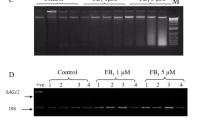
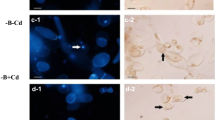
Abstract
Cell death is an important process of plant responses to development and biotic/abiotic stresses. In rice plants, PBZ1, a PR10 family protein, has been shown to accumulate in tissues undergoing cell death. However, the function of PBZ1 in cell death remains yet to be demonstrated. Here, we report that exogenous recombinant PBZ1 protein induces cell death in rice suspension-cultured cells (SCCs) and also in leaves of Nicotiana tabacum in a dosedependent manner. This finding was confirmed in vivo in transgenic Arabidopsis lines harboring the PBZ1 gene under the control of a dexamethasone (DEX)-inducible promoter. The DEX-treated leaves of transgenic Arabidopsis induced expression of PBZ1 at transcript and protein levels and showed cell death morphology. TUNEL analysis detected DNA fragmentation, a hallmark of programmed cell death, in rice SCCs treated with the PBZ1 protein. Recombinant PBZ1 protein also exhibited RNase activity and exhibited internalization inside BY-2 cells. Taken together, PBZ1 induces cell death not only in rice, but also in tobacco and Arabidopsis via its RNase activity inside the cell. PBZ1 could be used as a marker to understand the mechanism by which PBZ1 confers the cell death morphology in rice and other model plants.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aoyama, T., and Chua, N.H. (1997). A glucocorticoid-mediated transcriptional induction system in transgenic plants. Plant J. 11, 605–612.
Bantignies, B., Seguin, J., Muzac, I., Dedaldechamp, F., Gulick, P., and Ibrahim, R. (2000). Direct evidence for ribonucleolytic activity of a PR-10-like protein from white lupin roots. Plant Mol. Biol. 42, 871–881.
Bröker, L.E., Kruyt, F.A.E., and Giaccone, G. (2005). Cell death independent of caspases: a review. Clin. Cancer Res. 11, 3155–3162.
Bufe, A., Spangfort, M.D., Kahlert, H., Schlaak, M., and Becker, W.M. (1996). The major birch pollen allergen, bet V1, shows ribonuclease activity. Planta 199, 413–415.
Clough, S.J., and Bent, A.F. (1998). Floral dip: a simplified method for Agrobacterium-mediated transformation of Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant J. 16, 735–743.
Dangl, J.L., Lehnackers, H., Kiedrowski, S., Debener, T., Rupprecht, C., Arnold, M., and Somssich, I.E. (1991). In Advances in Molecular Genetics of Plant-Microbe Interactions. H. Hennecke, and D.P.S. Verma, eds. (Kluwer Academic, Dordrecht, The Netherlands), Vol. 1, pp. 78–83.
Fojtová, M., and Kovařík, A. (2000). Genotoxic effect of cadmium is associated with apoptotic changes in tobacco cells. Plant Cell Environ. 23, 531–537.
Goldraij, A., Kondo, K., Lee, C.B., Hancock, C.N., Sivaguru, M., Vazquez-Santana, S., Kim, S., Phillips, T.E., Cruz-Garcia, F., and McClure, B. (2006). Compartmentalization of S-RNase and HT-B degradation in self-incompatible Nicotiana. Nature 439, 805–810.
Haigis, M.C., and Raines, R.T. (2002). Secretory ribonucleases are internalized by a dynamin-independent endocytic pathway. J. Cell Sci. 116, 313–324.
Hwang, S.H., Lee, I.A., Yie, S.W., and Hwang, D.J. (2008). Identification of an OsPR10a promoter region responsive to salicylic acid. Planta 227, 1141–1150.
Jwa, N.S, Agrawal, G.K., Rakwal, R., Park, C.H., and Agrawal, V.P. (2001). Molecular cloning and characterization of a novel Jasmonate inducible pathogenesis-related class 10 protein gene, OsPR10, from rice (Oryza sativa L.) seedling leaves. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 286, 973–983.
Jwa, N.S., Agrawal, G.K., Tamogami, S., Yonekura, M., Han, O.S., Iwahashi, H., and Rakwal, R. (2006). Role of defense/stressrelated marker genes, proteins and secondary metabolites in defining rice self-defense mechanisms. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 44, 261–273.
Keogh, R.C., Deverall, B.J., and McLeod, S. (1980). Comparison of histological and physiological responses to Phakopsora pachyrhizi in resistant and susceptible soybean. Trans. Br. Mycol. Soc. 74, 329–333.
Kim, S.T., Cho, K.S., Yu, S., Kim, S.G., Hong, J.C., Han, C., Bae, D.W., Nam, M.H., and Kang, K.Y. (2003). Proteomic analysis of differentially expressed proteins induced by rice blast fungus and elicitor in suspension-cultured rice cells. Proteomics 3, 2368–2378.
Kim, S.T., Kim, S.G., Hwang, D.H., Kang, S.Y., Kim, H.J., Lee, B.H., Lee, J.J., and Kang, K.Y. (2004). Proteomic analysis of pathogen-responsive proteins from rice leaves induced by rice blast fungus, Magnaporthe grisea. Proteomics 4, 3569–3578.
Kim, S.T., Kim, S.G., Kang, Y.H., Wang, Y., Kim, J.Y., Yi, N., Kim, J.K., Rakwal, R., Koh, H.J., and Kang, K.Y. (2008a). Proteomics analysis of rice lesion mimic mutant (spl1) reveals tightly localized probenazole-induced protein (PBZ1) in cells undergoing programmed cell death. J. Proteome Res. 7, 1750–1760.
Kim, S.T., Yu, S., Kang, Y.H., Kim, S.G., Kim, J.Y., Kim, S.H., and Kang, Y.H. (2008b). The rice pathogen-related protein 10 (JIOsPR10) is induced by abiotic and biotic stresses and exhibits ribonuclease activity. Plant Cell Rep. 27, 593–603.
Koukalová, B., Kovařík, A., Fajkus, J., and Široký, J. (1997). Chromatin fragmentation associated with apoptotic changes in tobacoo cells exposed to cold stress. FEBS Lett. 414, 289–292.
Leland, P.A., and Raines, R.T. (2001). Cancer chemotherapy-ribonucleases to the rescue. Chem. Biol. 8, 405–413.
Liu, J.J., and Ekramoddoullah, A.K.M. (2006). The family 10 of plant pathogenesis-related proteins: Their structure, regulation, and function in response to biotic and abiotic stresses. Physiol. Mol. Plant Pathol. 68, 3–13.
Luu, D.T., Qin, X., Morse, D., and Cappadocia, M. (2000). S-RNase uptake by compatible pollen tubes in gametophytic self-incompatibility. Nature 407, 649–650.
Makarov, A.A., and Ilinskaya, O.N. (2003). Cytotoxic ribonucleases: molecular weapons and their targets. FEBS Lett. 540, 15–20.
Midoh, N., and Iwata, M. (1996). Cloning and characterization of a probenazole-inducible gene for an intracellular pathogenesis-related protein in rice. Plant Cell Physiol. 37, 9–18.
Moiseyev, G.P., Fedoreyeva, L.I., Zhuravlev, Y.N., Yasnetslaya, E., Jekel, P.A., and Beintema, J.J. (1997). Primary structures of two ribonucleases from ginseng calluses new members of the PR-10 family of intracellular pathogenesis-related plant proteins. FEBS Lett. 407, 207–210.
Nakashita, H., Yasuda, M., Nishioka, M., Hasegawa, S., Arai, Y., Uramoto, M., Yoshida, S., and Yamaguchi, I. (2002). Chloroisonicotinamide derivative induces a broad range of disease resistance in rice and tobacco. Plant Cell Physiol. 43, 823–831.
Ohira, K., Ojima, K., and Fujiwara, A. (1973). Studies on the nutrition of rice cell culture. A simple, defined medium for rapid growth in suspension culture. Plant Cell Physiol. 14, 1113–1121.
Park, C.J., Kim, K.J., Shin, R., Park, J.M., Shin, Y.C., and Paek, K.H. (2004). Pathogenesis-related protein 10 isolated from hot pepper functions as a ribonuclease in an antiviral pathway. Plant J. 37, 186–198.
Rakwal, R., Agrawal, G.K., and Yonekura, M. (2001). Lightdependent induction of OsPR10 in rice (Oryza sativa L.) seedlings by the global stress signaling molecule jasmonic acid and protein phosphatase 2A inhibitors. Plant Sci. 161, 469–479.
Swoboda, I., Hoffmann-Sommergrube, K., O’Riordain, G., Scheiner, O., Heberle-Bors, E., and Vicente, O. (1996). Bet V1 proteins, the major birch pollen allergens and members of a family of conserved pathogenesis-related proteins, show ribonuclease activity in vitro. Physiol. Plant 96, 433–438.
Takayoshi, I., Shigemi, S., Ichiro, M., and Yuko O. (2007). Probenazole-induced accumulation of salicylic acid confers resistance to Magnaporthe grisea in adult rice plants. Plant Cell Physiol. 48, 915–924.
Tanaka, N., Matsuoka, M., Kitano, H., Asano, T., Kaku, H., and Komatsu, S. (2006). gid1, a gibberellin-insensitive dwarf mutant, shows altered regulation of probenazole-inducible protein (PBZ1) in response to cold stress and pathogen attack. Plant Cell Environ. 29, 619–631.
Turner, J.G., and Novacky, A. (1974). The quantitative relation between plant and bacterial cells involved in the hypersensitive reaction. Phytopathology 64, 885–890.
Walter, M.H., Liu, J.W., Wünn, J., and Hess, D. (1996). Bean ribonuclease-like pathogenesis-related protein genes (Ypr10) display complex patterns of developmental, dark-induced and exogenous-stimulus-dependent expression. Eur. J. Biochem. 239, 281–293.
Wyllie, A.H., Kerr, J.F., and Currie, A.R. (1980). Cell death: the significance of apoptosis. Int. Rev. Cytol. 68, 251–306.
Yang, S.W., Kim, S.K., and Kim, W.T. (2004). Perturbation of NgTRF1 expression induces apoptosis-like cell death in tobacco BY-2 cells and implicates NgTRF1 in the control of telomere length and stability. Plant Cell 16, 3370–385.
Zhou, X.J., Lu, S., Xu, Y.H., Wang, J.W., and Chen, X.Y. (2002). A cotton cDNA (GaPR-10) encoding a pathogenesis-related 10 protein with in vitro ribonuclease activity. Plant Sci. 162, 629–636.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
These authors contributed equally to this work.
About this article
Cite this article
Kim, S.G., Kim, S.T., Wang, Y. et al. The RNase activity of rice probenazole-induced protein1 (PBZ1) plays a key role in cell death in plants. Mol Cells 31, 25–31 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10059-011-0004-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10059-011-0004-z