, Gu J, Lowenstein MB, Calvo A, Gomez-Reino JJ, Siri DA, Tomsic M, Alecock E, Woodworth T, Genovese MC (2010) Comparison of TCZ monotherapy versus methotrexate monotherapy in patients with moderate to severe rheumatoid arthritis: the AMBITION study. Ann Rheum Dis 69:88–96
Choy E, Sattar N (2009) Interpreting lipid levels in the context of high-grade inflammatory states with a focus on rheumatoid arthritis: a challenge to conventional cardiovascular risk actions. Ann Rheum Dis 68:460–469
Kremer JM, van Vollenhoven RF, Ridley DJ et al (2008) Relationship between patient characteristics and the development of serious infections in patients receiving tocilizumab: results from long-term extension studies with a follow-up duration of 1.5 years. Arthritis Rheum 58:S783–S784
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Disclosures
None.
Ethical approval
Our study was approved according to the local ethical committee inside all hospitals that participated in this study. All selected patients have given written informed consents, before being enrolled in the study.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Elmedany, S.H., Mohamed, A.E. & Galil, S.M.A. Efficacy and safety profile of intravenous tocilizumab versus intravenous abatacept in treating female Saudi Arabian patients with active moderate-to-severe rheumatoid arthritis. Clin Rheumatol 38, 2109–2117 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10067-019-04508-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10067-019-04508-2