Abstract
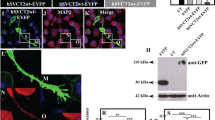
Neural epidermal growth factor-like protein-like 2 (NELL2) is a secreted glycoprotein that is predominantly expressed in the nervous system, but little is known about the intracellular movement and secretion mechanism of this protein. By monitoring the localization and movements of enhanced green fluorescent protein (EGFP)-labeled NELL2 in living cultured hippocampal neuroprogenitor HiB5 cells, we determined the subcellular localization of NELL2 and its intracellular movement and secretion mechanism. Cterminal EGFP-fused NELL2 showed a typical expression pattern of secreted proteins, especially with respect to its localization in the endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus, and punctate structures. Vesicles containing NELL2 exhibited bidirectional movement in HiB5 cells. The majority of the vesicles (70.1%) moved in an anterograde direction with an average velocity of 0.454 μm/s, whereas some vesicles (28.7%) showed retrograde movement with an average velocity of 0.302 μm/s. The movement patterns of NELL2 vesicles were dependent upon the presence of microtubules in HiB5 cells. Anterograde movement of NELL2 did not lead to a detectable accumulation of NELL2 in the peripheral region of the cell, indicating that it was secreted into the culture medium. We also showed that the N-terminal 29 amino acids of NELL2 were important for secretion of this protein. Taken together, these results strongly suggest that the N-terminal region of NELL2 determines both the pattern of its intracellular expression and transport of NELL2 vesicles by high-velocity movement. Therefore, NELL2 may affect the cellular activity of cells in a paracrine or autocrine manner.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aihara, K., Kuroda, S., Kanayama, N., Matsuyama, S., Tanizawa, K., and Horie, M. (2003). A neuron-specific EGF family protein, NELL2, promotes survival of neurons through mitogen-activated protein kinases. Brain Res. Mol. Brain Res. 116, 86–93.
Barkus, R.V., Klyachko, O., Horiuchi, D., Dickson, B.J., and Saxton, W.M. (2008). Identification of an axonal kinesin-3 motor for fast anterograde vesicle transport that facilitates retrograde transport of neuropeptides. Mol. Biol. Cell 19, 274–283.
Goldstein, L.S., and Yang, Z. (2000) Microtubule-based transport systems in neurons: the roles of kinesins and dyneins. Annu. Rev. Neurosci. 23, 39–71.
Ha, C.M., Choi, J., Choi, E.J., Costa, M.E., Lee, B.J., and Ojeda, S.R. (2008). NELL2, a neuron-specific EGF-like protein, is selectively expressed in glutamatergic neurons and contributes to the glutamatergic control of GnRH neurons at puberty. Neuroendocrinology 88, 199–211.
Hwang, E.M., Kim, D.G., Lee, B.J., Choi, J., Kim, E., Park, N., Kang, D., Han, J., Choi, W.S., Hong, S.G., et al. (2007). Alternative splicing generates a novel non-secretable cytosolic isoform of NELL2. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 353, 805–811.
Jeong, J.K., Ryu, B.J., Choi, J., Kim, D.H., Choi, E.J., Park, J.W., Park, J.J., and Lee, B.J. (2008). NELL2 participates in formation of the sexually dimorphic nucleus of the pre-optic area in rats. J. Neurochem. 106, 1604–1613.
Kim, H., Ha, C.M., Choi, J., Choi, E.J., Jeon, J., Kim, C., Park, S.K., Kang, S.S., Kim, K., and Lee, B.J. (2002). Ontogeny and the possible function of a novel epidermal growth factorlike repeat domain-containing protein, NELL2, in the rat brain. J. Neurochem. 83, 1389–1400.
Kim, D.G., Hwang, E.M., Yoo, J.C., Kim, E., Park, N., Rhee, S., Ha, C.M., Hong, S.G., and Park, J.Y. (2010). Identification and characterization of a truncated isoform of NELL2. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 391, 529–534.
Kuroda, S., and Tanizawa, K. (1999). Involvement of epidermal growth factor-like domain of NELL proteins in the novel proteinprotein interaction with protein kinase C. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 265, 752–757.
Kuroda, S., Oyasu, M., Kawakami, M., Kanayama, N., Tanizawa, K., Saito, N., Abe, T., Matsuhashi, S., and Ting, K. (1999). Biochemical characterization and expression analysis of neural thrombospondin1-like proteins NELL1 and NELL2. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 265, 151–160.
Lee, J.R., Shin, H., Ko, J., Choi, J., Lee, H., and Kim, E. (2003). Characterization of the movement of the kinesin motor KIF1A in living cultured neurons. J. Biol. Chem. 278, 2624–2629.
Luce, M.J., and Burrows, P.D. (1999). The neuronal EGF-related genes NELL1 and NELL2 are expressed in hemopoietic cells and developmentally regulated in the B lineage. Gene 231, 121–126.
Matsuhashi, S., Noji, S., Koyama, E., Myokai, F., Ohuchi, H., Taniguchi, S., and Hori, K. (1995). New gene, nel, encoding a M(r) 93 K protein with EGF-like repeats is strongly expressed in neural tissues of early stage chick embryos. Dev. Dyn. 203, 212–222.
Matsuyama, S., Aihara, K., Nishino, N., Takeda, S., Tanizawa, K., Kuroda, S., and Horie, M. (2004). Enhanced long-term potentiation in vivo in dentate gyrus of NELL2-deficient mice. Neuroreport 15, 417–420.
Matsuyama, S., Doe, N., Kurihara, N., Tanizawa, K., Kuroda, S., Iso, H., and Horie, M. (2005). Spatial learning of mice lacking a neuron-specific epidermal growth factor family protein, NELL2. J. Pharmacol. Sci. 98, 239–243.
Munemasa, Y., Chang, C.S., Kwong, J.M., Kyung, H., Kitaoka, Y., Caprioli, J., and Piri, N. (2012). The neuronal EGF-related gene Nell2 interacts with Macf1 and supports survival of retinal ganglion cells after optic nerve injury. PLoS One 7, e34810.
Nelson, B.R., Claes, K., Todd, V., Chaverra, M., and Lefcort, F. (2004). NELL2 promotes motor and sensory neuron differentiation and stimulates mitogenesis in DRG in vivo. Dev. Biol. 270, 322–335.
Noda, Y., Sato-Yoshitake, R., Kondo, S., Nangaku, M., and Hirokawa, N. (1995). KIF2 is a new microtubule-based anterograde motor that transports membranous organelles distinct from those carried by kinesin heavy chain or KIF3A/B. J. Cell Biol. 129, 157–167.
Oyasu, M., Kuroda, S., Nakashita, M., Fujimiya, M., Kikkawa, U., and Saito, N. (2000). Immunocytochemical localization of a neuronspecific thrombospondin-1-like protein, NELL2: light and electron microscopic studies in the rat brain. Mol. Brain Res. 76, 151–160.
Park, N., Yoo, J.C., Ryu, J., Hong, S.G., Hwang, E.M., Park, J.Y. (2012). Copine1 enhances neuronal differentiation of the hippocampal protenitor HiB5 cells. Mol. Cells 34, 549–554.
Stern, K.A., Smit, G.D., Place, T.L., Winistorfer, S., Piper, R.C., and Lill, N.L. (2007) Epidermal growth factor receptor fate is controlled by Hrs tyrosine phosphorylation sites that regulate Hrs degradation. Mol. Cell. Biol. 27, 888–898.
Vugmeyster, Y., Berliner E., and Gelles, J. (1998). Release of isolated single kinesin molecules form microtubules. Biochemistry 37, 747–757.
Watanabe, T.K., Katagiri, T., Suzuki, M., Shimizu, F., Fujiwara, T., Kanemoto, N., Nakamura, Y., Hirai, Y., Maekawa, H., and Takahashi, E. (1996). Cloning and characterization of two novel human cDNAs (NELL1 and NELL2) encoding proteins with six EGF-like repeats. Genomics 38, 273–276.
Yamazaki, H., Nakata, T., Okada, Y., and Hirokawa, N. (1995). KIF3A/B: a heterodimeric kinesin superfamily protein that works as a microtubule plus end-directed motor for membrane organelle transport. J. Cell Biol. 130, 1387–1399.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
These authors contributed equally to this work.
About this article
Cite this article
Ha, C.M., Hwang, E.M., Kim, E. et al. The molecular mechanism of NELL2 movement and secretion in hippocampal progenitor HiB5 cells. Mol Cells 36, 527–533 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10059-013-0216-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10059-013-0216-5